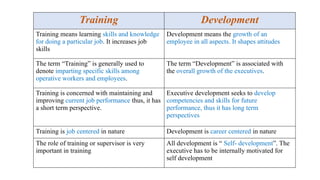
Training, Development and Outsourcing: Training: Need, Importance and
Objectives, Methods of Training; Executive Development Programs: Need and Techniques. Outsourcing: Concept and Evolutions, Reasons and Criteria for
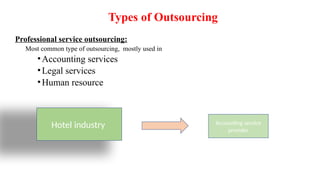
Outsourcing, Types of Outsourcing, Problems and Remedial Measures of
Outsourcing, Future Outsourcing in India.