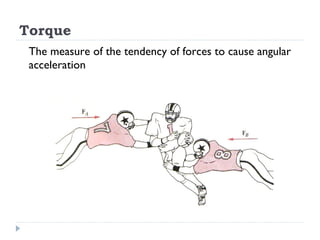
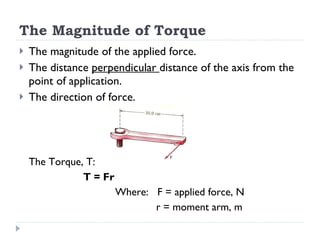
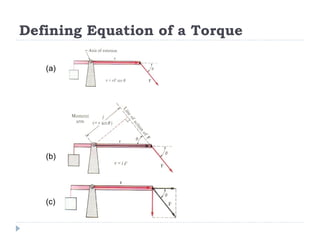
Torque is a measure of the tendency of forces to cause angular acceleration. The magnitude of torque depends on the applied force and the perpendicular distance between the axis of rotation and the point where the force is applied. Torque is calculated as the product of the applied force and the moment arm. For equilibrium, the resultant external force and torque about any axis must be zero. Center of mass is the average point where the entire mass of an object may be considered to be concentrated.