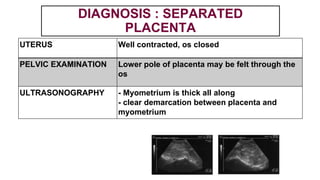
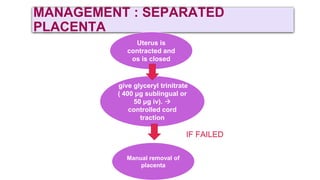
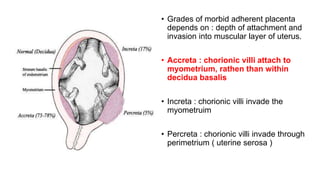
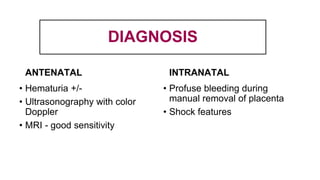
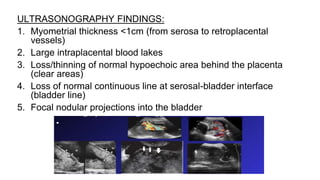
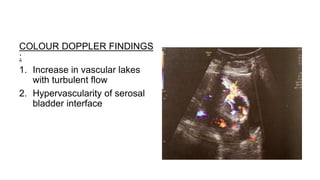
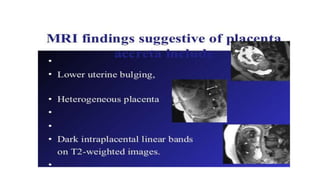
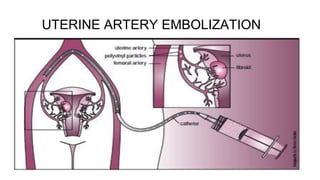
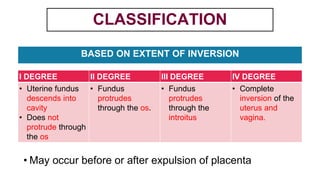
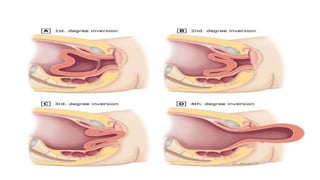
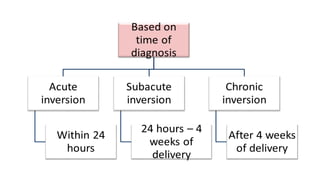
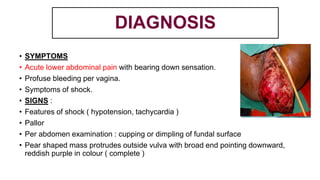
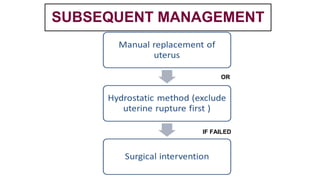
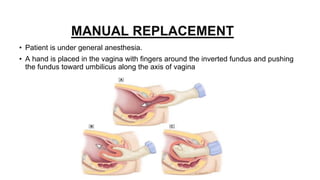
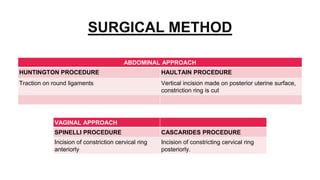
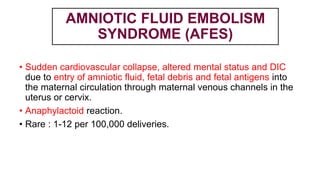
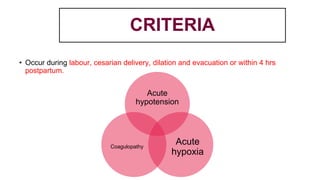
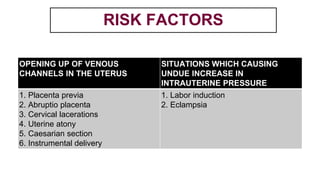
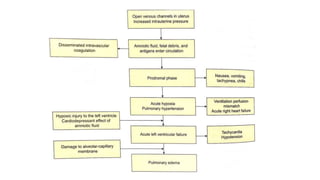
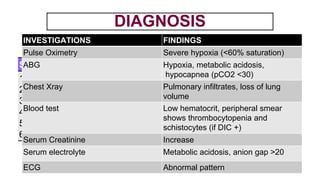
This document provides information on third stage complications of labour including secondary postpartum hemorrhage, retained placenta, morbidly adherent placenta, inversion of the uterus, and amniotic fluid embolism. It discusses the causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and management of these complications. Key points covered include the definition of retained placenta, grades of morbidly adherent placenta, risk factors for placenta accreta, and manual and hydrostatic methods for managing an inverted uterus.