This document discusses various types of polymorphism in C#, including single inheritance, multi-level inheritance, hierarchical inheritance, and aggregation. Single inheritance allows a derived class to inherit properties and behaviors from a single base class. Multi-level inheritance involves inheriting from another inherited class. Hierarchical inheritance involves inheriting from a single base class but having multiple derived classes. Aggregation represents a "has-a" relationship where one class contains an instance of another class. The document provides examples to illustrate each type of polymorphism.


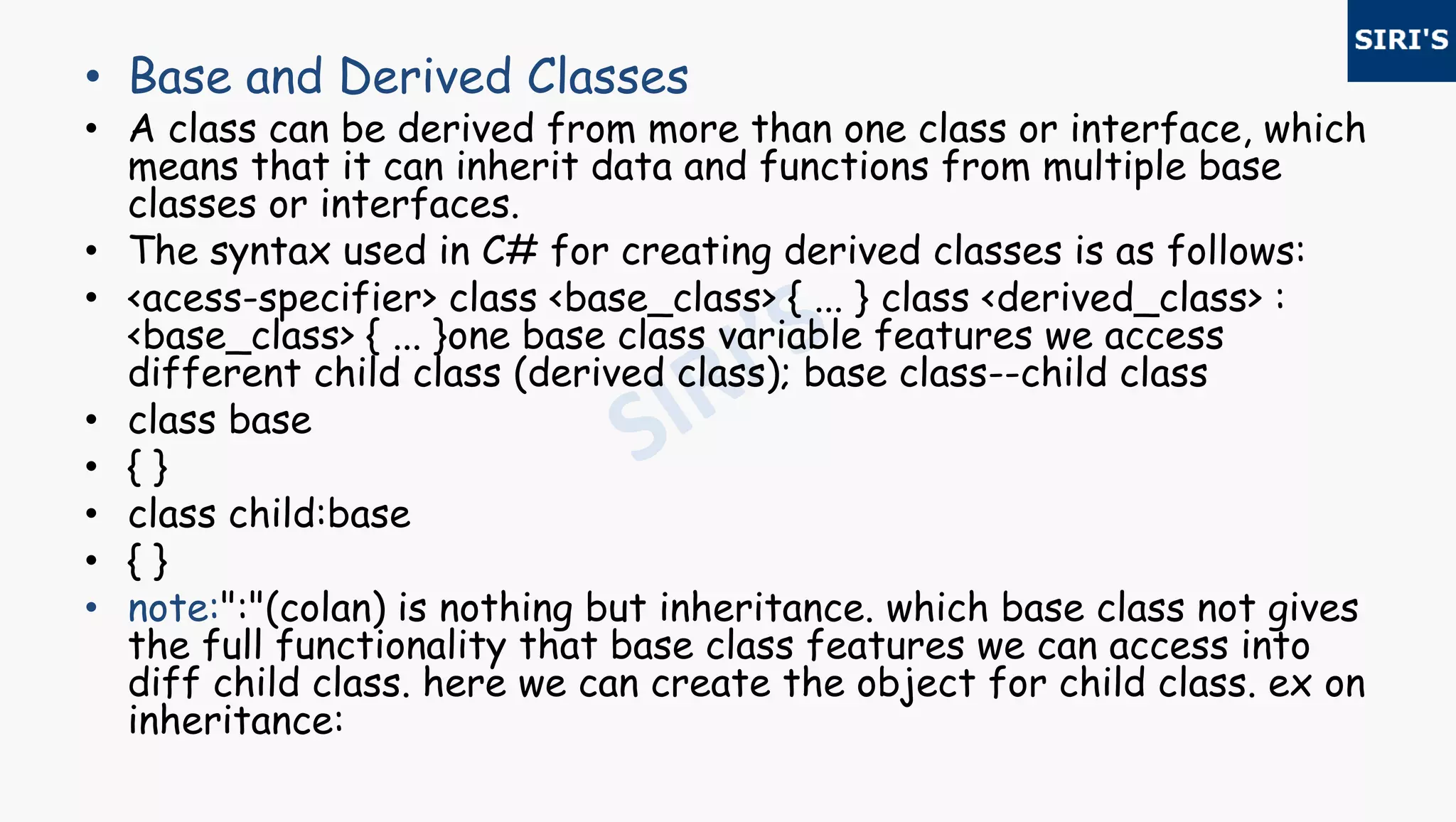
![class emp//base class
• { protected int sal;//variables
• public void esal()//method
• { sal = 15000;
• Console.WriteLine(sal.ToString()); } }
• class dept:emp//base class inherits into child classes
• { int bonus,ta,ts;
• public void tsal()
• { bonus = 5000;
• ta = 600;
• ts = sal + bonus + ta;
• Console.WriteLine("the total salary is:" + ts.ToString());
• Console.ReadLine(); }
• static void Main(string[] args)
• { dept obj = new dept();//object
• obj.esal();
• obj.tsal(); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/29c-170628165446/75/29csharp-4-2048.jpg)

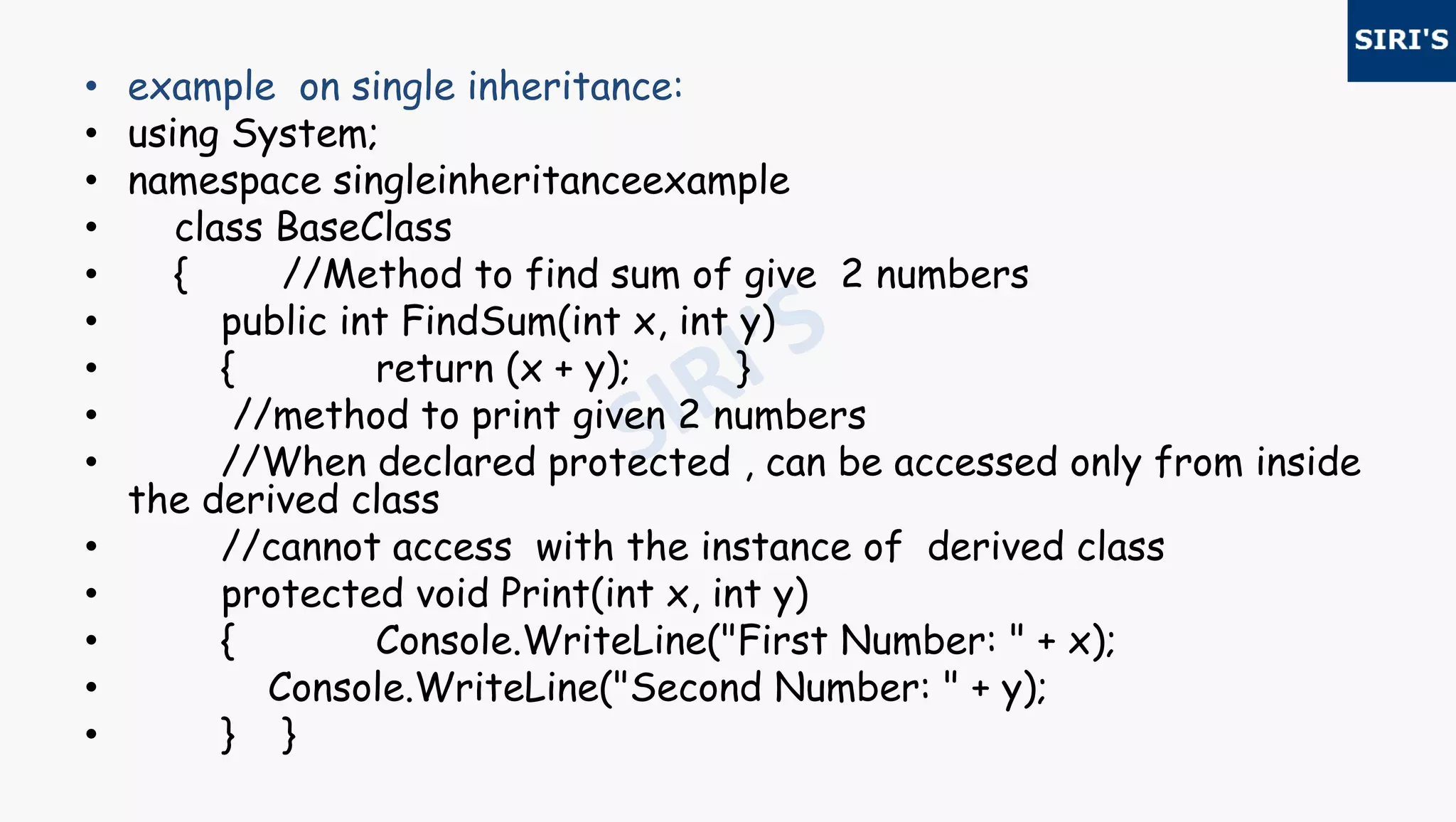
![• class Derivedclass : BaseClass
• { public void Print3numbers(int x, int y, int z)
• { Print(x, y); //We can directly call baseclass members
• Console.WriteLine("Third Number: " + z);
• }
• static void Main(string[] args)
• { //Create instance for derived class, so that base class members
• // can also be accessed
• //This is possible because derivedclass is inheriting base class
• Derivedclass instance = new Derivedclass();
• instance.Print3numbers(30, 40, 50); //Derived class internally calls base
class method.
• int sum = instance.FindSum(30, 40); //calling base class method with derived
class instance
• Console.WriteLine("Sum : " + sum);
• Console.Read();
• } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/29c-170628165446/75/29csharp-7-2048.jpg)


![• } }
• public class Animal : Bird//child class 2
• { public void animaldet()
• { persondet();
• birddet();
• Console.WriteLine("this is the Animal Class");
• }
• static void Main(string[] args)
• { Animal obj = new Animal();
• obj.persondet();
• obj.birddet();
• obj.animaldet();
• Console.ReadLine();
• } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/29c-170628165446/75/29csharp-10-2048.jpg)


![• class C : A//child class2
• { public void getinfo()
• { msg();
• Console.WriteLine( "this is c class Method");
} }
• static void Main(string[] args)
• { B obj1 = new B();//creat child class 1 obj1
• obj1.info();
• C obj2 = new C();//create child class 2 obj2
• obj2.getinfo();
• Console.ReadLine(); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/29c-170628165446/75/29csharp-13-2048.jpg)


