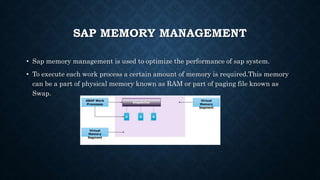
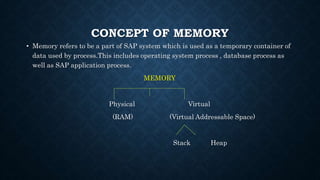
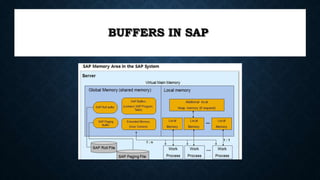
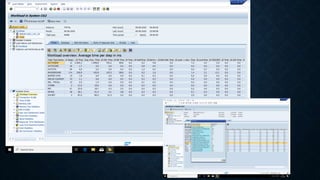
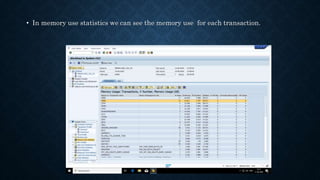
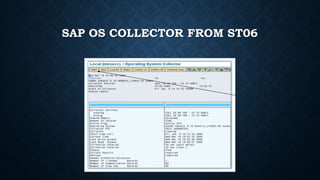
The document discusses SAP memory management and workload analysis. It describes how SAP uses memory and buffers, and how tools like ST03N and ST06 can be used to analyze workload, memory usage, and system performance. Key points covered include the different types of SAP buffers, how to tune buffer sizes, using ST02 for buffer management, and analyzing workload, transactions, memory usage, and hardware resources using ST03N and ST06.