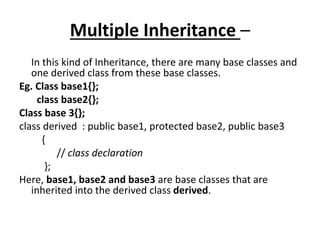
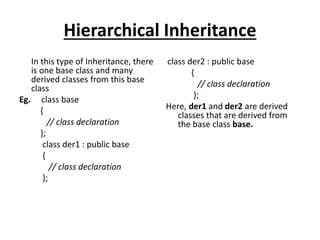
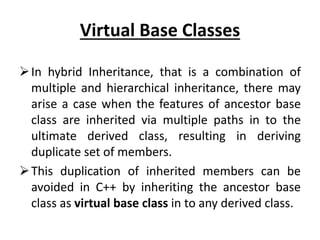
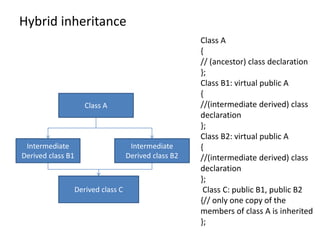
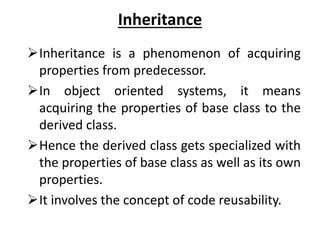
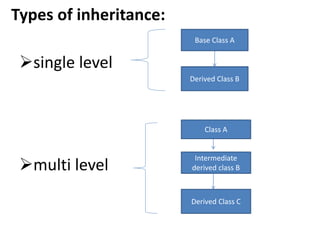
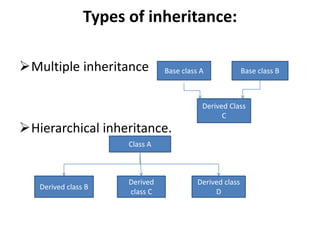
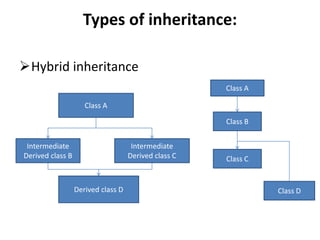
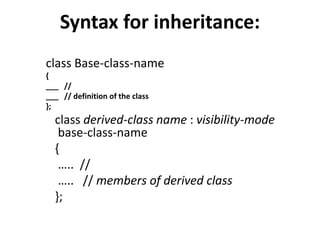
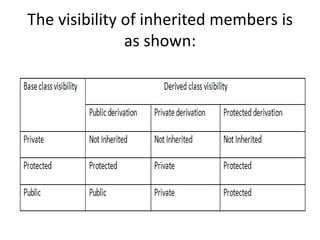
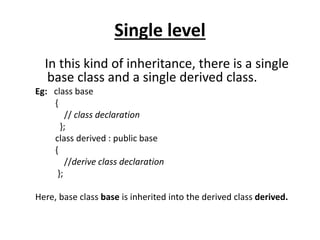
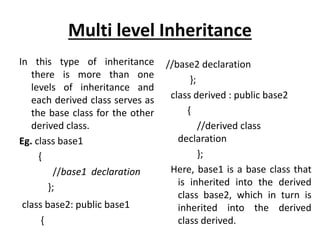
Inheritance allows new classes called derived classes to inherit properties from existing classes called base classes. There are different types of inheritance including single, multi-level, multiple, and hierarchical. Inheritance promotes code reusability and faster development. Derived classes inherit all features of the base class and can add new features. Constructors must be defined in derived classes to pass parameters to base class constructors. Abstract classes are designed only to act as base classes to be inherited by other classes.






![Question to implement
A class A{
char name[] …….
int roll_no; ……
+void get();
+void show(); };
B class B: public A
float m1,m2,m3; {
+void take(); …..
+void put(); };
C
class C: public B
float percentage; {
+void cal_per(); …..
+void disp_result(); };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-210908161912/85/Inheritance-15-320.jpg)