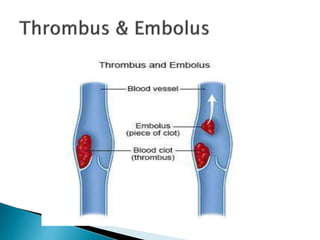
An embolus is a blockage of a blood vessel, typically caused by a blood clot or substance, leading to serious medical emergencies such as various types of embolisms. Thrombosis refers to blood clot formation in vessels, while treatment options include catheter-based procedures like embolectomy and thrombectomy, as well as open surgery. Symptoms to assess include pain, swelling, and changes in skin temperature and color, alongside diagnostic tests like ultrasound and CT scans.