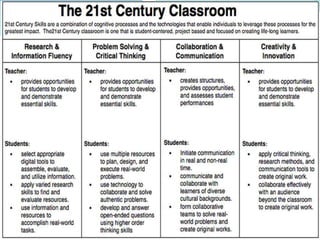
The document discusses 21st century pedagogy and skills for teachers and students. It emphasizes developing skills like critical thinking, problem solving, communication, collaboration and digital literacy. 21st century learning is described as being learner-centered, personalized, relevant and adaptable. The roles of the teacher shift from being teacher-centered to facilitating student-centered learning. Teaching of key subjects like language, mathematics and science is discussed, highlighting the importance of developing conceptual understanding and problem solving abilities in students.