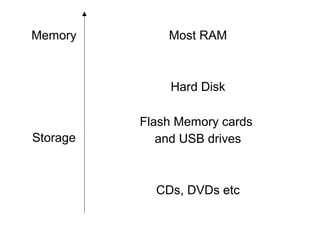
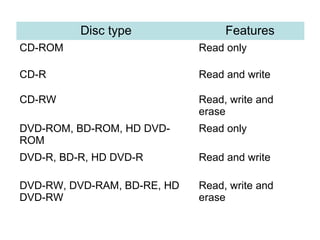
Storage holds data and information for future use. Common storage mediums include hard disks, CDs, DVDs, memory cards, and USB flash drives. Storage devices, like hard disks, record and retrieve data from these storage mediums. Hard disks use magnetic disks to store data in tracks and sectors. They have faster access times than optical discs but slower times than memory. Other storage media include floppy disks, optical discs like CDs and DVDs, and flash memory cards.