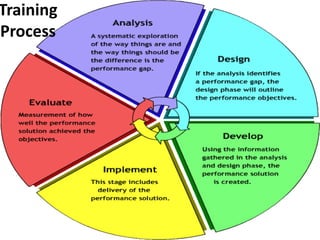
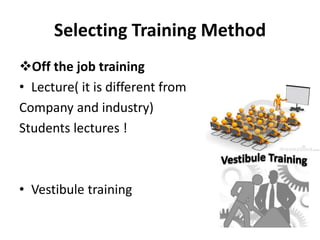
The document discusses orientation, training, and employee development. It defines orientation as providing new employees with background information to reduce anxiety and make them feel welcome. Training increases productivity and job satisfaction by keeping skills up to date. Common training methods include on-the-job and off-the-job instruction. Employee development involves ongoing training to enhance skills and stay current on new developments, and benefits both employees and employers.