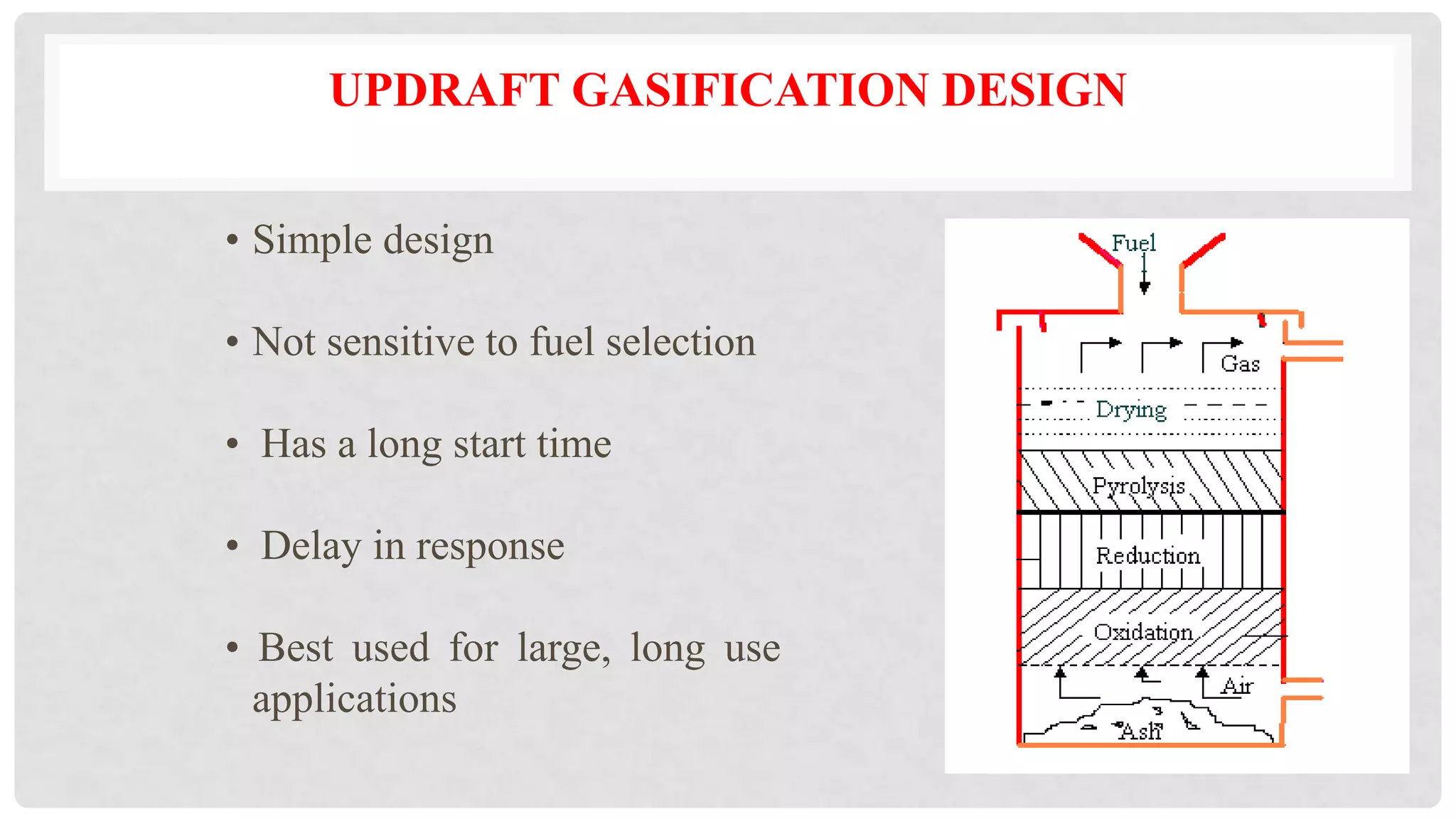
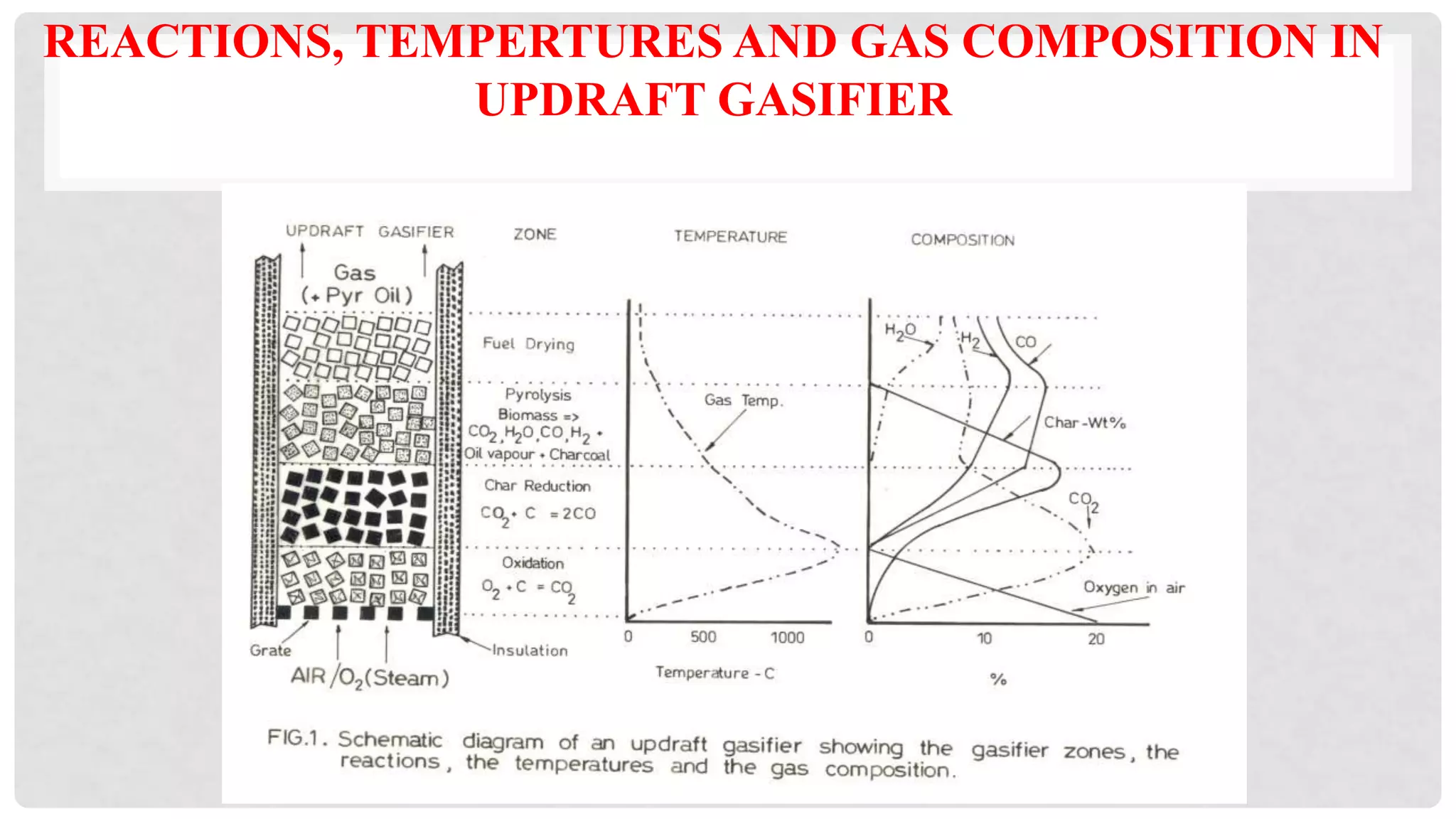
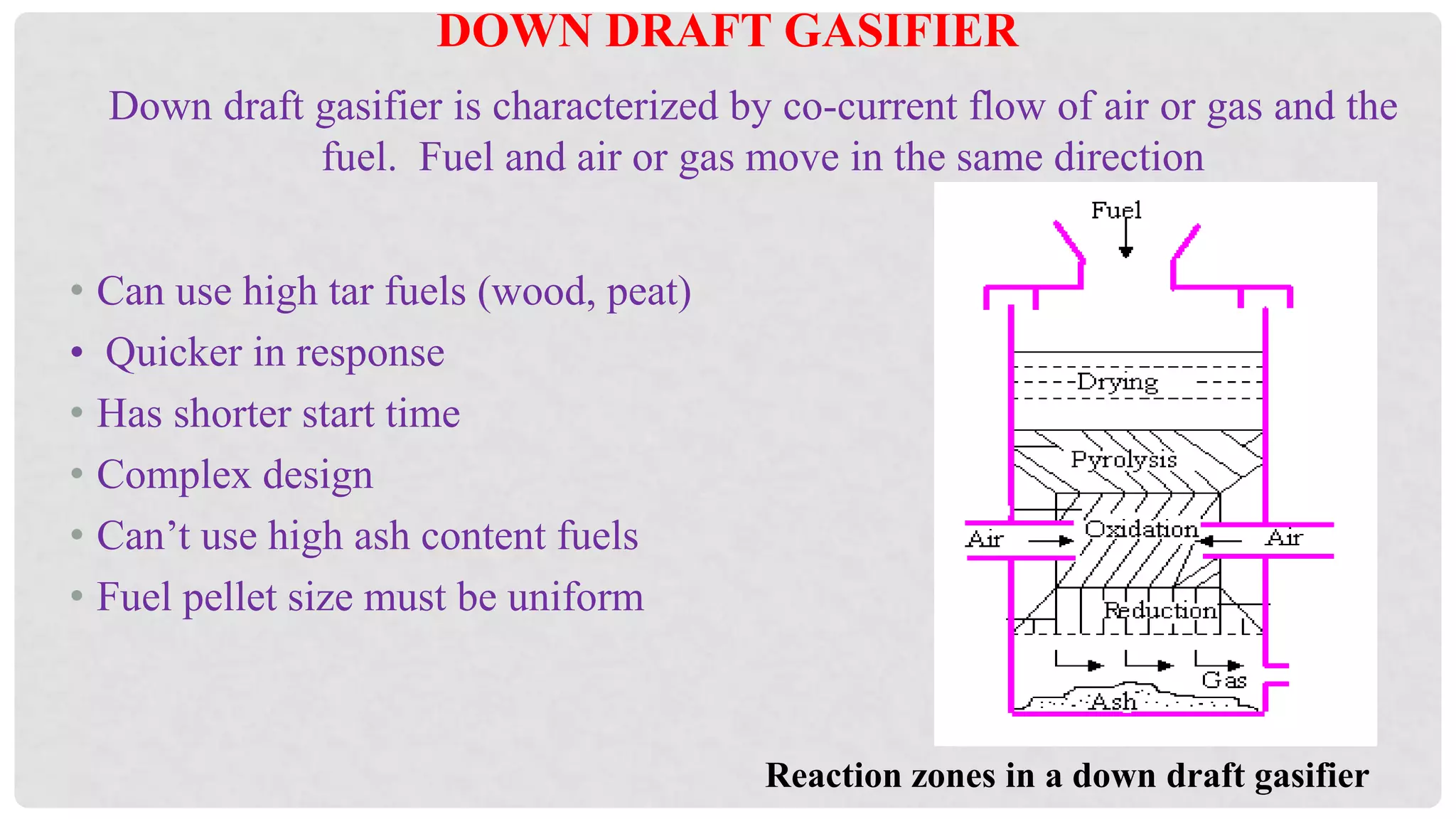
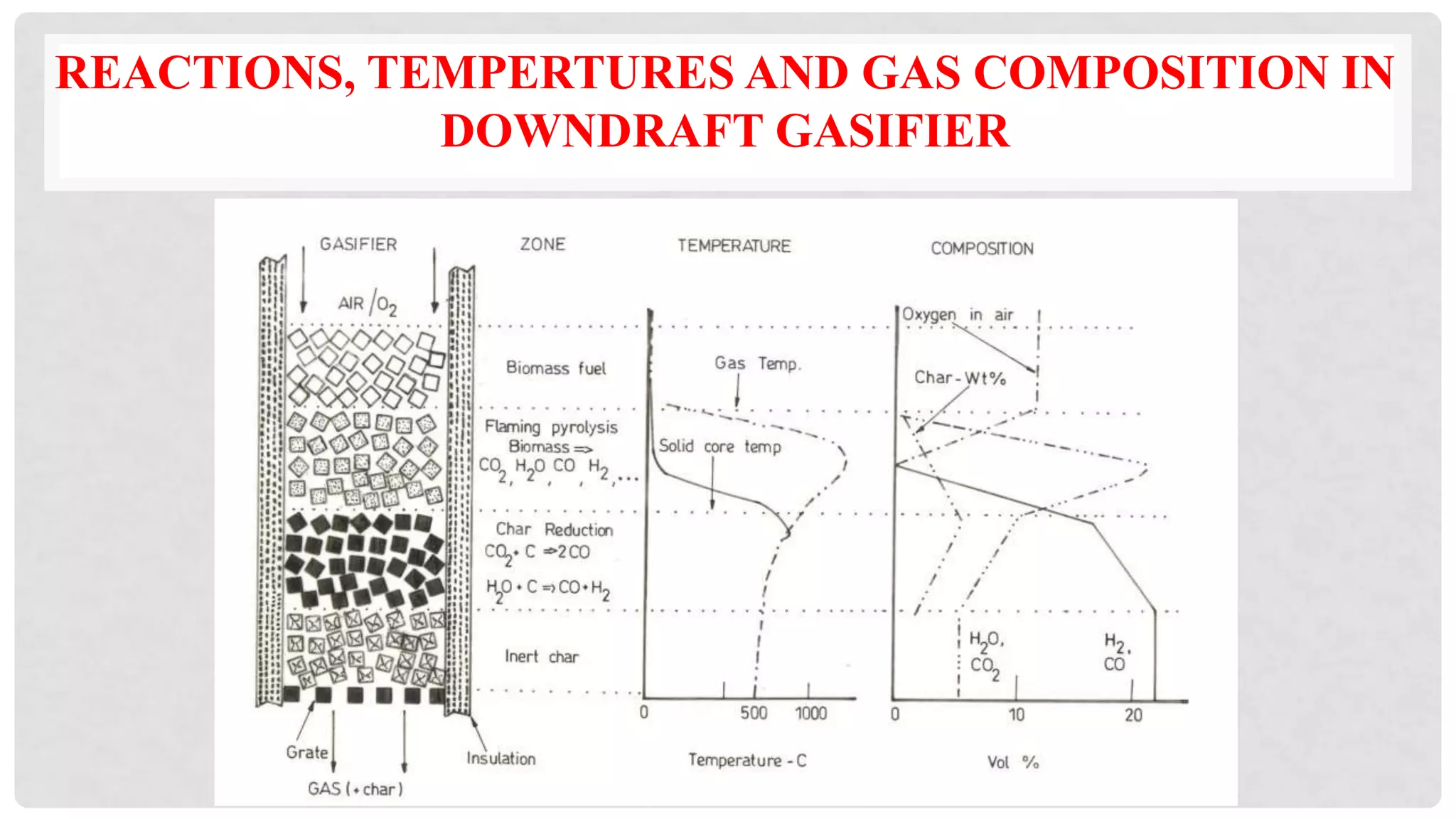
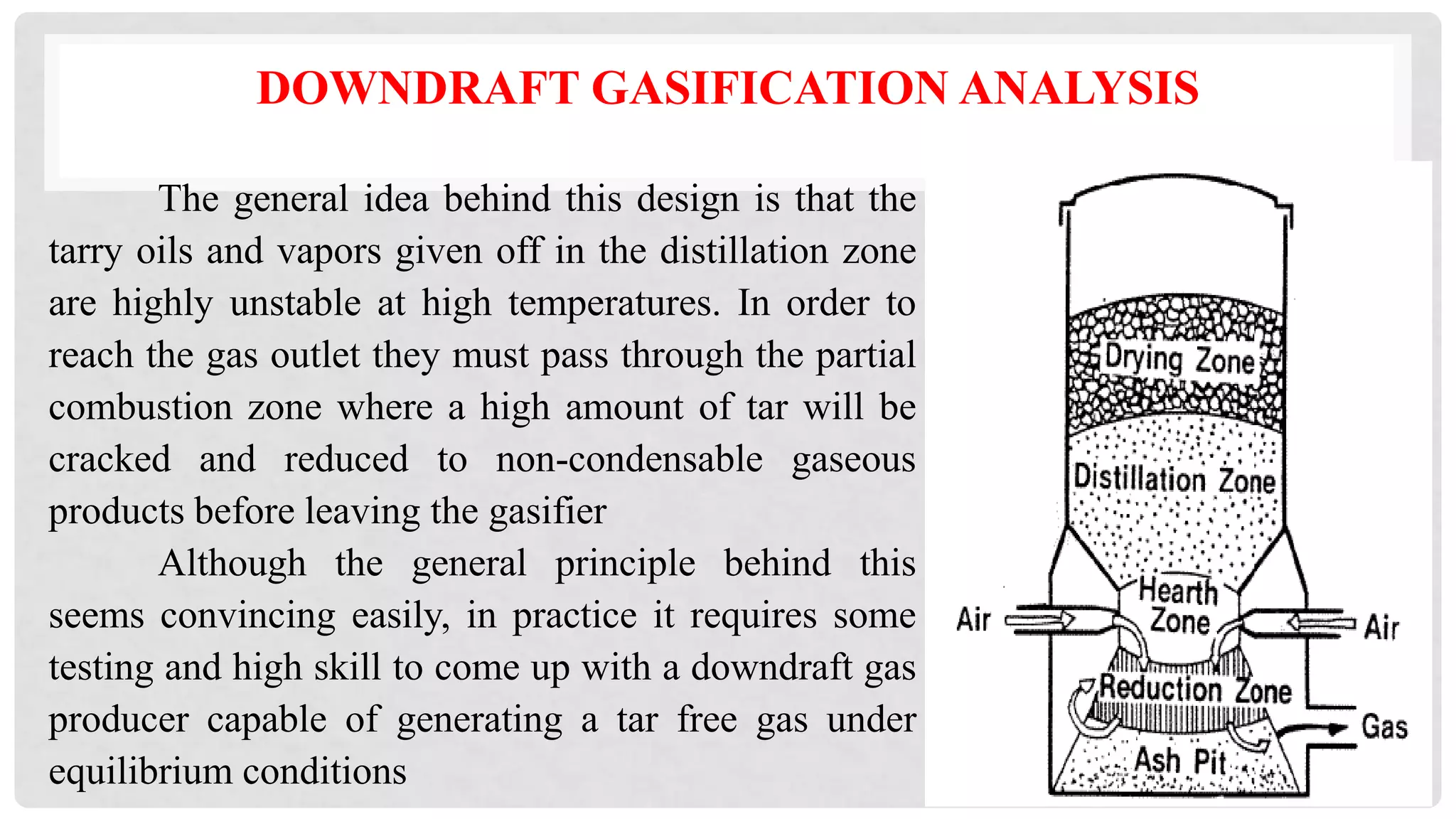
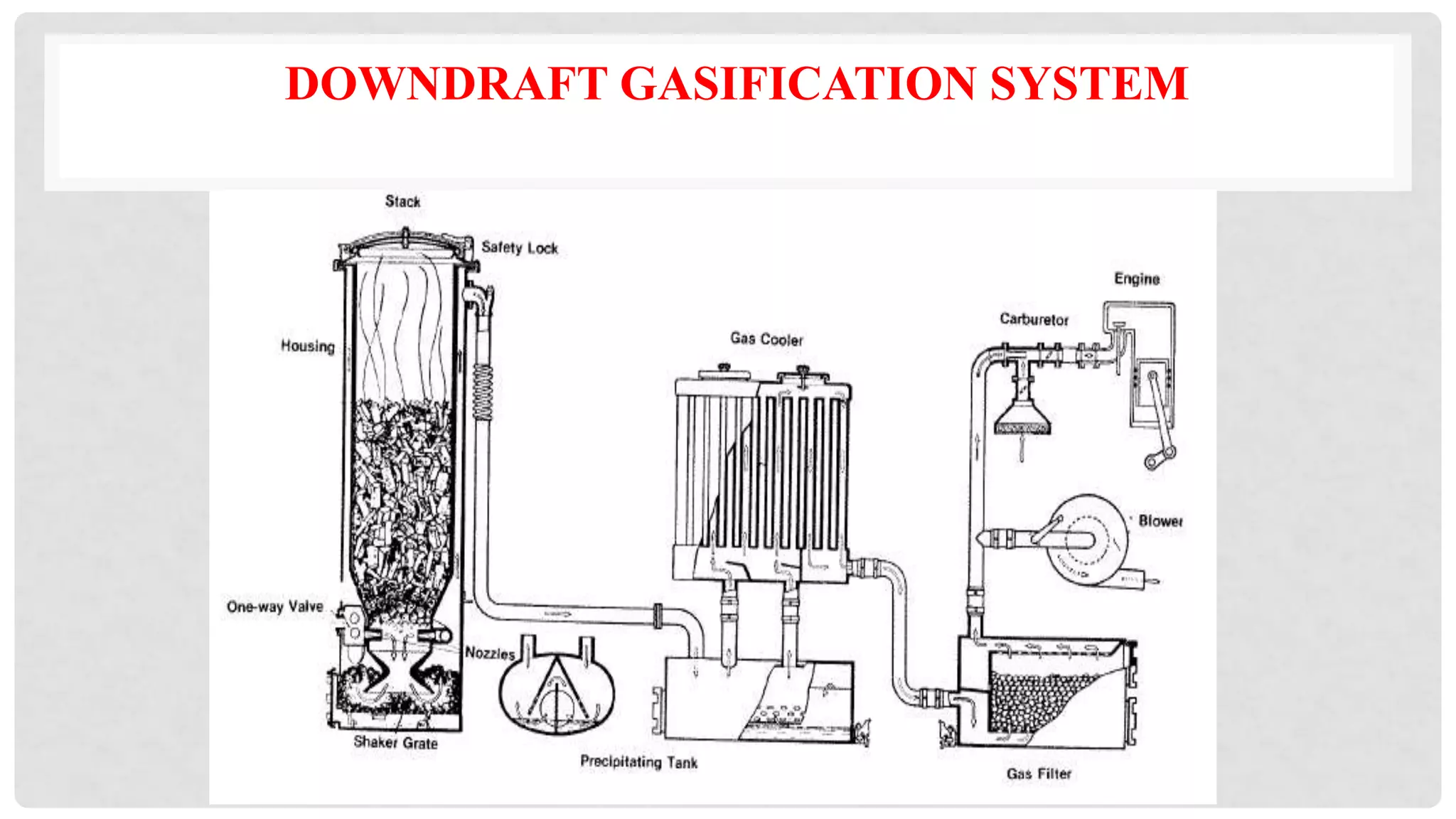
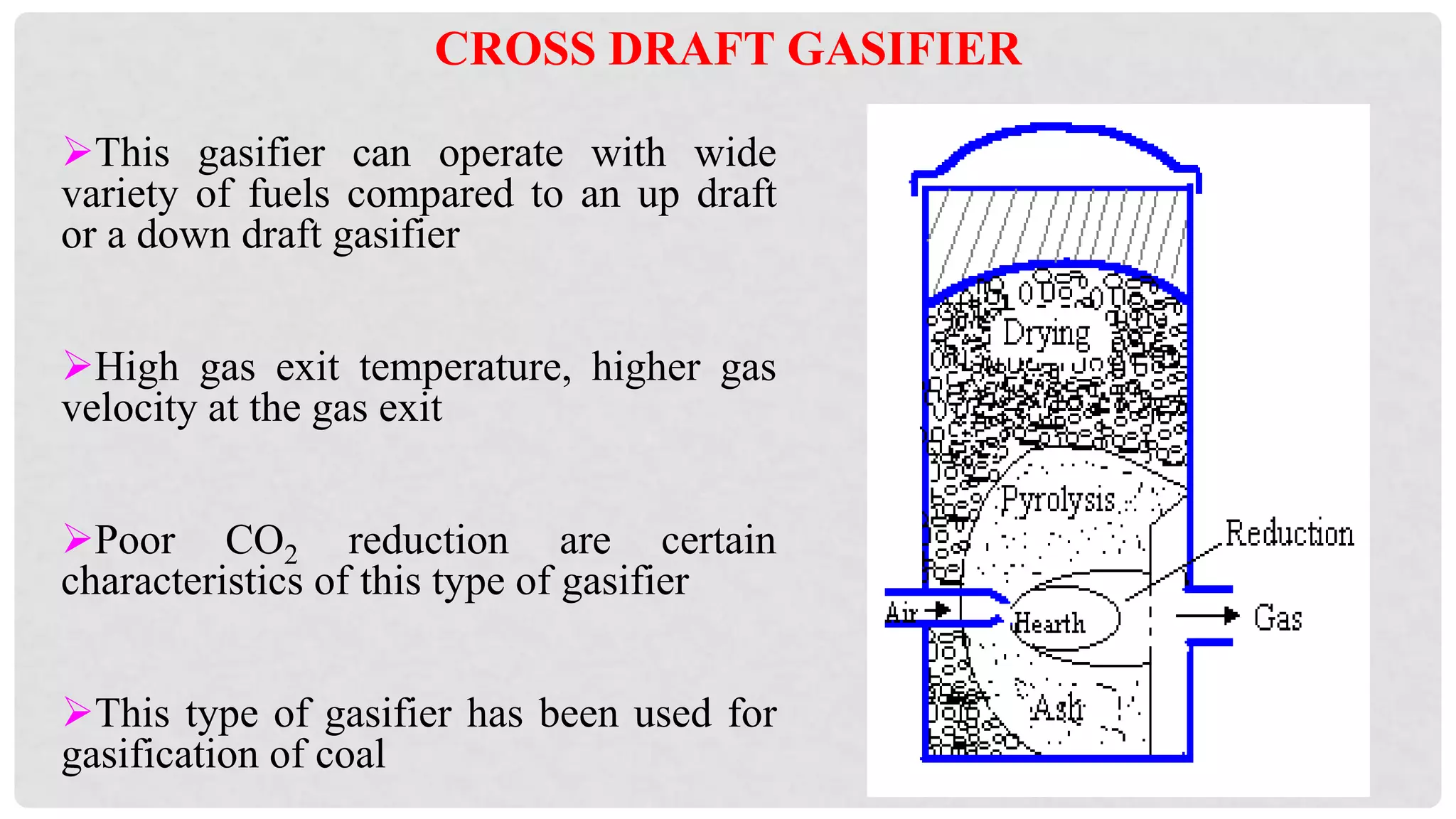
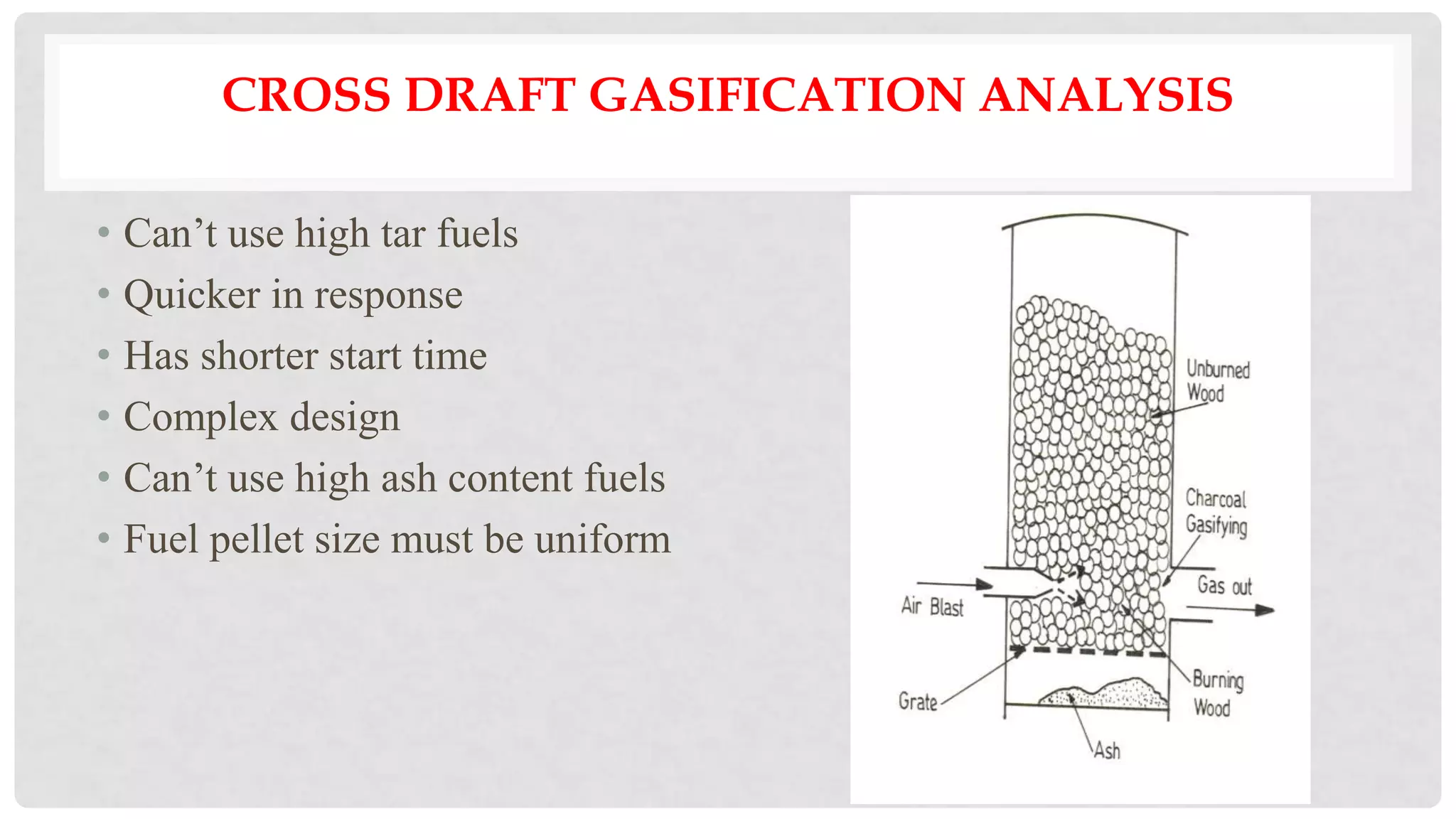
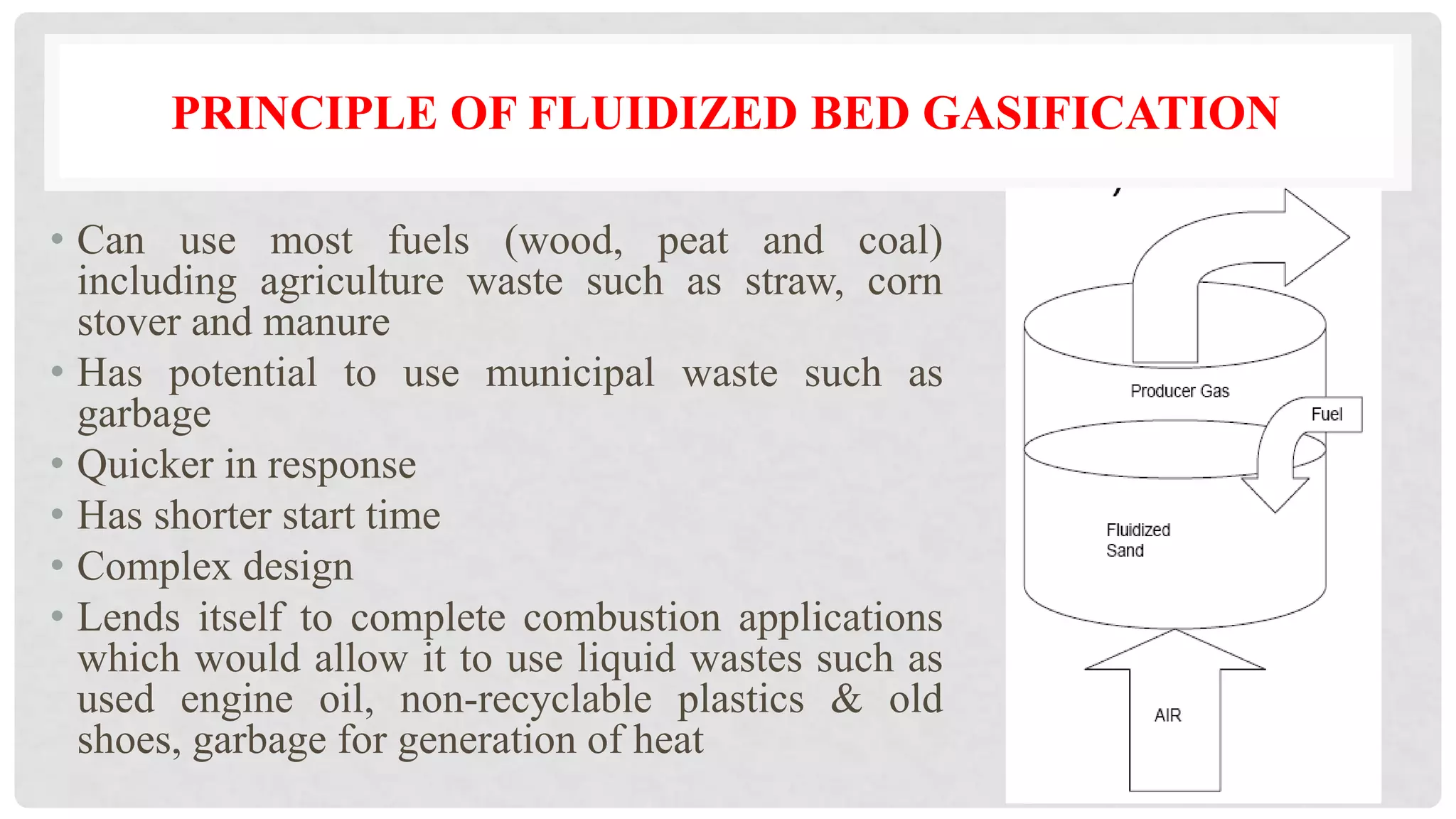
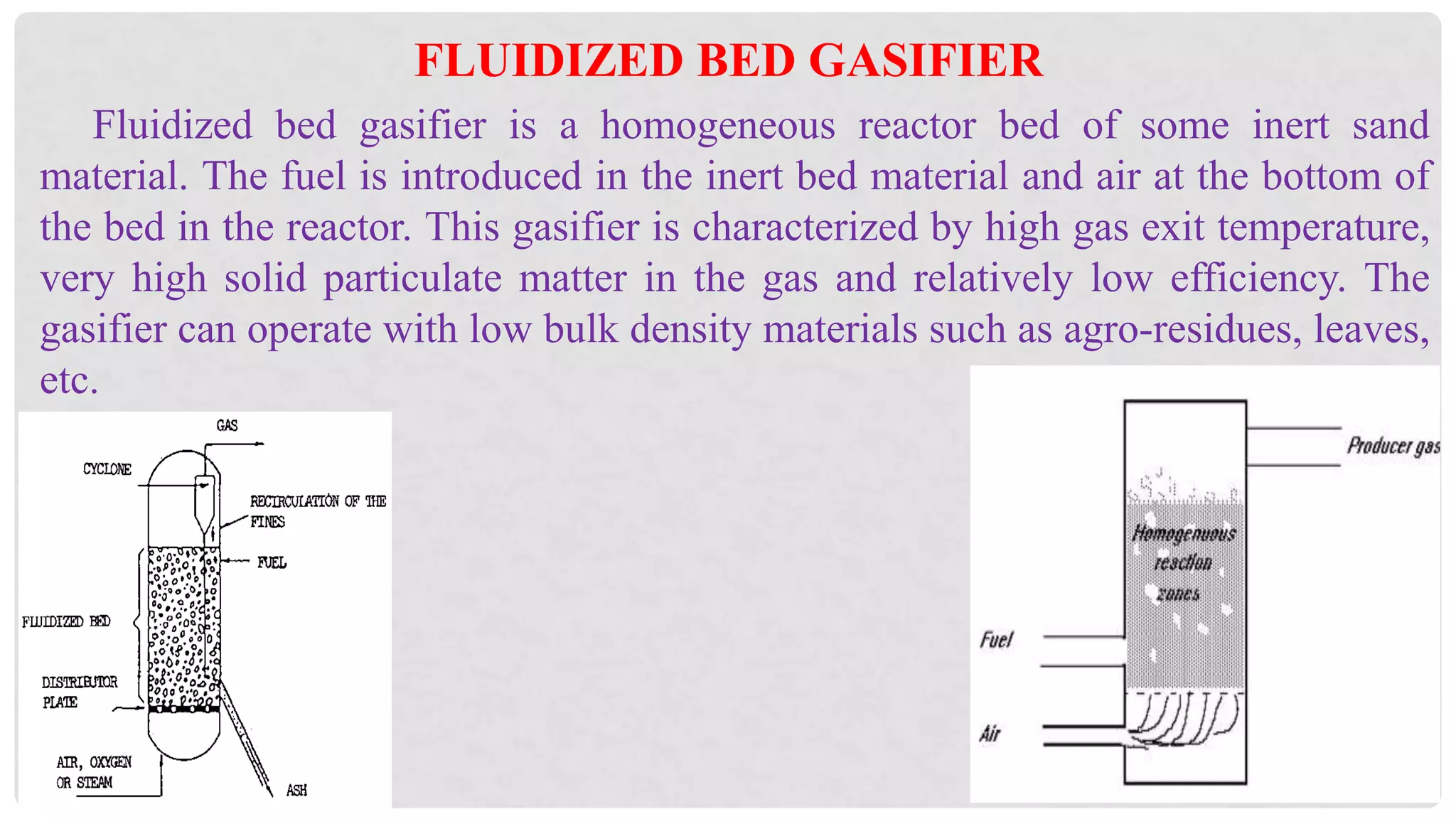
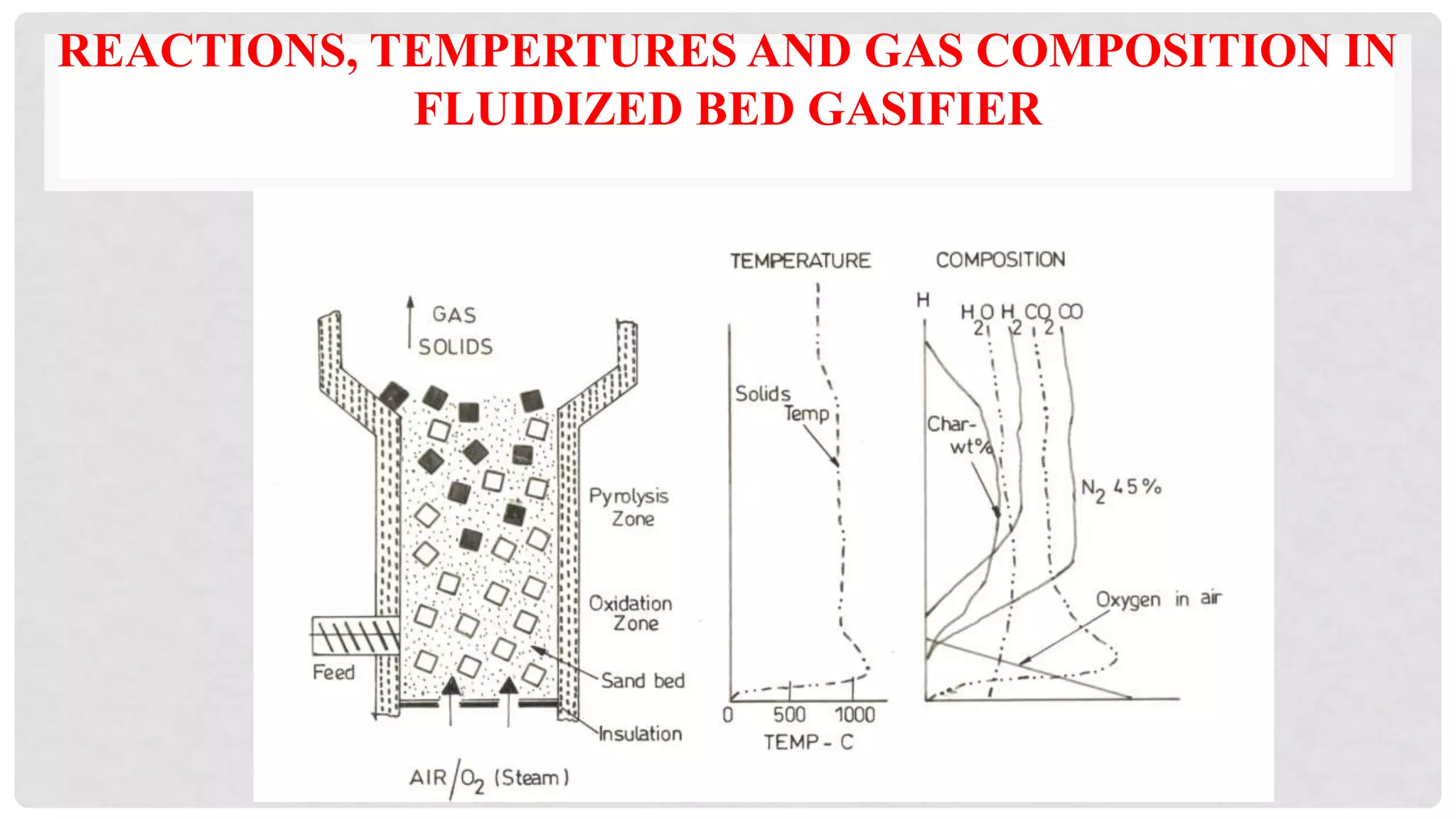
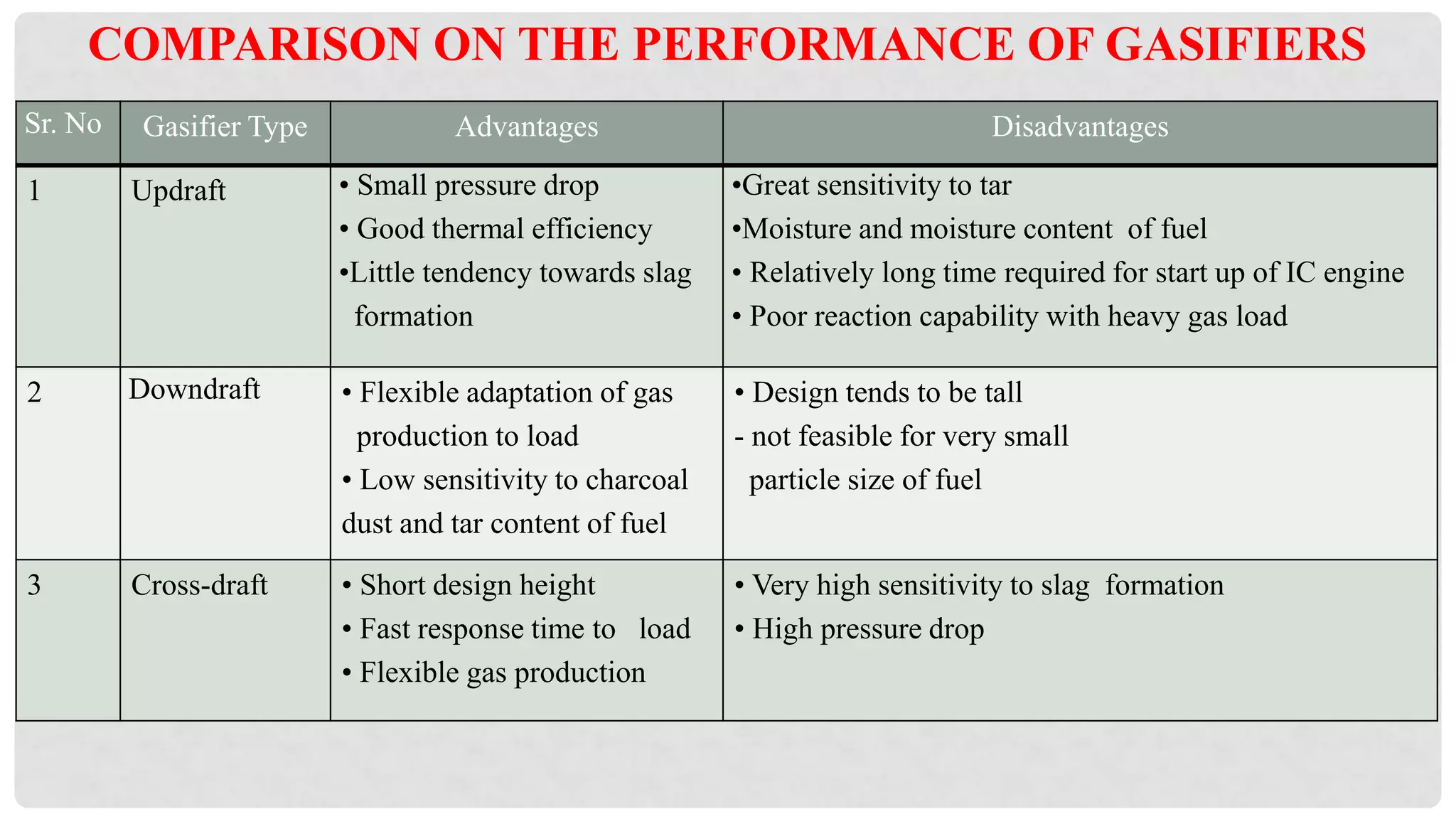
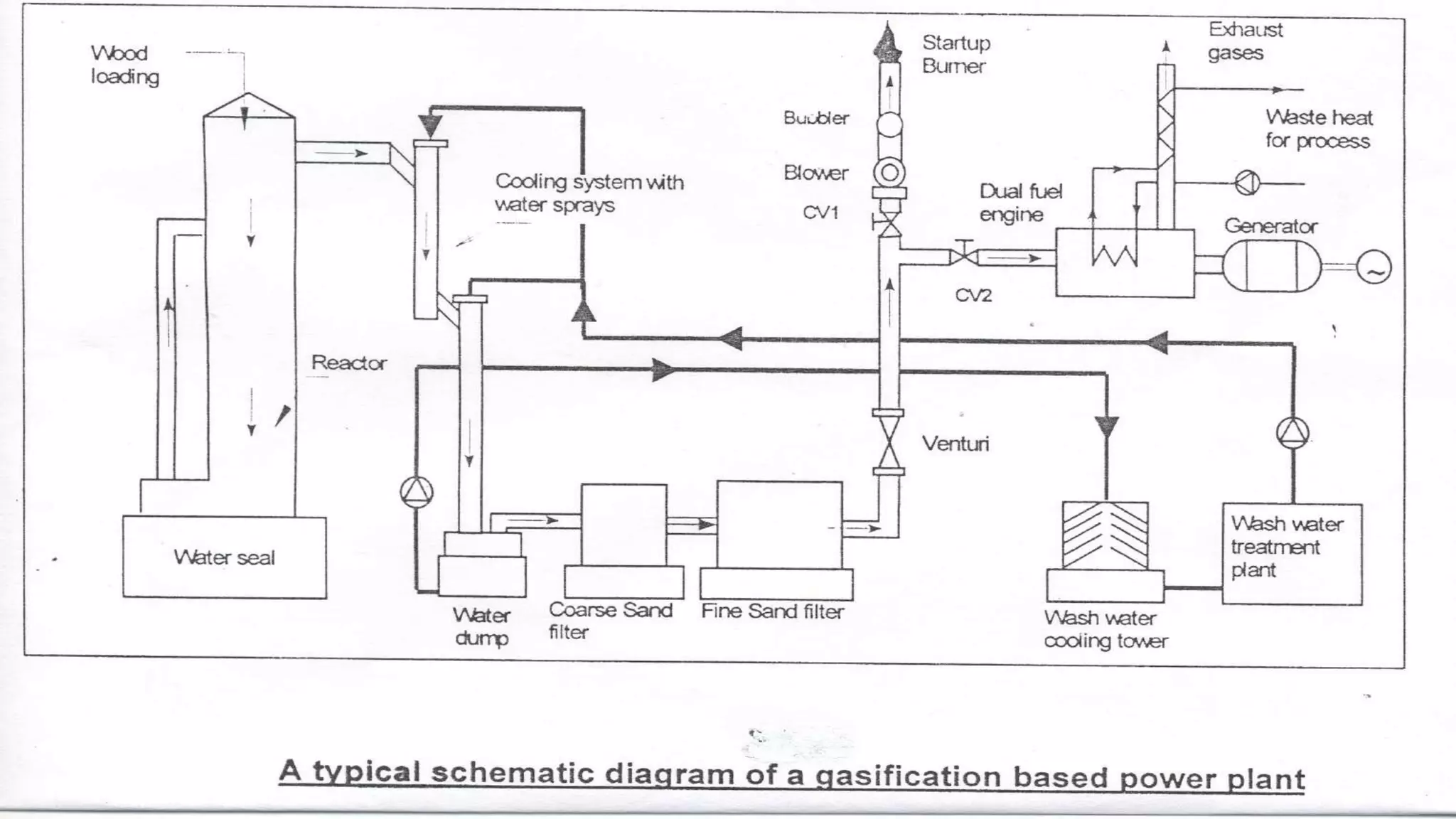
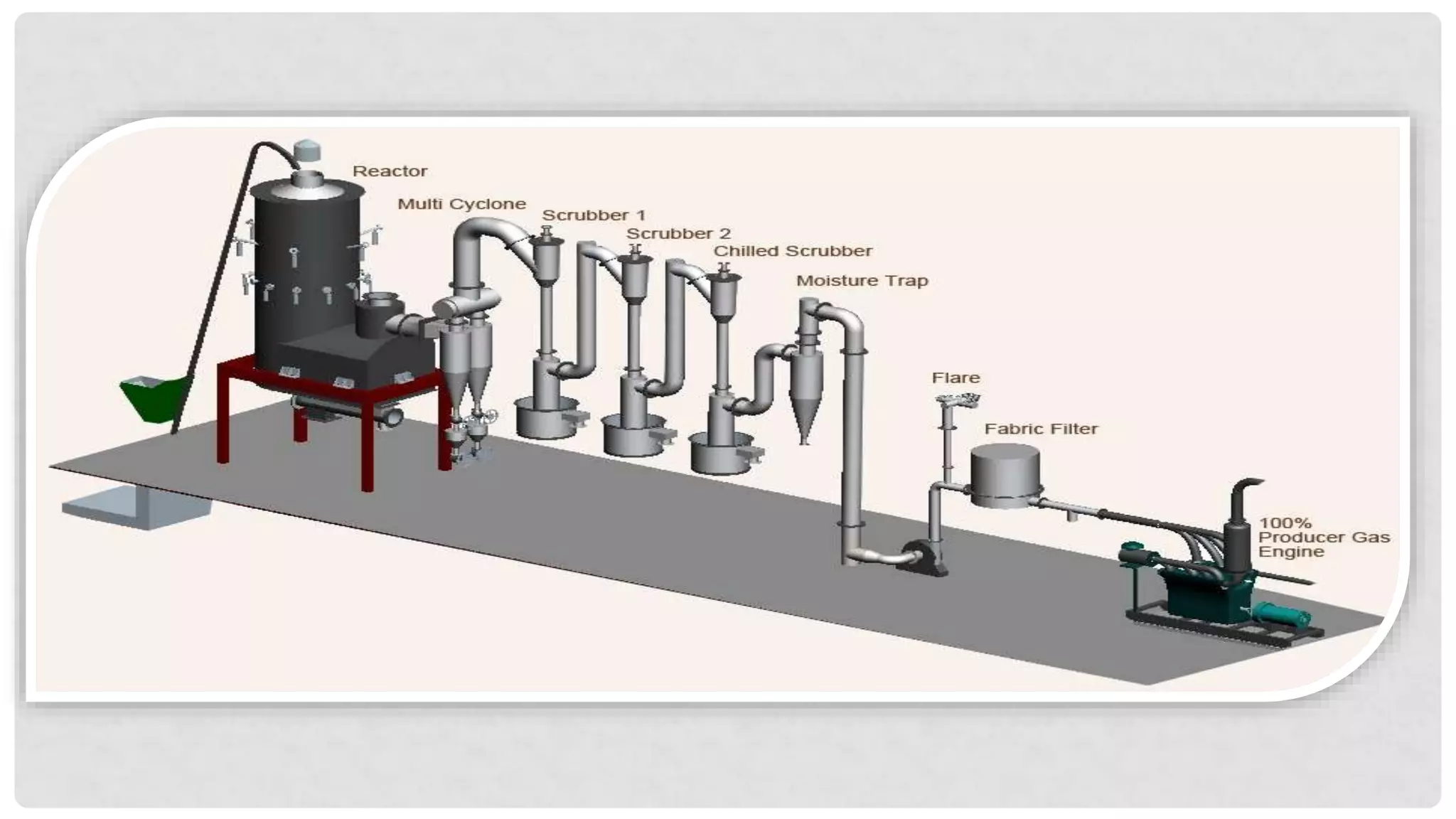
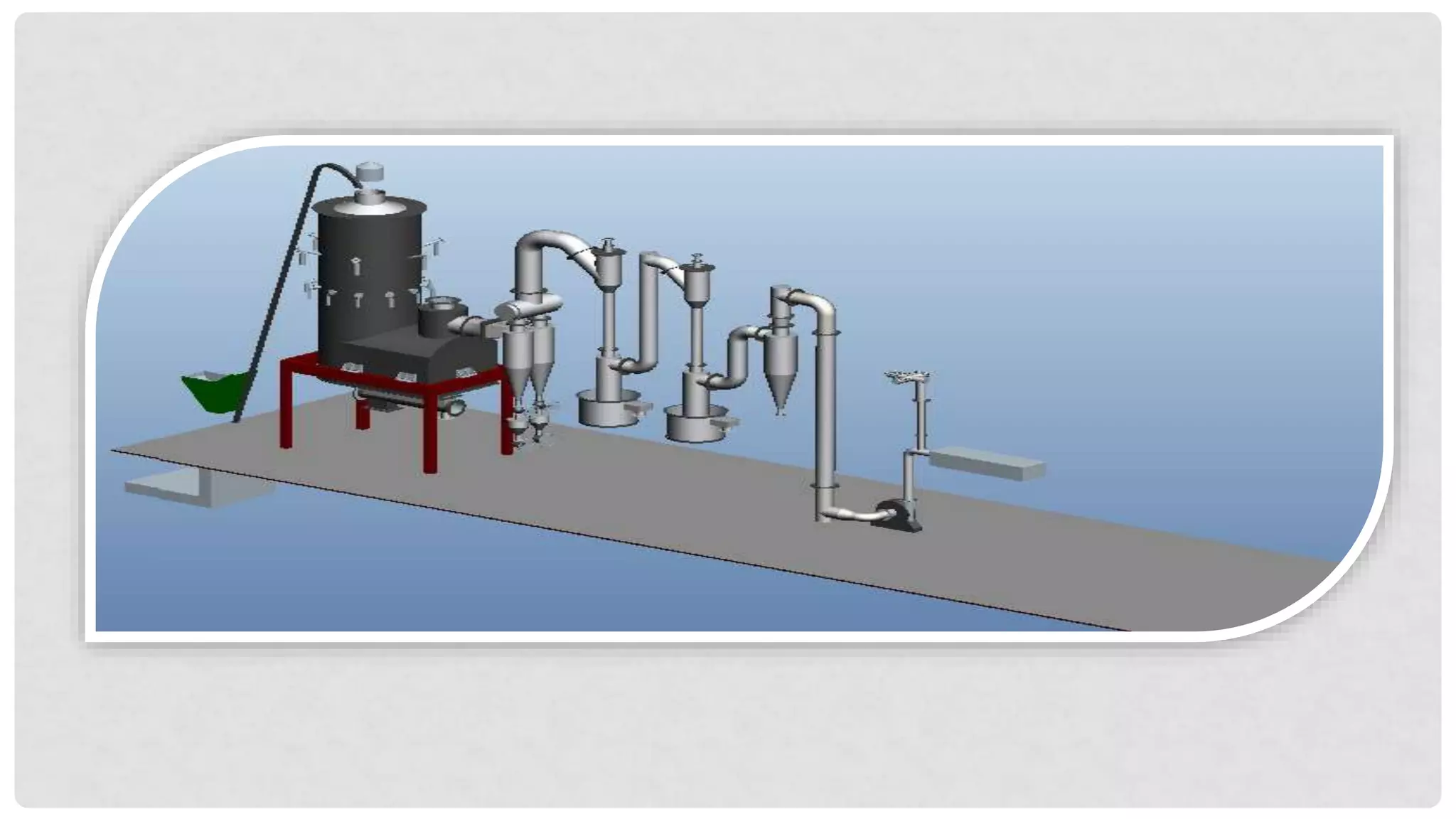
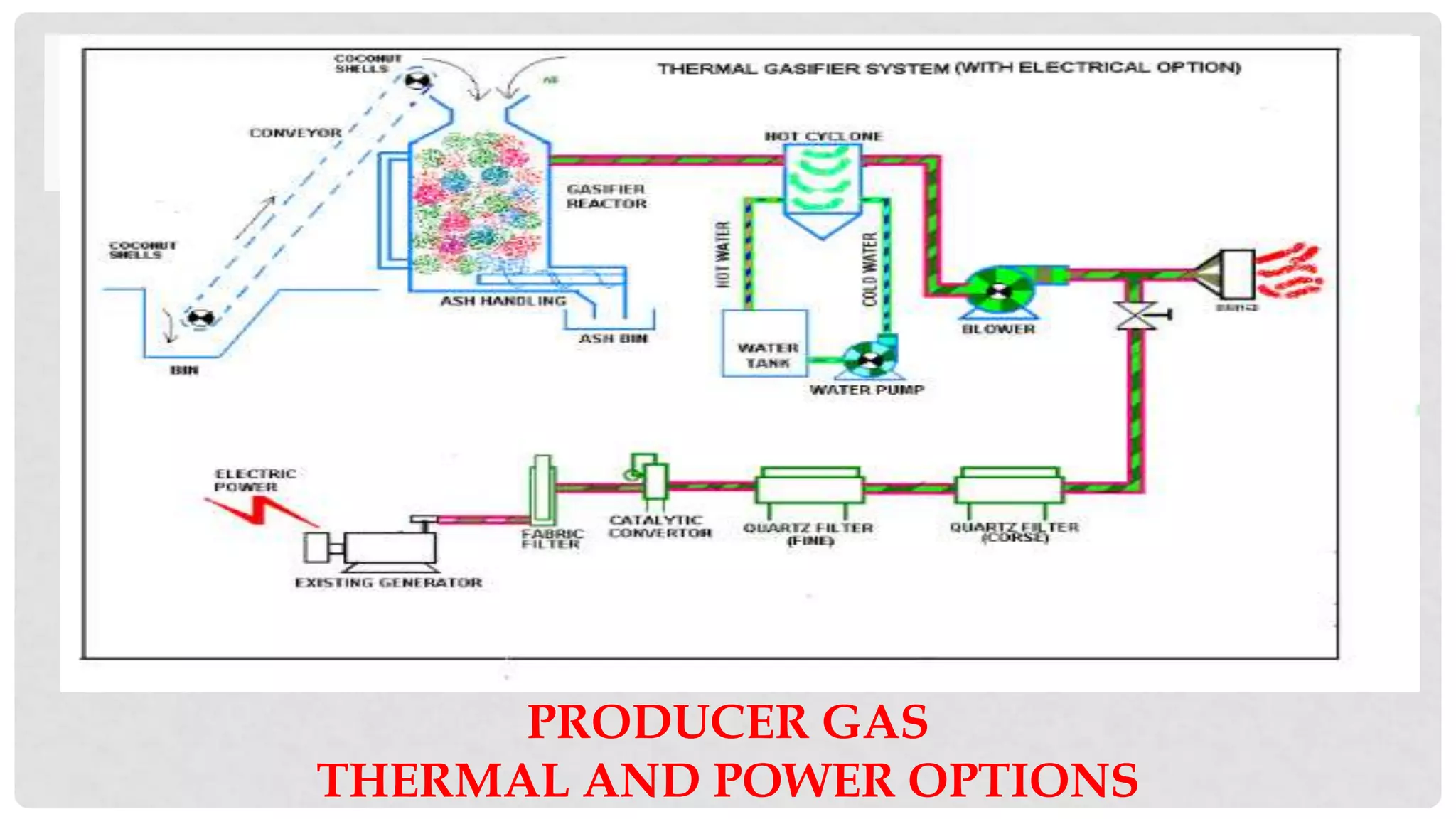
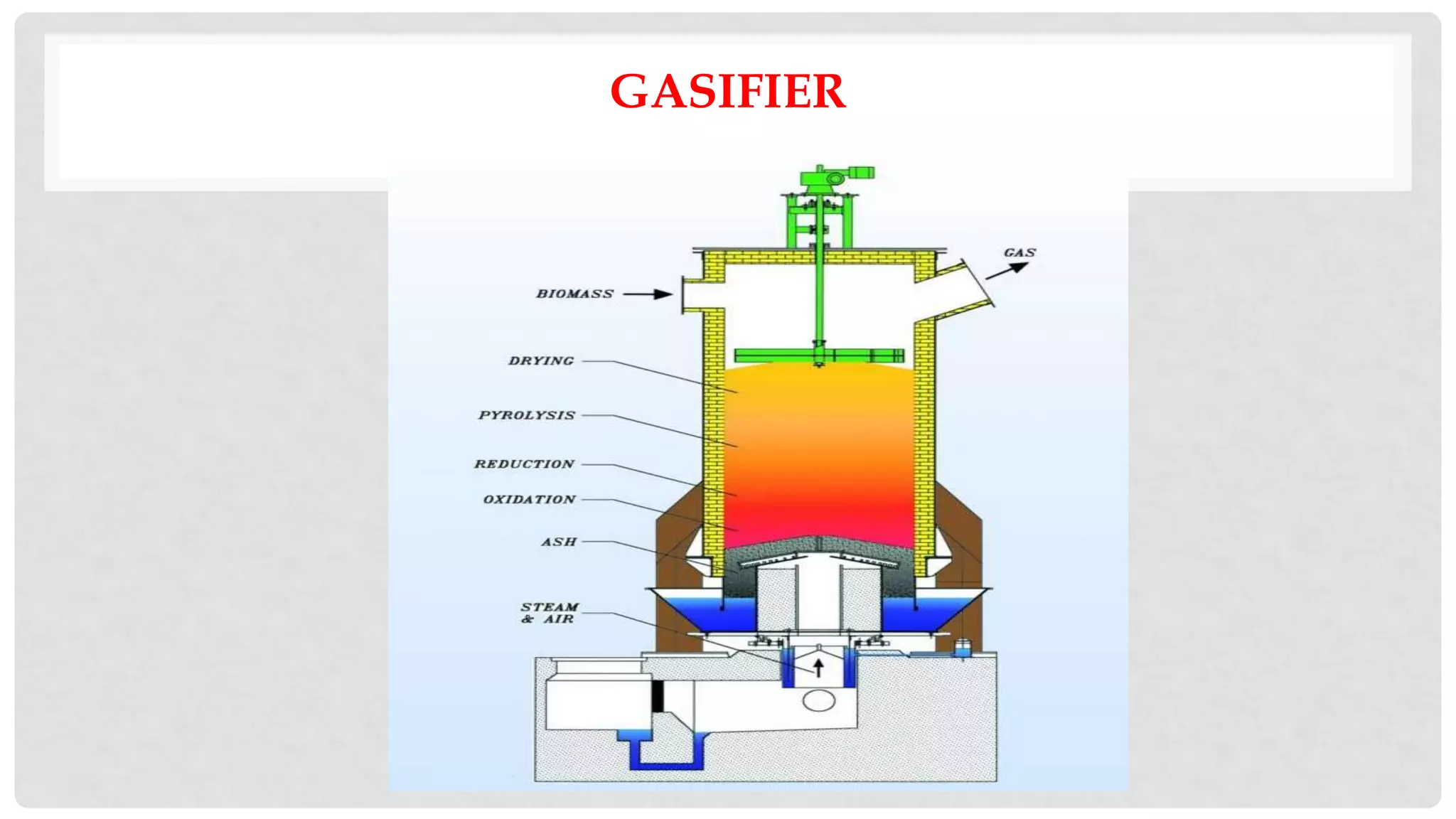
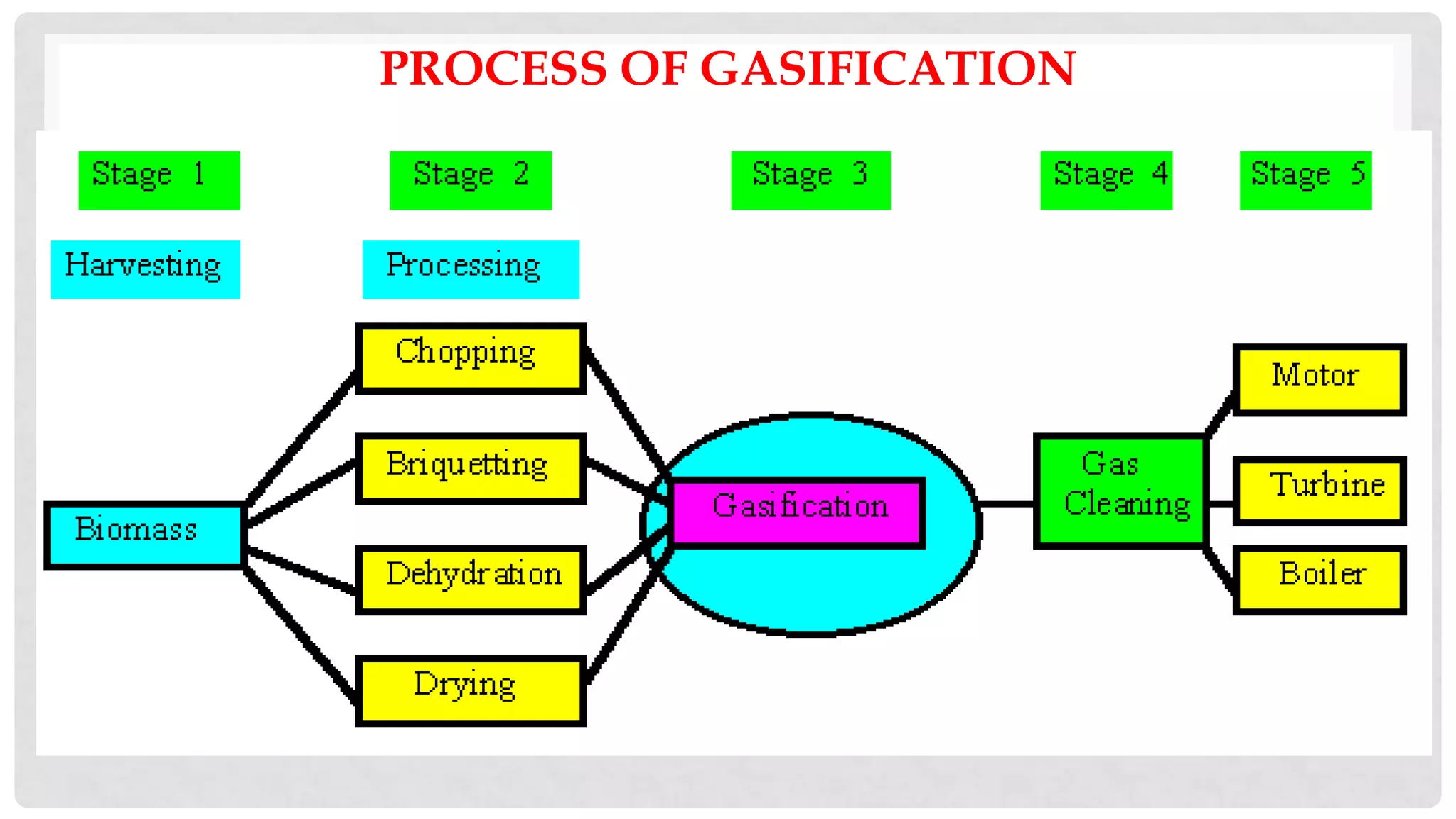
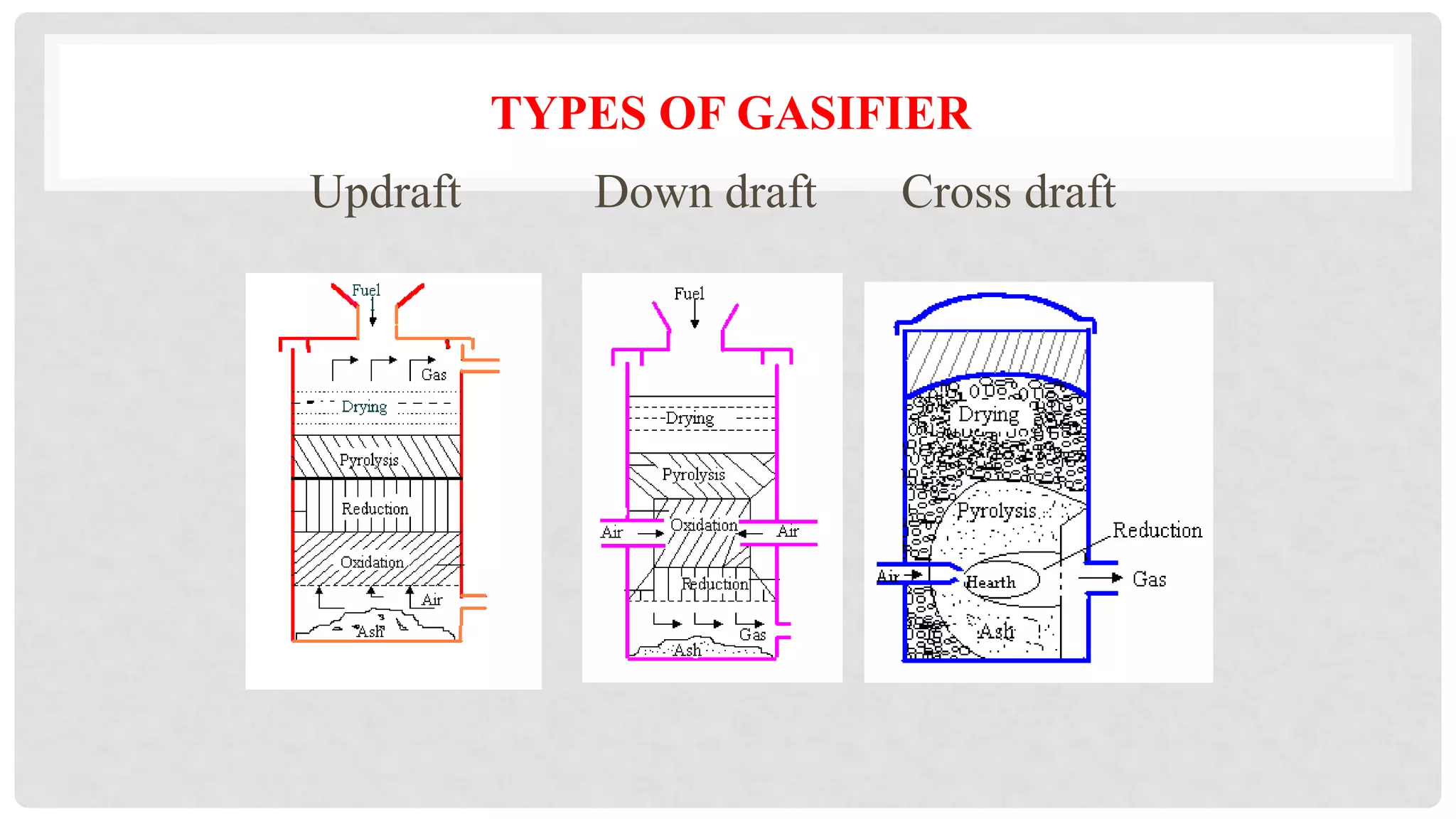
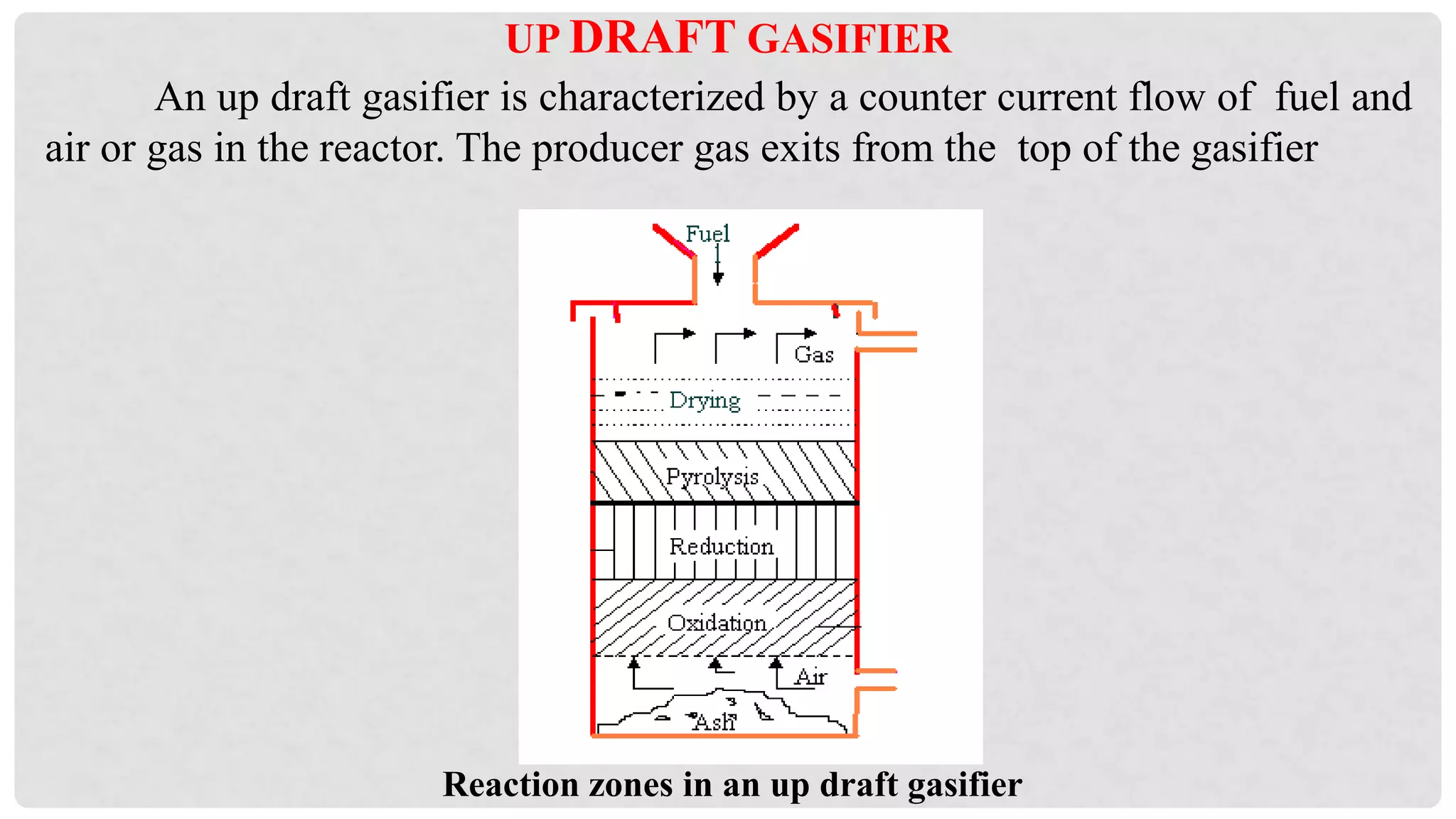
The document discusses various types of gasifiers used for converting biomass into producer gas through gasification, a partial oxidation process. It outlines the features, advantages, and disadvantages of different gasifier designs, including updraft, downdraft, cross-draft, and fluidized bed gasifiers, along with their operational principles and the gas production process. Key characteristics such as gas composition and performance metrics are highlighted to provide insights into the effectiveness of each gasifier type.




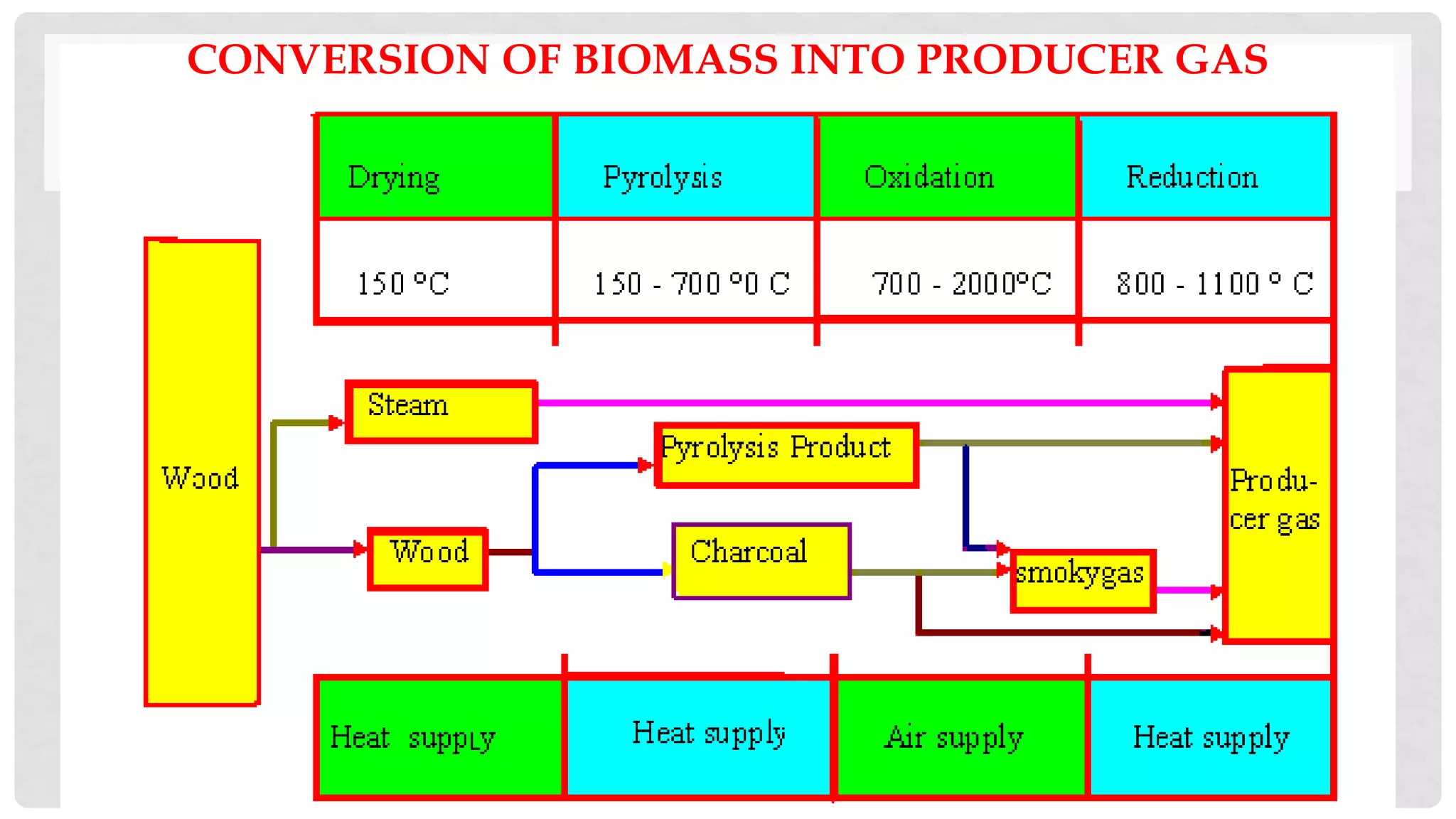


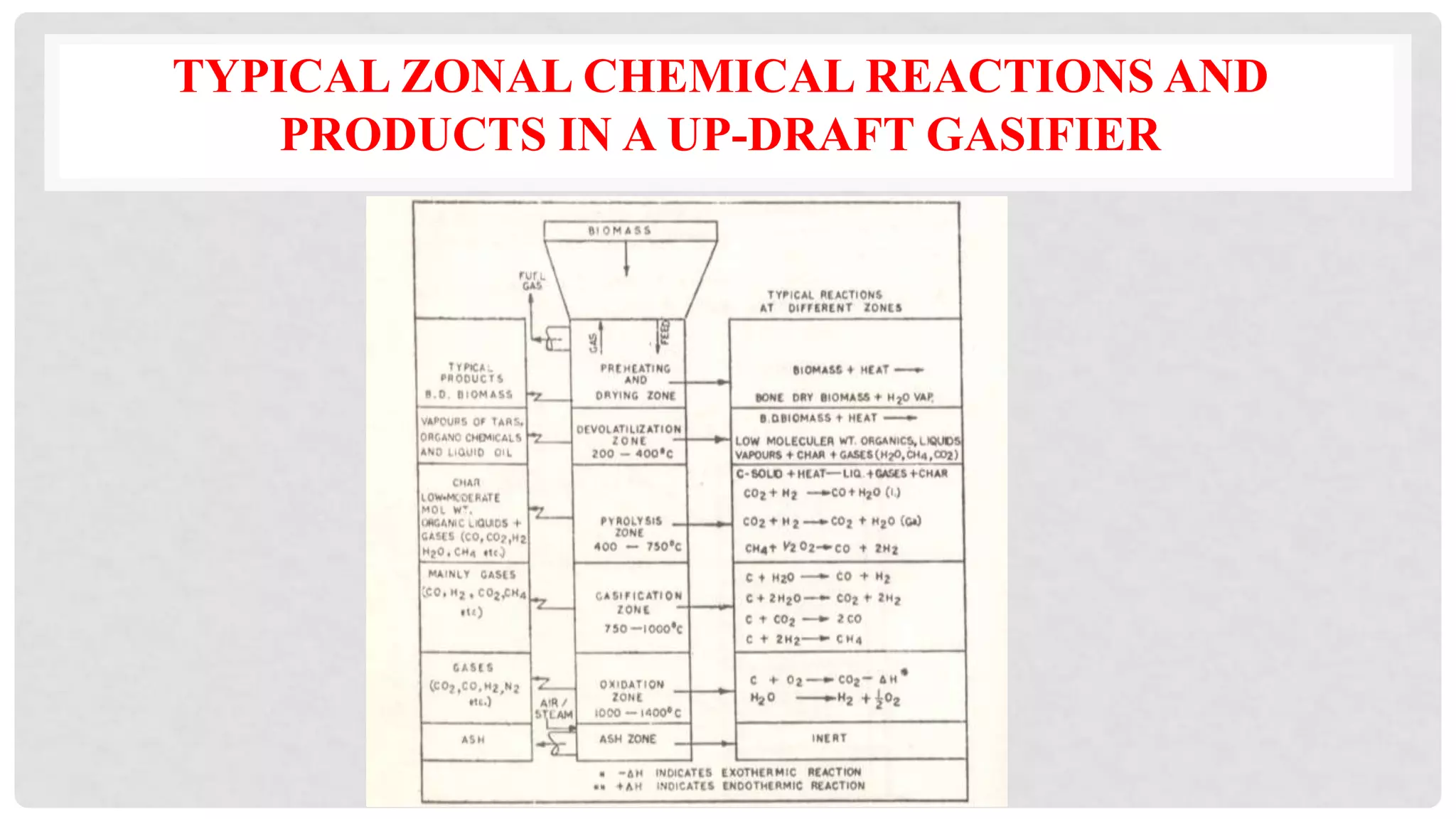
![THERMO-CHEMICAL REACTIONS OCCURRING
IN GASIFICATION
REDUCTION ZONE
Products of partial combustion – H2O, CO2 and uncombusted and partially cracked
pyrolytic products undergo the following chemical reactions in the red-hot charcoal
bed
C + CO2 = 2CO (- 164.9 MJ/kg mole) [Boudouard reaction]
C +H2O = CO + H2 (- 122.6 MJ/kg mole) [water gas ]
CO + H2O = CO + H2 (+ 42 MJ/kg mole) [water shift reaction]
C + 2H2 = CH4 (+ 75 MJ/kg mole) [Methane reaction]
CO2 + H2 = CO + H2O (- 42.3 MJ/kg mole)
Low reduction zone temperature yields low calorific value of gas
Average temp is 850 0C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/23-221030115515-41c8a097/75/23-TYPES-OF-GASIFIER-ppt-13-2048.jpg)