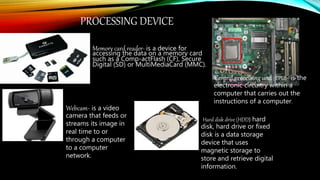
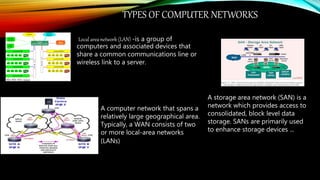
The document defines a computer and describes its basic components and functions. It states that a computer is an electronic device that processes data according to programmed instructions. It then explains the main functions of a computer as input, output, processing, and storage of data. The document proceeds to describe common input devices like keyboards, mice, and scanners. It also details processing devices such as CPUs and storage devices including hard drives, CDs, and memory sticks. Output devices such as monitors, printers, and headphones are also outlined. The document concludes by defining types of computers and networks, transmission media, and major internal computer parts.