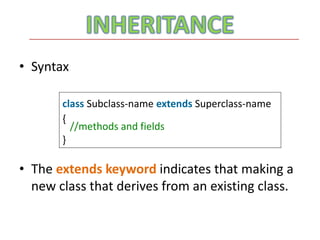
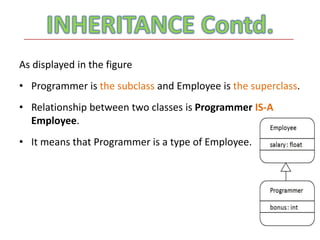
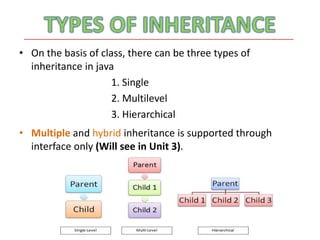
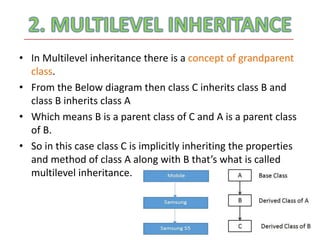
The document discusses inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as deriving a new class from an existing class, known as the base or parent class. The new class is called the subclass or child class. The subclass inherits all variables and methods from the parent class. There are three types of inheritance in Java: single inheritance where one subclass extends one superclass, multilevel inheritance where a subclass extends another subclass which extends a superclass, and hierarchical inheritance where a superclass has multiple subclasses.


![class Employee
{
float salary=40000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee
{
int bonus=10000;
public static void main(String args[])
{
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
} }
OUTPUT: Programmer salary is:40000.0
Bonus of programmer is:10000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180127182713/85/Java-Inheritance-5-320.jpg)

![class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
} }
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
} }
Class Dog inherits the properties of
Class Animal.
class TestInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Dog d=new Dog();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}}
OUTPUT:
barking...
eating...
Animal
Void eat()
Dog
Void bark()
Void eat()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180127182713/85/Java-Inheritance-8-320.jpg)
![class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
}}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
}}
class BabyDog extends Dog
{
void weep()
{
System.out.println("weeping...");
}}
class TestInheritance2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
BabyDog d=new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.bark();
d.eat();
}}
Output:
weeping...
barking...
eating...
Animal
Void eat()
Dog
Void bark()
Void eat()
BabyDog
void weep()
void bark()
Void eat()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180127182713/85/Java-Inheritance-10-320.jpg)

![class Animal
{
void eat()
{
System.out.println("eating...");
} }
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark()
{
System.out.println("barking...");
} }
class Cat extends Animal
{
void meow()
{
System.out.println("meowing...");
} }
class TestInheritance3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cat c=new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
}}
Output:
meowing...
eating...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180127182713/85/Java-Inheritance-12-320.jpg)