Embed presentation
Downloaded 32 times


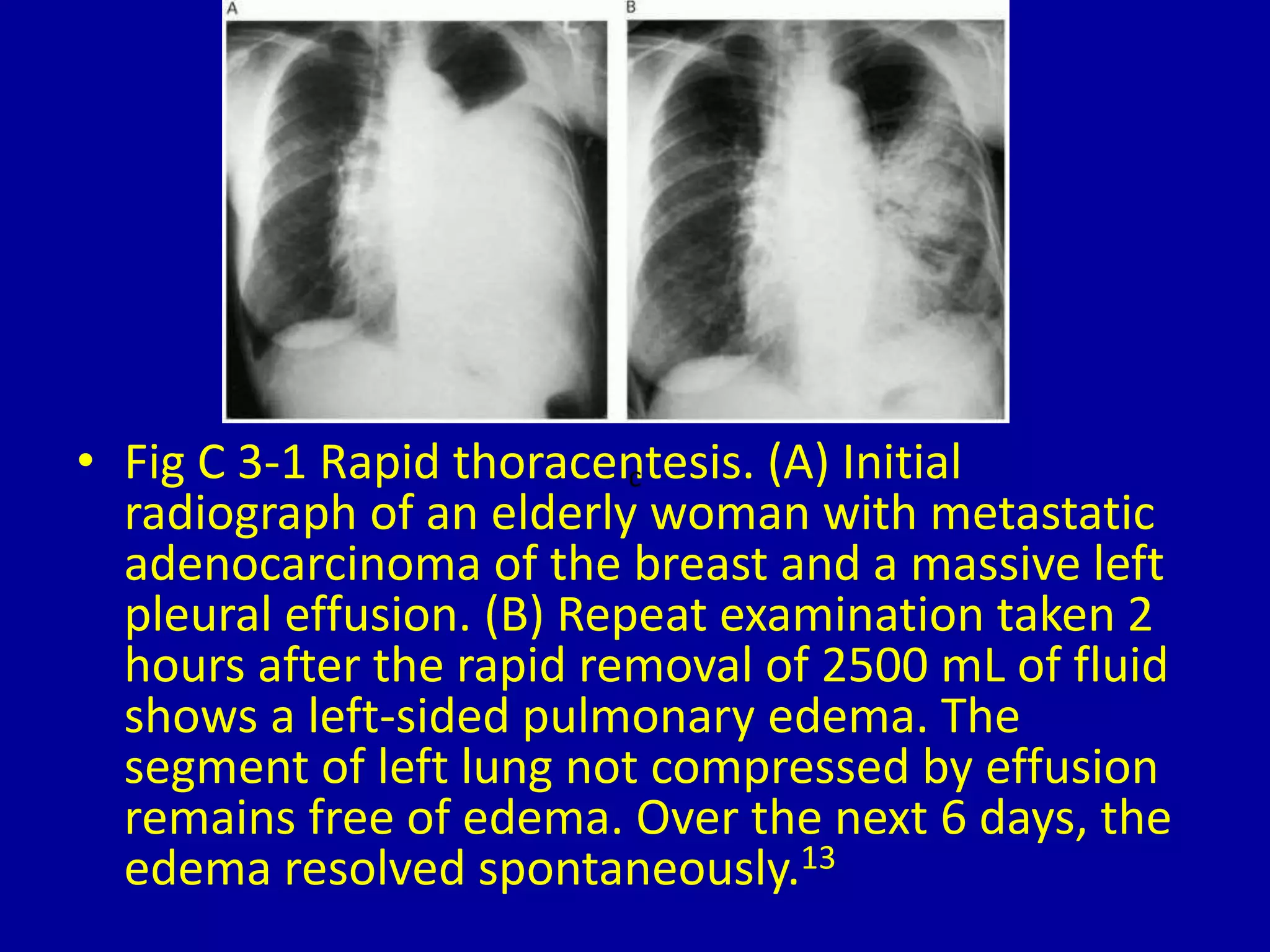
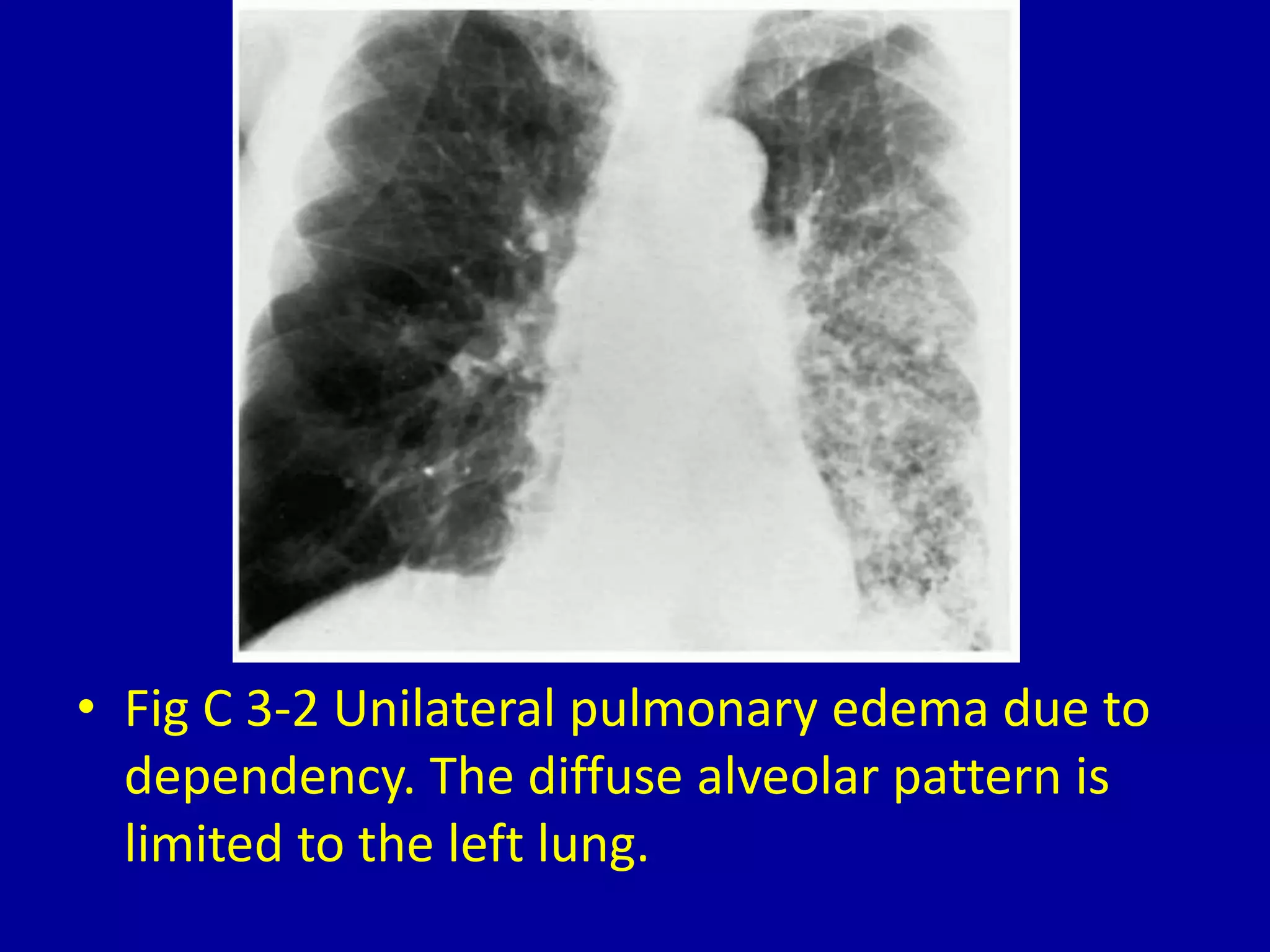
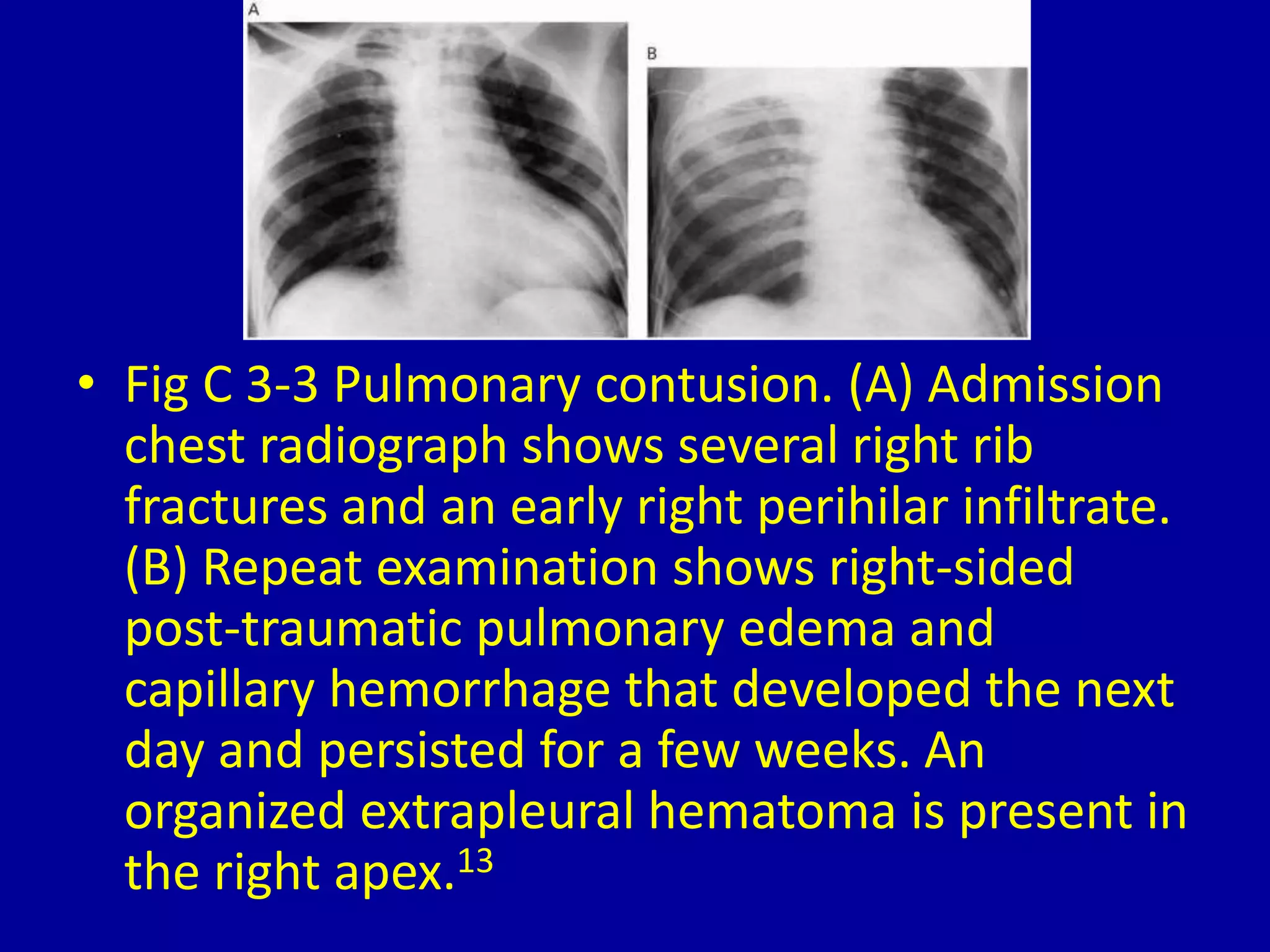
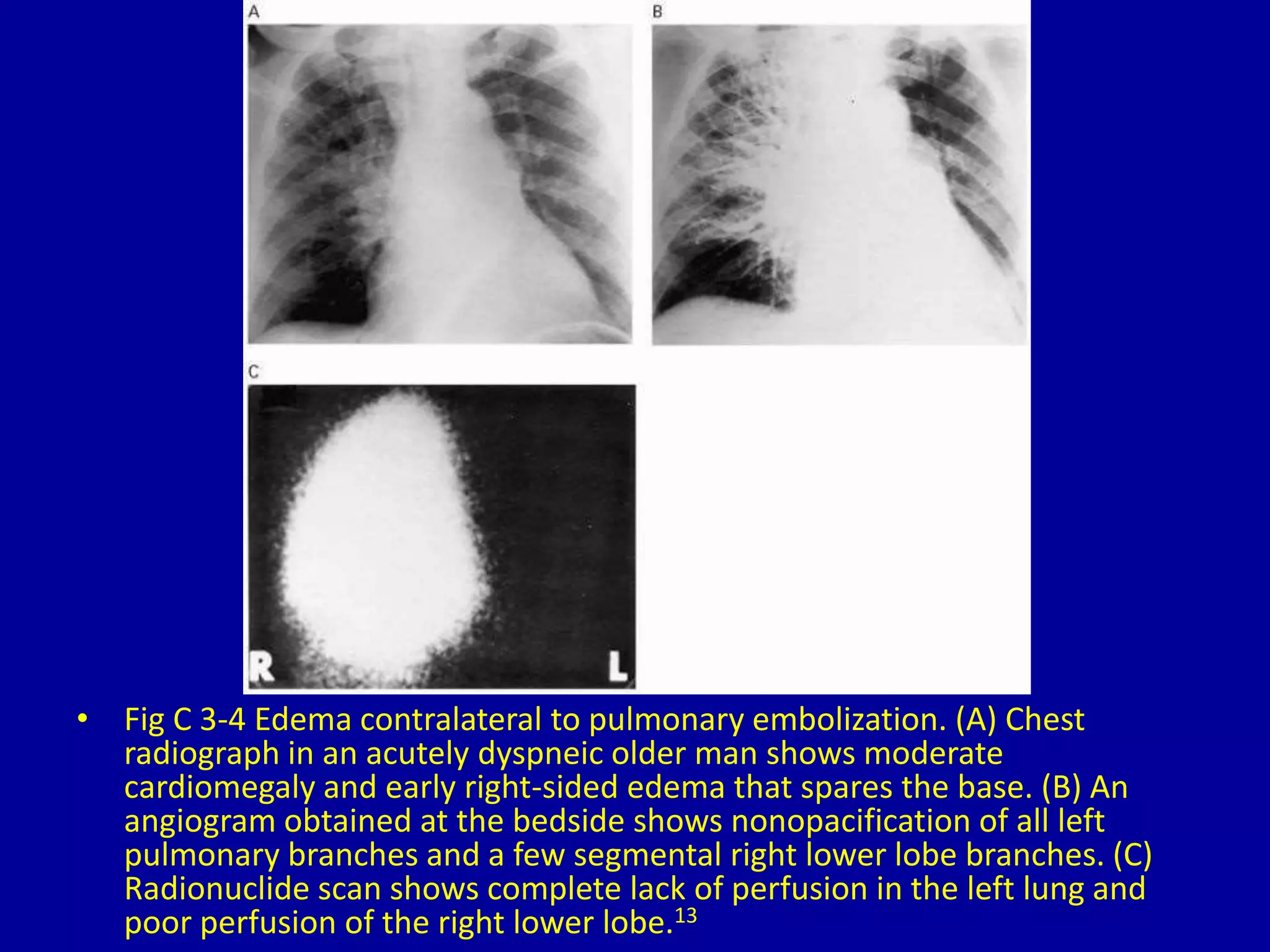


Unilateral pulmonary edema can develop through three main patterns: 1) Rapid thoracentesis can cause pulmonary edema on the side where a large pleural effusion was removed as fluid shifts into the exposed lung. 2) Dependency can lead to pulmonary edema localized to the dependent lung when a patient is lying on one side for a prolonged period. 3) Pulmonary contusions or embolisms can induce pulmonary edema on the side that is injured or blocked, with the edema sparing the bases initially in some cases.






