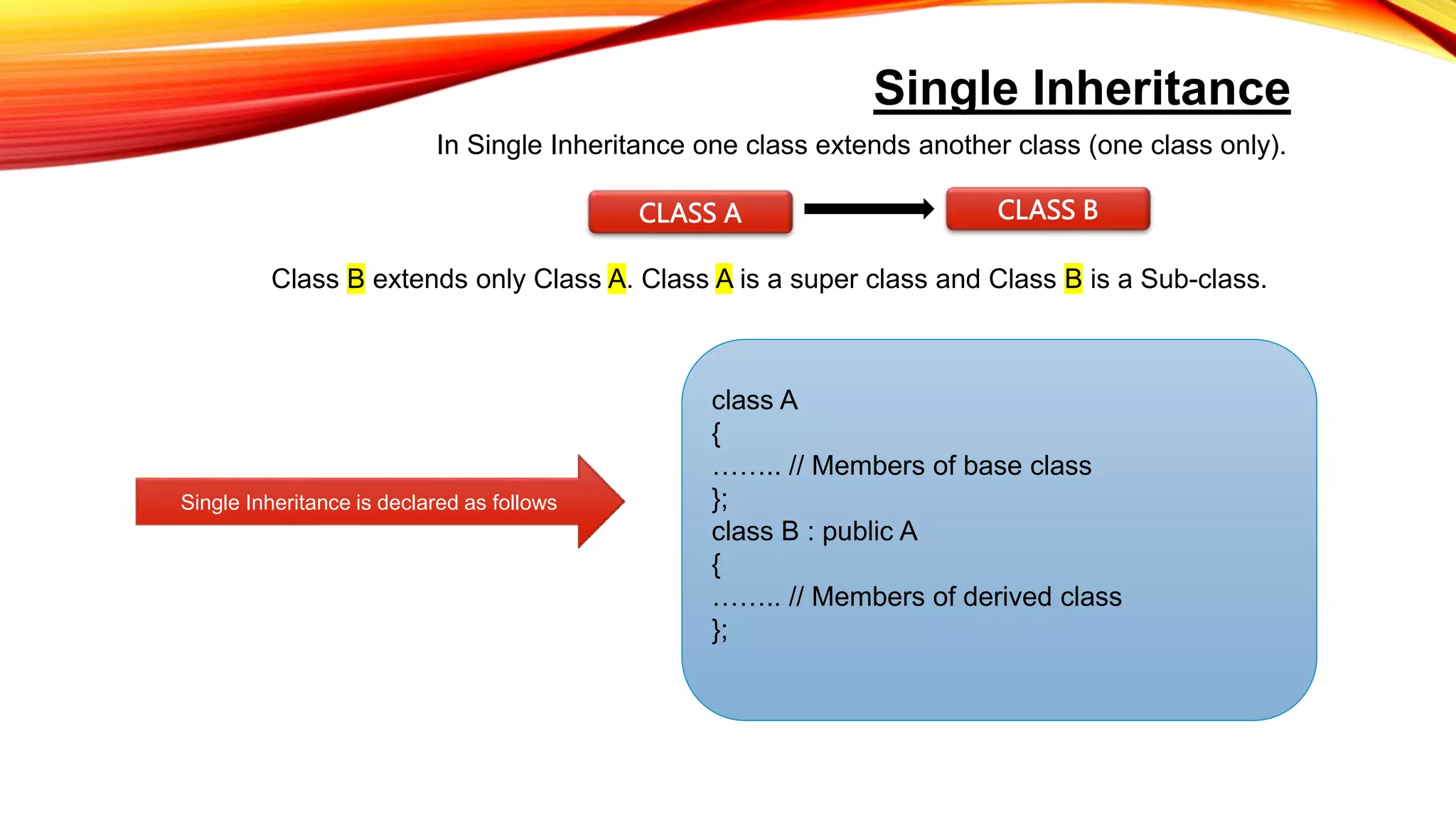
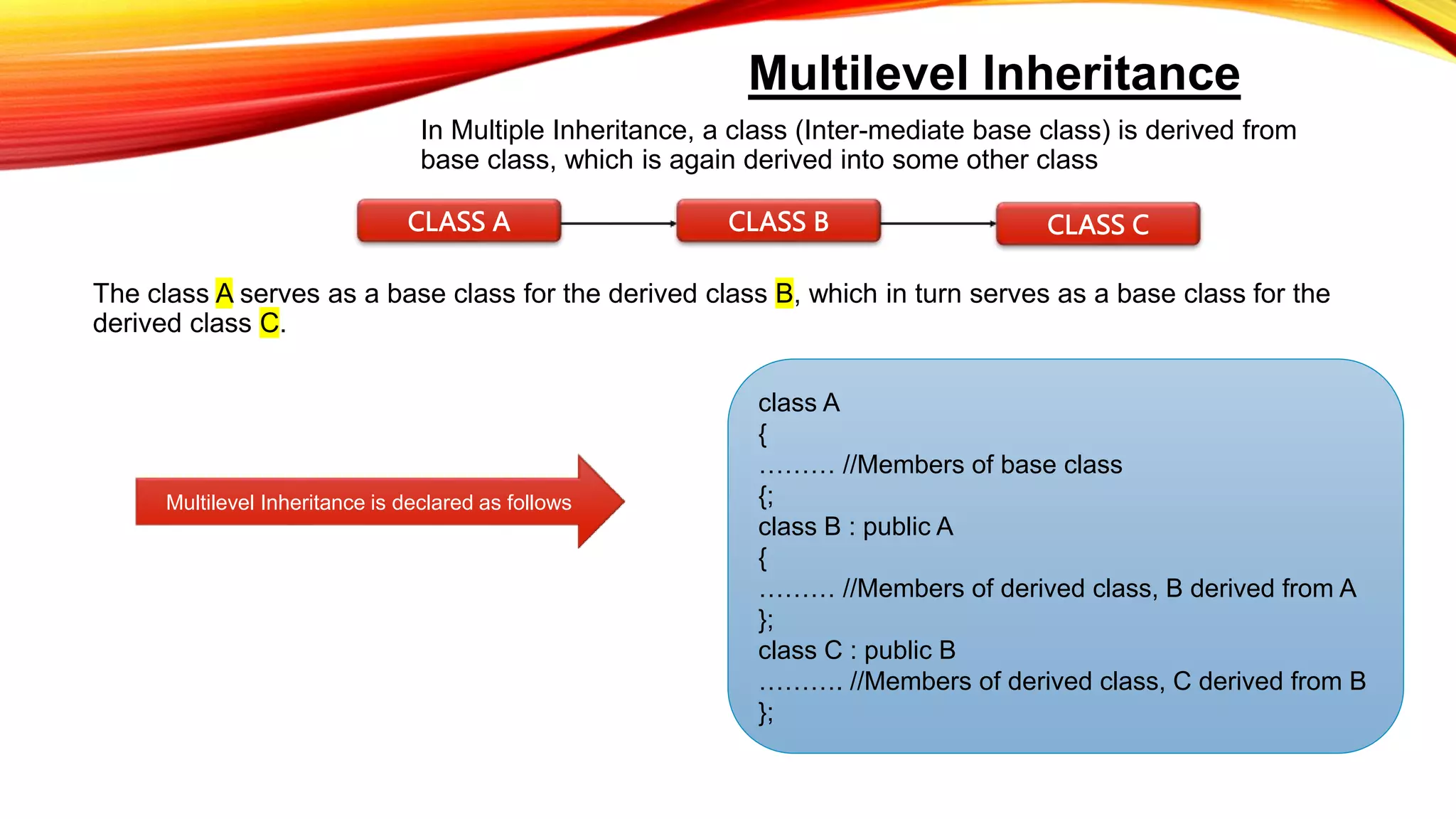
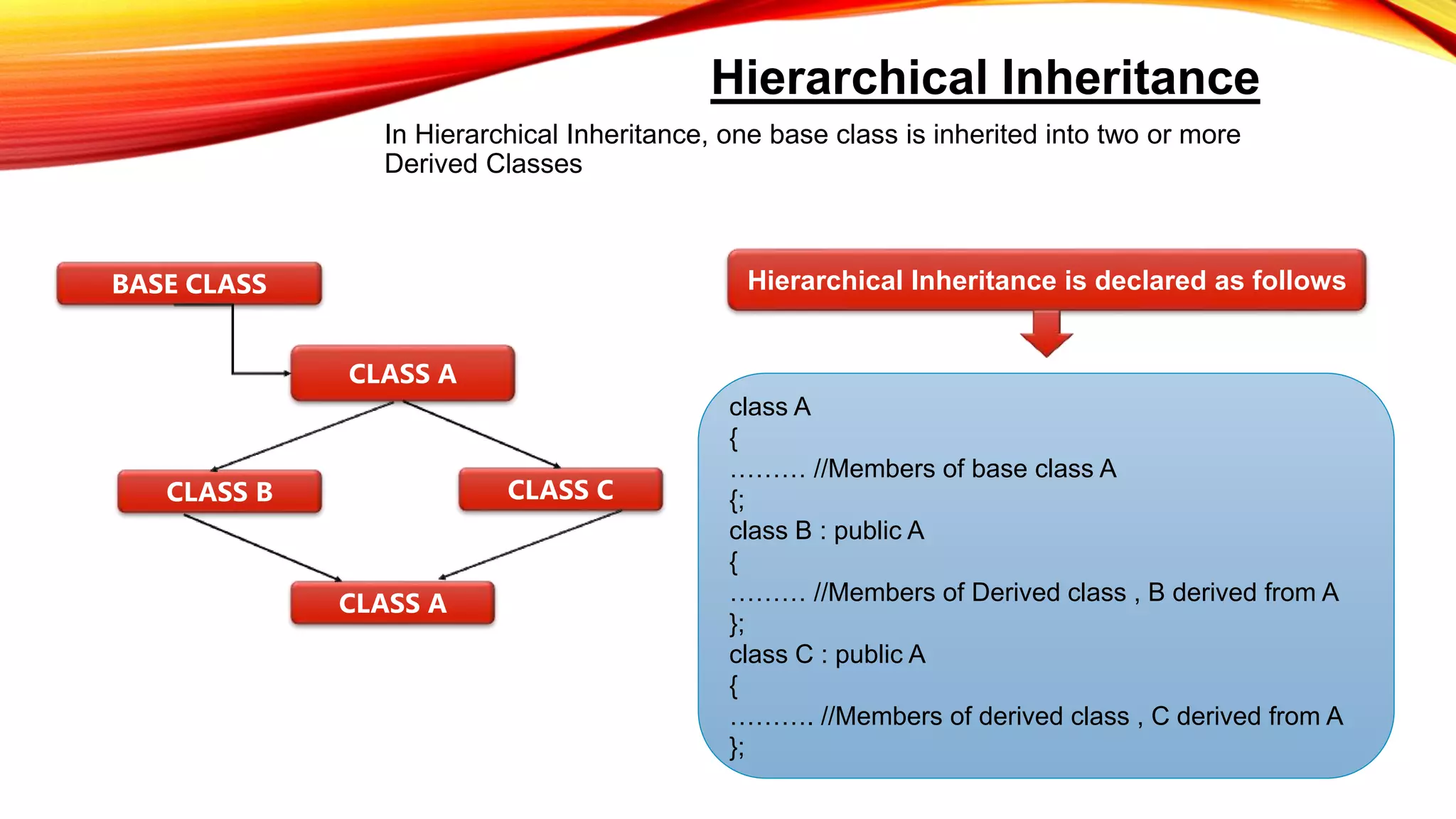
Single inheritance allows a derived class to inherit from one base class. Multilevel inheritance allows a class to inherit from an intermediate base class which itself inherits from another base class. Multiple inheritance allows a class to inherit from more than one base class. Hierarchical inheritance involves one base class being inherited by two or more derived classes. Hybrid inheritance uses more than one type of inheritance to derive a new subclass. The main advantages of inheritance are reusability and saving time and effort by allowing code to be reused in various situations as needed.