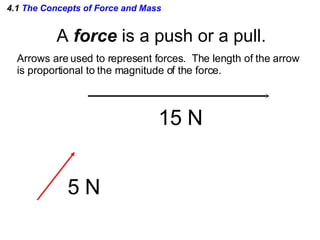
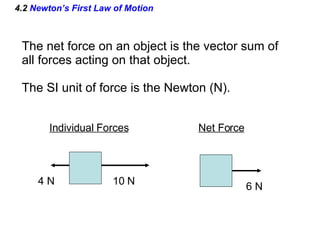
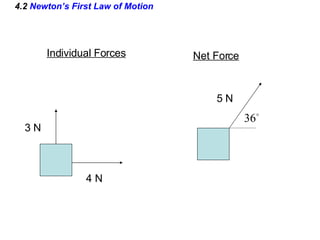
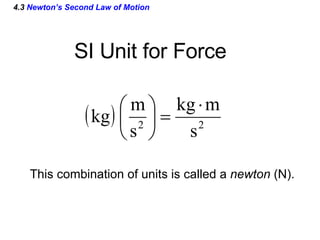
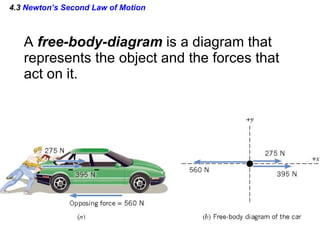
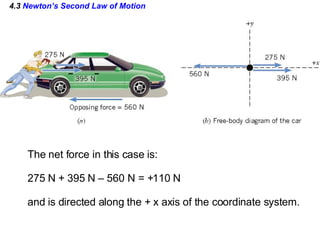
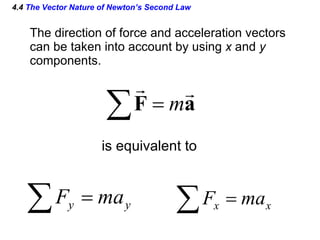
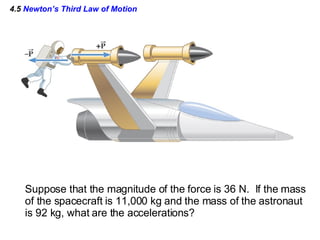
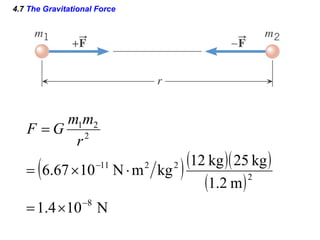
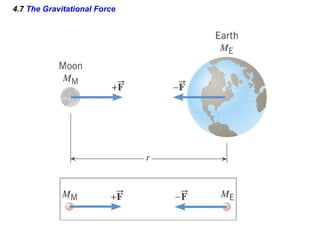
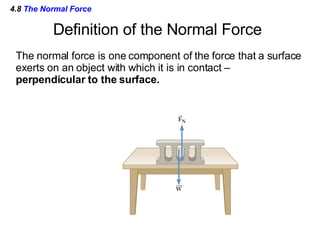
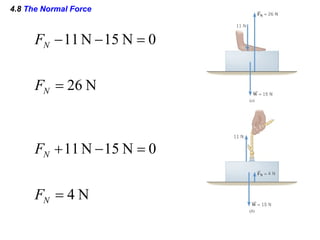
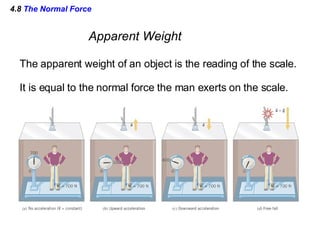
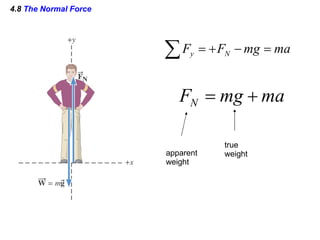
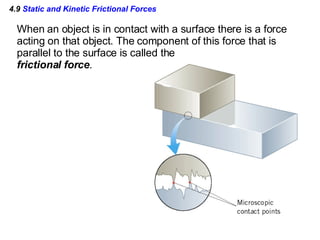
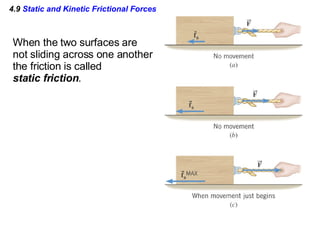
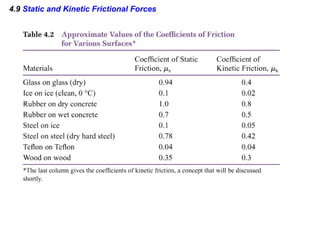
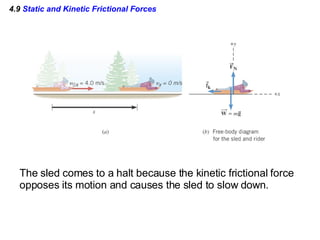
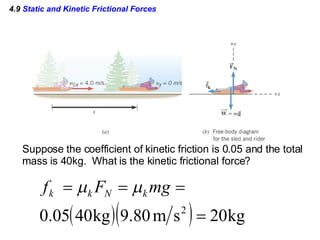
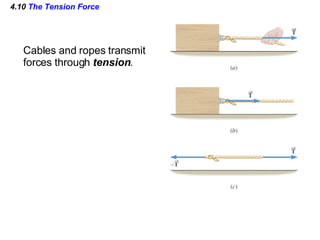
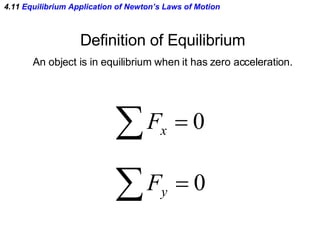
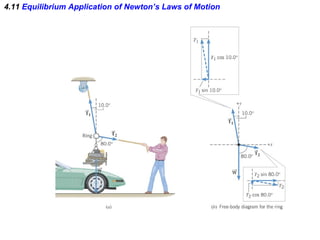
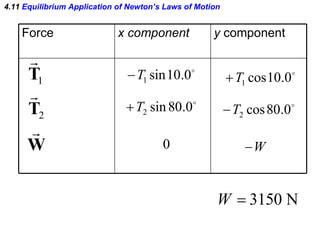
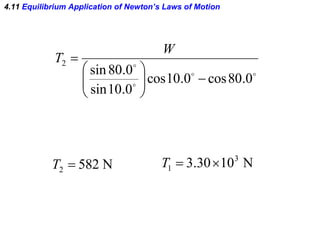
This document provides an overview of Newton's laws of motion. It defines key concepts like force, mass, inertia, and explains Newton's three laws. Newton's first law states that an object remains at rest or in motion unless acted on by a net force. The second law relates the net force on an object to its acceleration. The third law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. Examples of different force types like friction and gravity are also described.