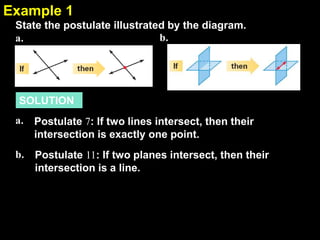
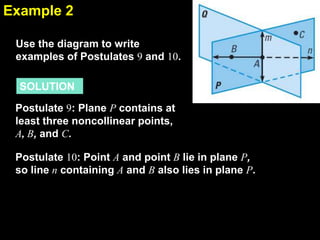
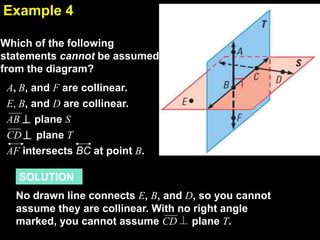
1) The document discusses geometry postulates and using diagrams to illustrate and apply postulates. It provides examples of writing statements that illustrate specific postulates based on diagrams.
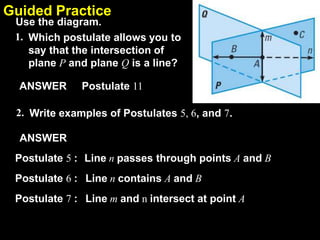
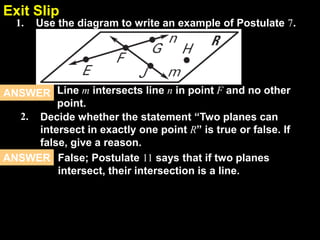
2) Students are asked to identify which postulate a diagram or statement illustrates. One example asks which postulate allows you to say that the intersection of two planes is a line.
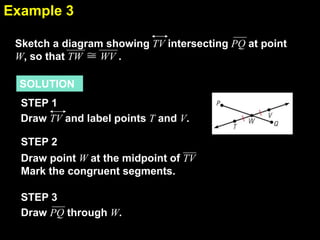
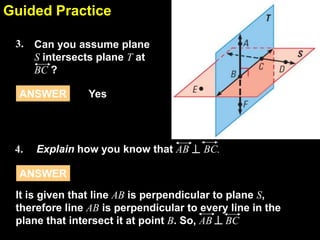
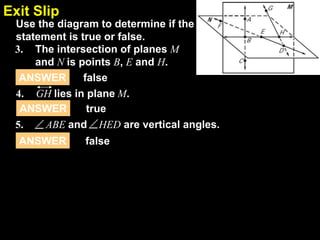
3) The document contains guided practice problems asking students to write statements applying specific postulates based on diagrams, and questions testing understanding of concepts like intersections of lines and planes.