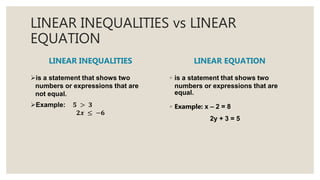
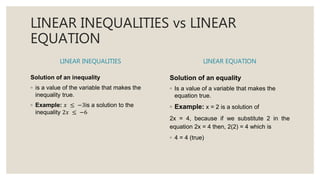
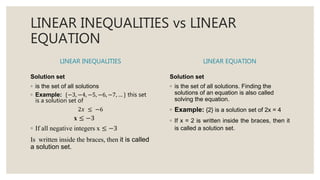
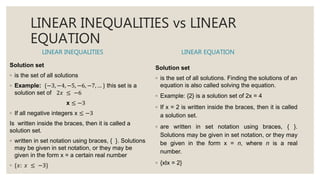
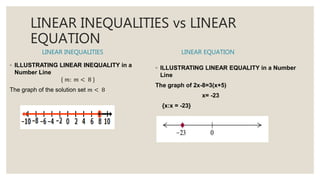
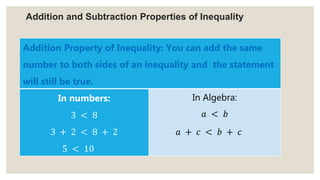
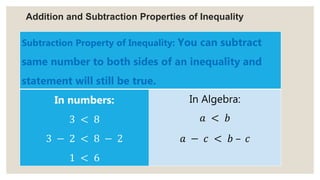
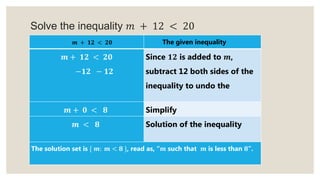
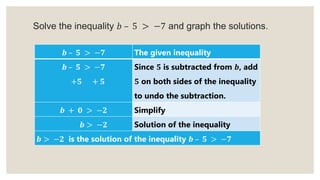
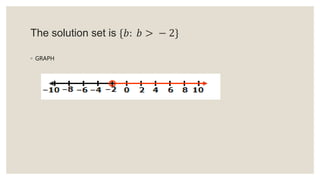
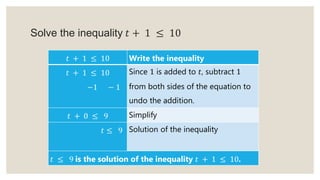
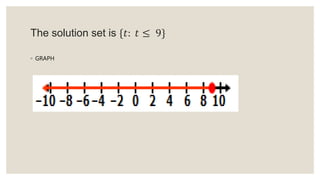
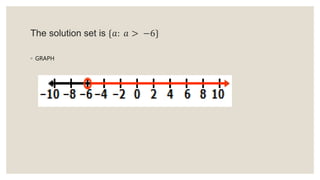
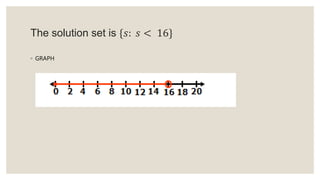
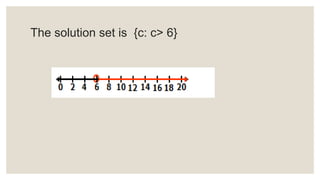
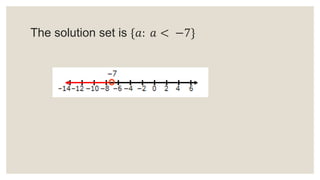
This document provides an overview of linear inequalities and equations for a mathematics class. It defines key terms like linear inequality, solution set, and graphs examples of solving different types of linear inequalities. Students are asked to solve sample inequalities, write the solution sets using set notation, and graph the solutions. The document compares linear inequalities and equations, and covers various properties for solving inequalities, including addition/subtraction, multiplication/division, and dealing with negative numbers.