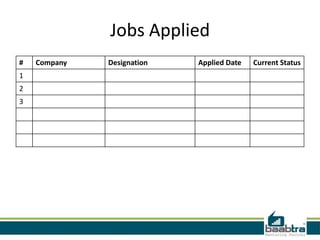
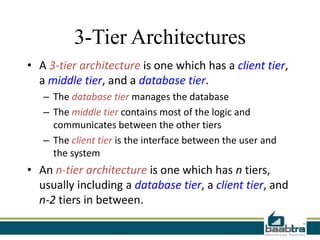
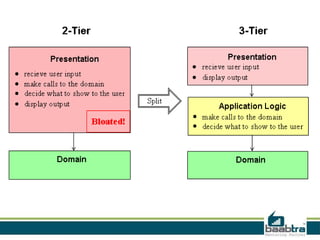
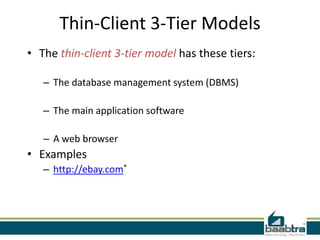
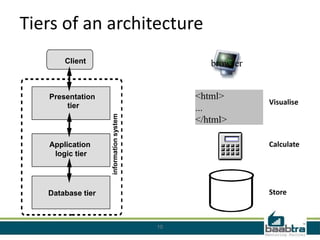
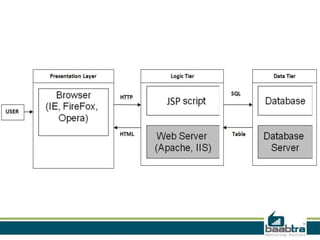
This document discusses 3-tier architectures. It begins by defining a 3-tier architecture as one with a client, middle, and database tier. The client tier handles the user interface, the middle tier contains most of the logic and communication, and the database tier manages the database. It then discusses thin-client and thick-client 3-tier models and provides examples of each. The rest of the document explains the roles and examples of the presentation, application logic, and database tiers. It concludes by listing some advantages of 3-tier architectures such as independence of layers, easier maintenance, reusability, and faster development.