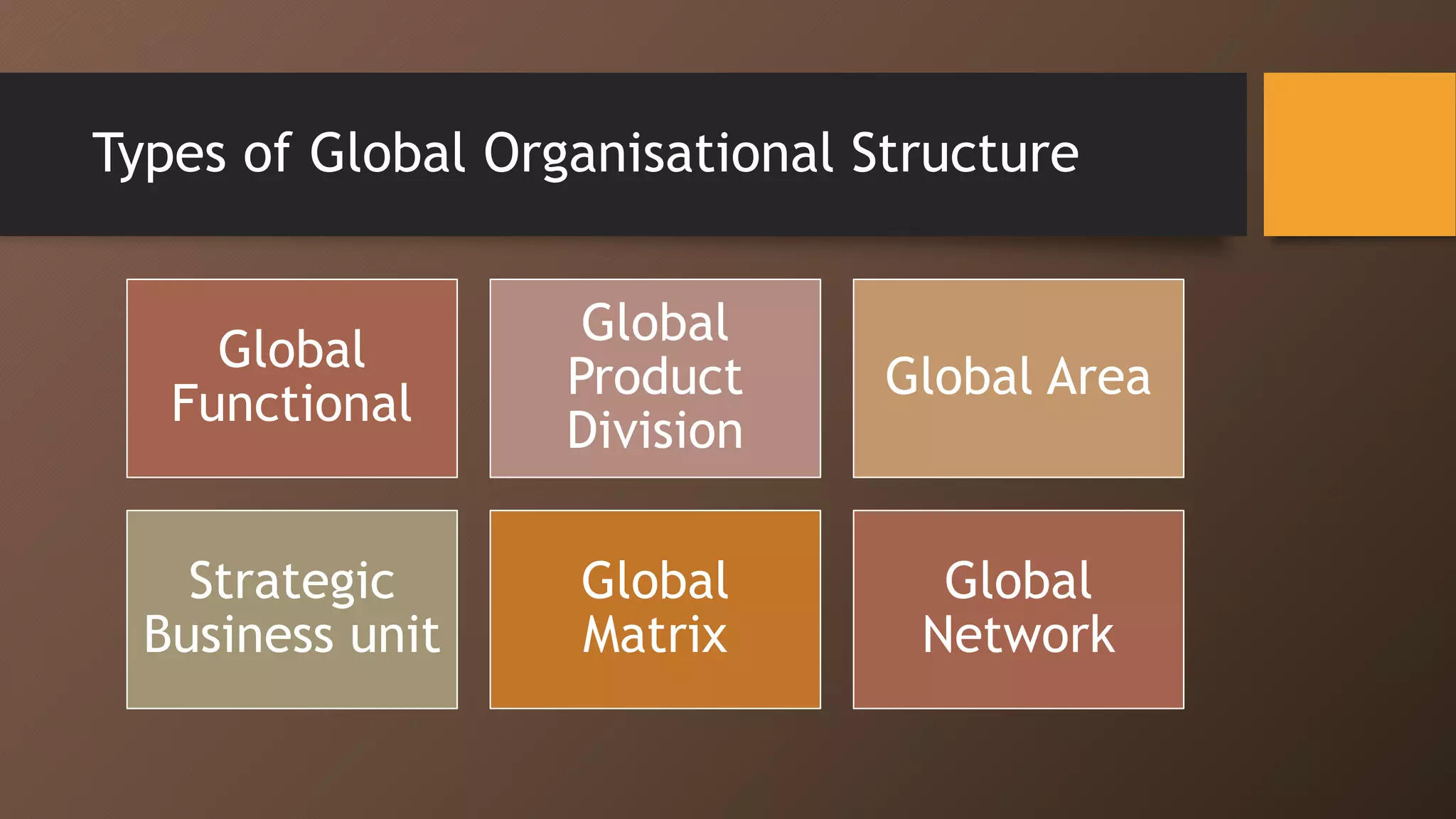
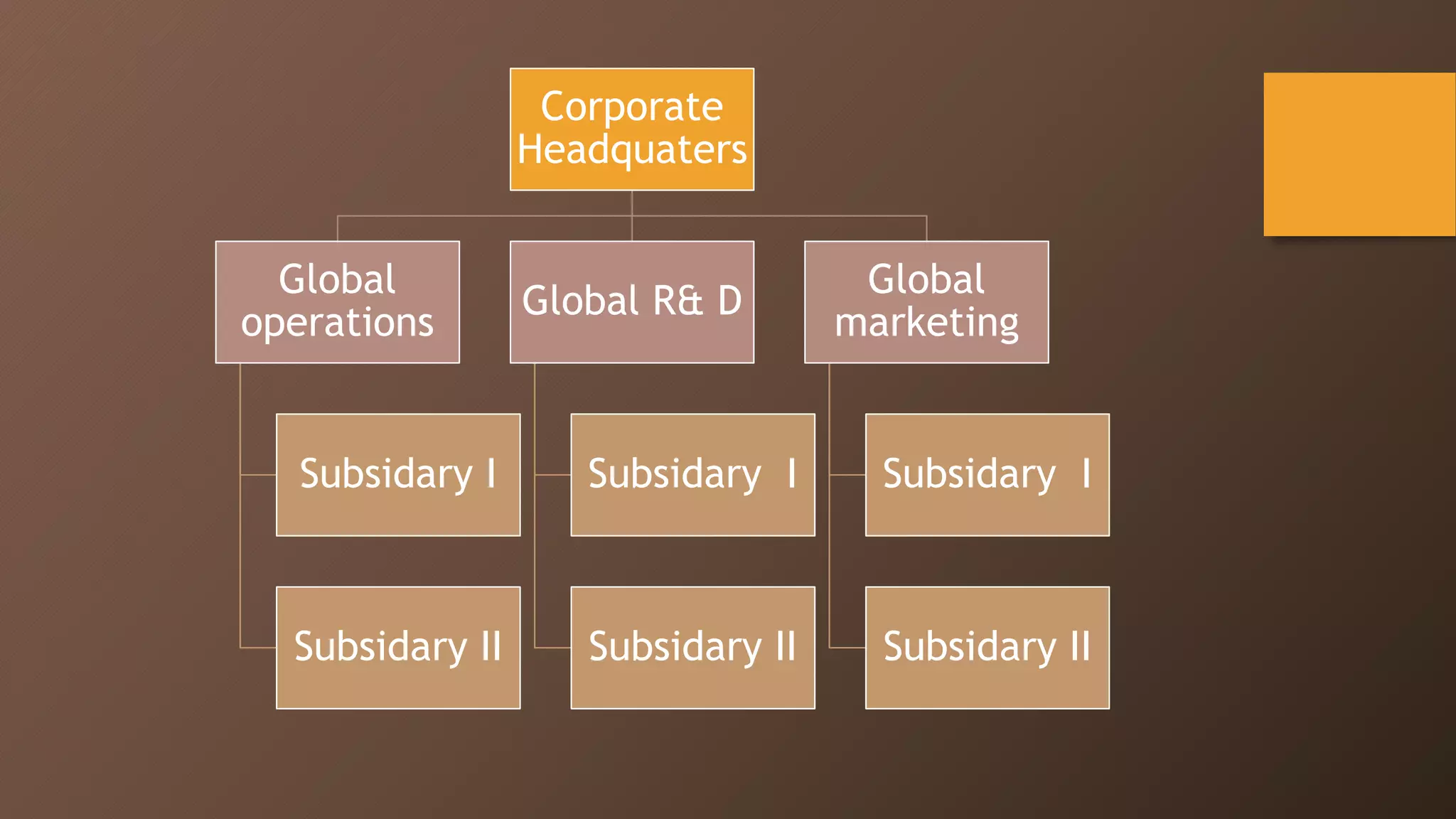
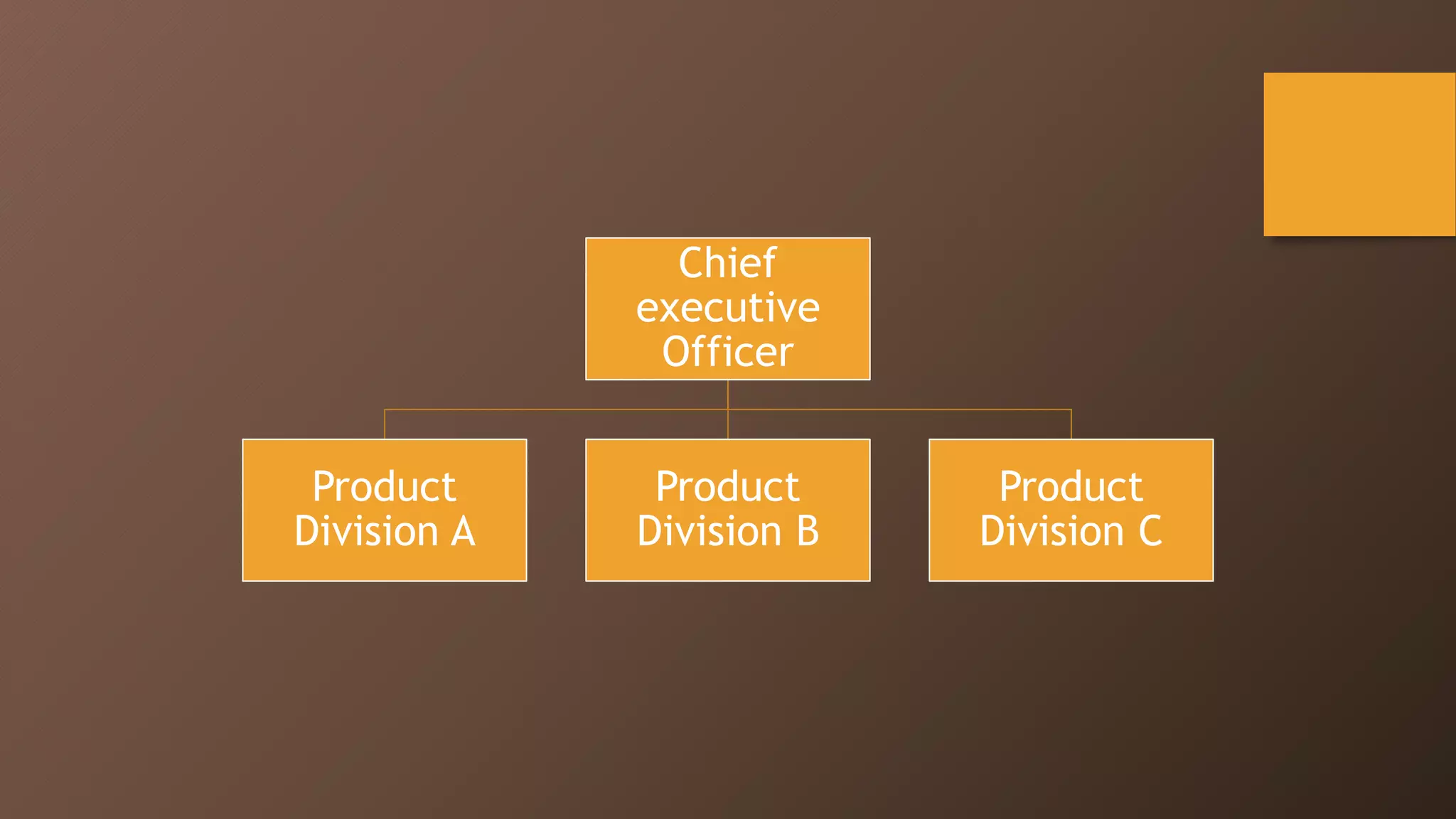
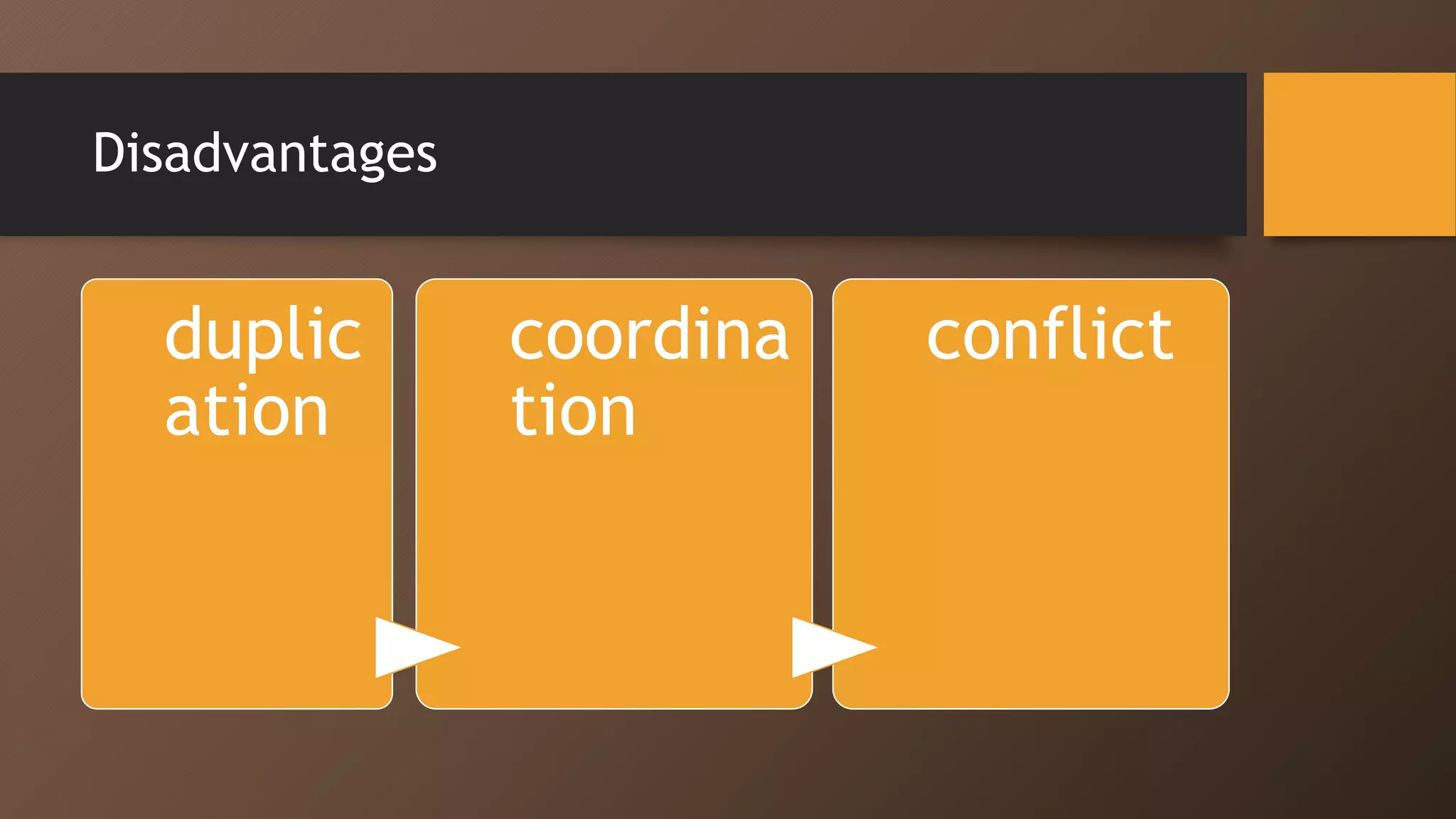
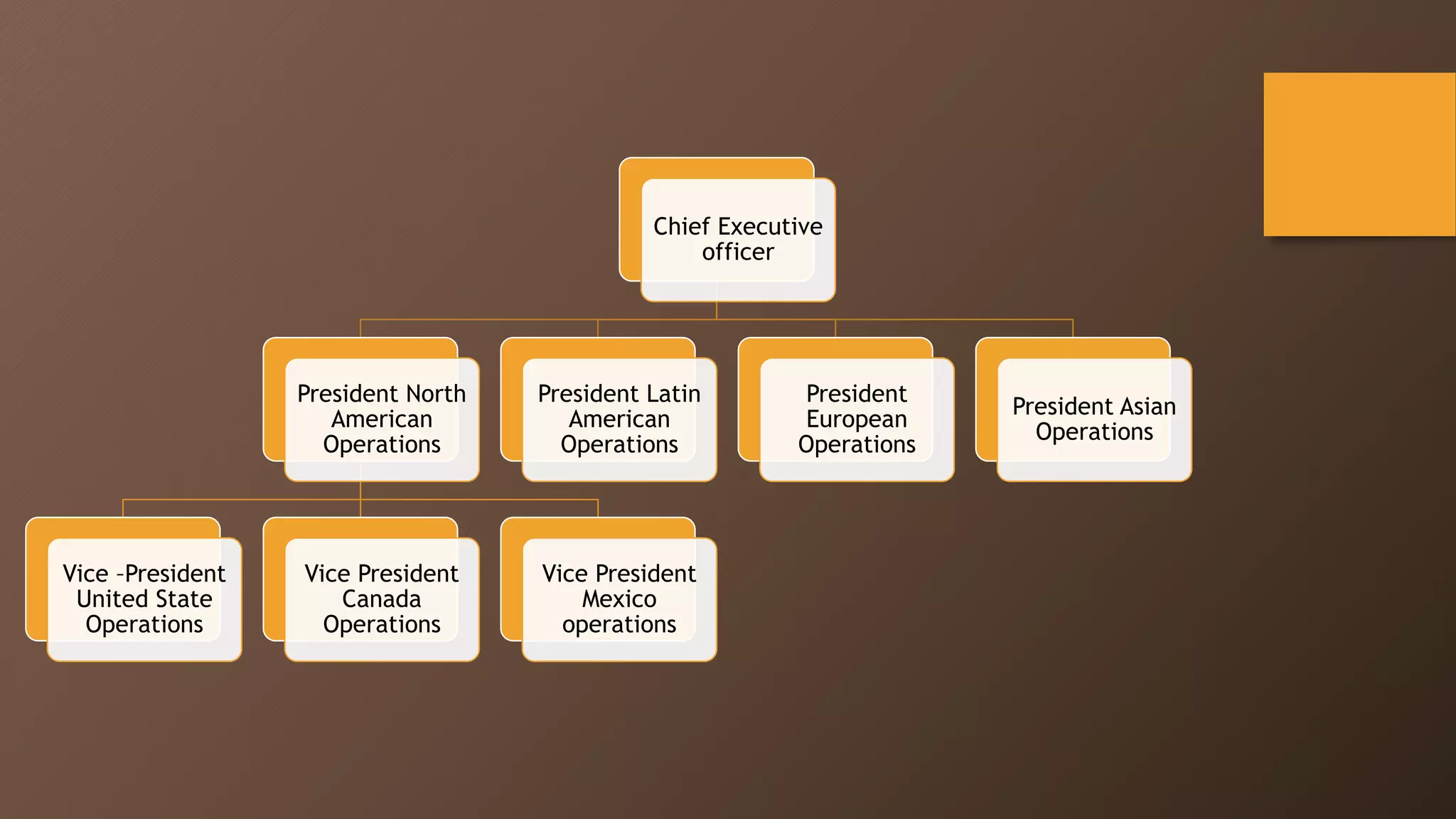
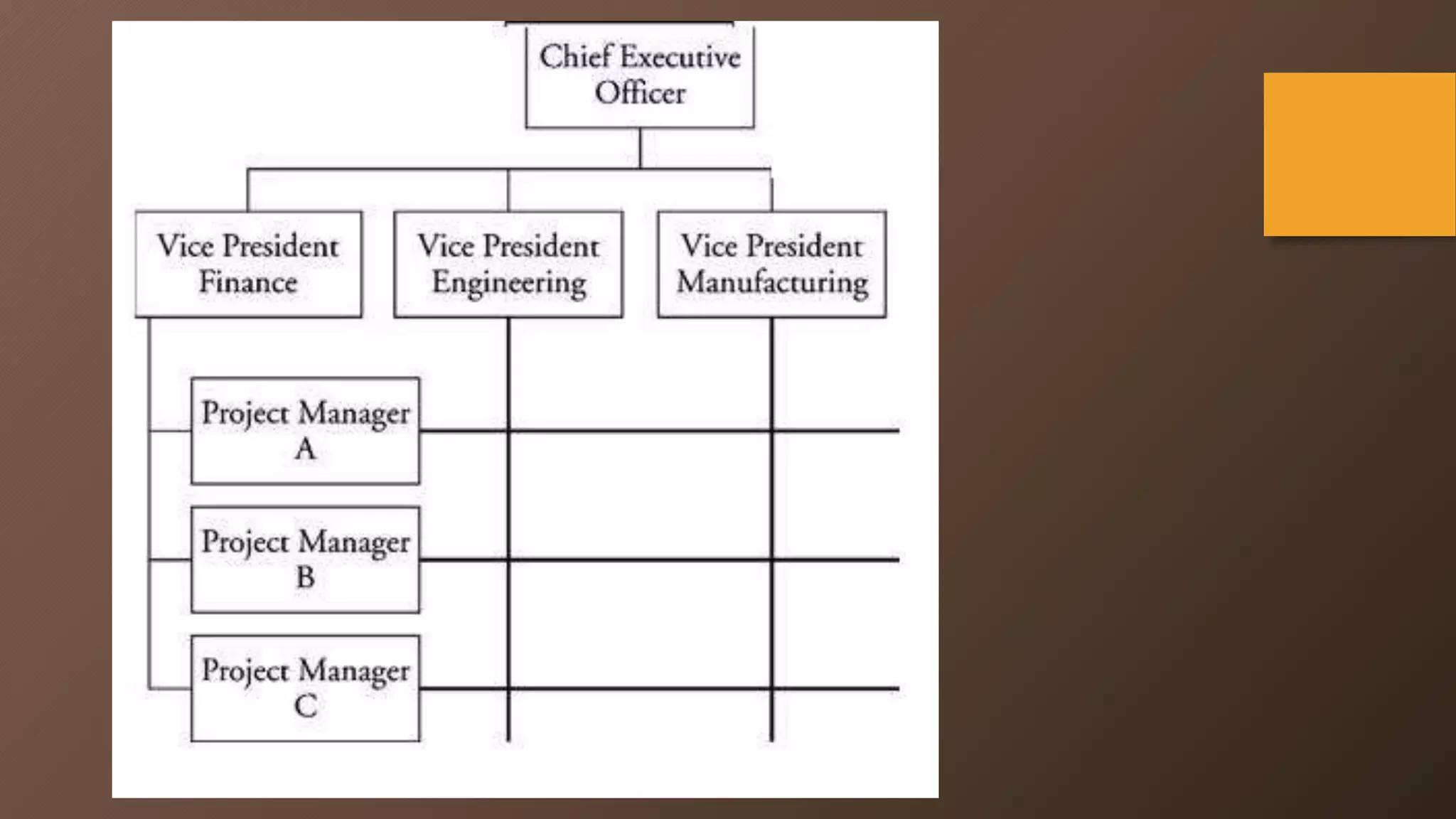
The document discusses different types of global organizational structures used by multinational companies. It describes global functional, product division, area, strategic business unit, matrix, and network structures. For each structure, it provides details on how it is organized and advantages and disadvantages. The global functional structure centralizes decision making at headquarters while the product division structure assigns worldwide responsibility for product groups to separate divisions. The area structure establishes regional headquarters responsible for affiliates in their geographic areas.