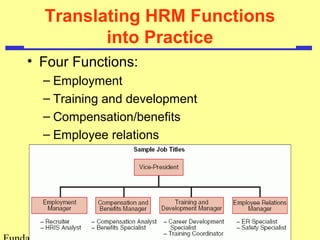
The document outlines the fundamentals of human resource management (HRM) emphasizing its strategic role in organizations. It discusses key functions such as staffing, training, motivation, and maintenance, while addressing external influences like globalization and legislation. Additionally, it highlights the importance of effective communication, ethical considerations, and HRM's impact on organizational performance.