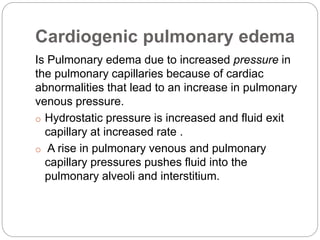
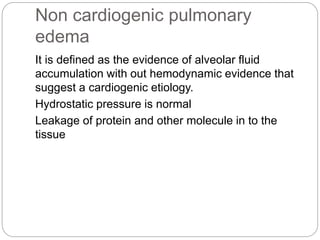
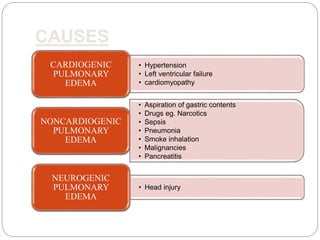
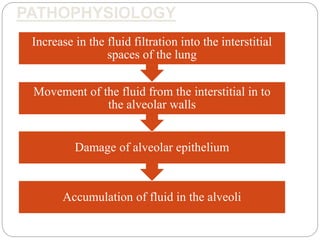
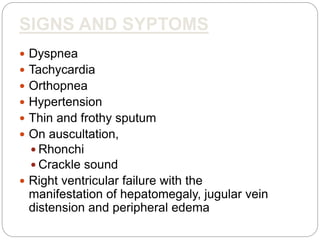
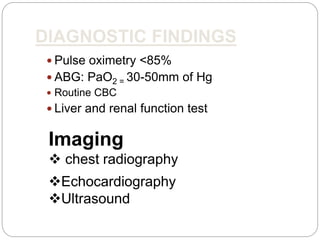
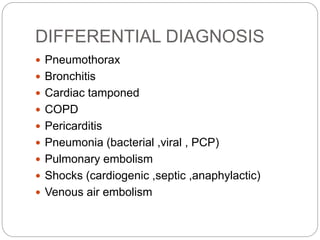
Pulmonary edema is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the lungs, which can be caused by conditions that increase hydrostatic pressure (cardiogenic) or abnormalities that damage the lung tissue and cause fluid leakage (noncardiogenic). Common symptoms include dyspnea, cough, and crackles heard on auscultation. Diagnosis involves chest imaging, blood gases, and echocardiogram. Treatment focuses on correcting hypoxemia with oxygen supplementation and reducing pulmonary hydrostatic pressure through diuretics, afterload reducers, and positioning the patient upright.








![COMPLICATIONS
leg swelling(edema),
abdominal swelling(ascites),
Pleural effusion,
Congestion & swelling of liver,
acute heart attack (myocardial infarction [MI]),
cardiogenic shock,
arrhythmias,
electrolyte disturbances,
mesenteric insufficiency,
protein enteropathy,
respiratory arrest, and death.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ab3e786b-c7ed-4491-8354-be8d157596a1-161225130100/85/group-3-20-320.jpg)
