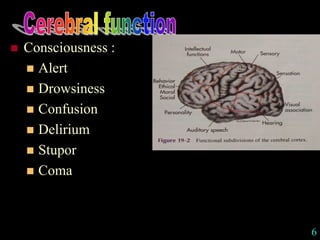
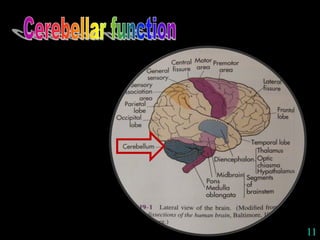
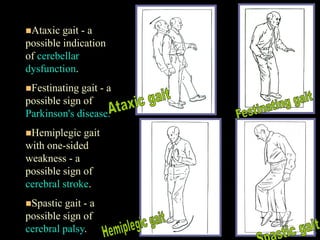
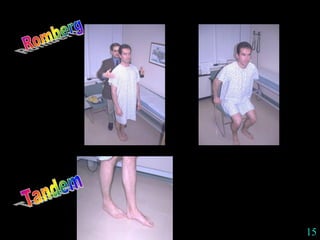
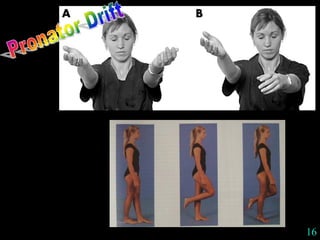
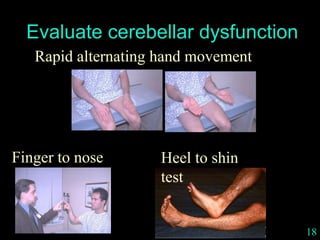
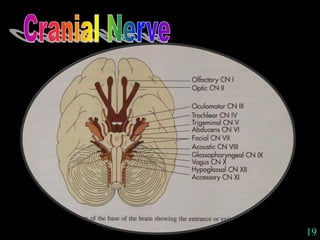
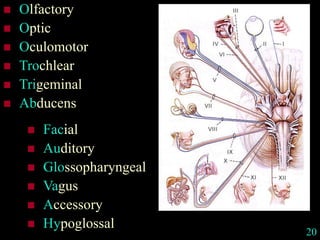
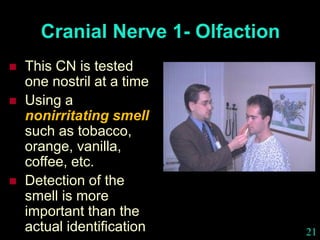
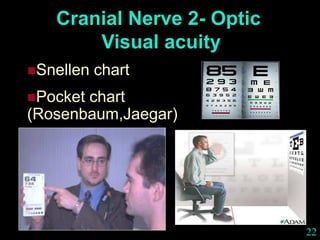
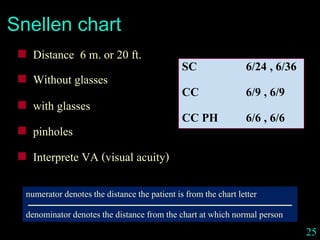
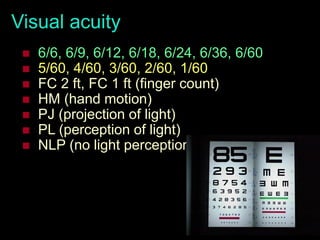
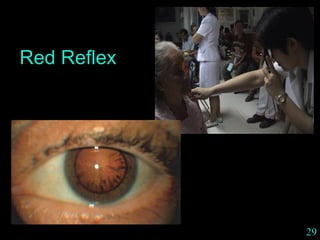
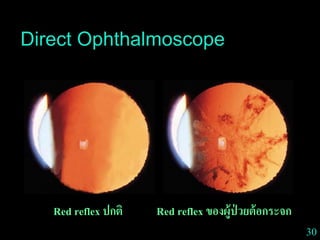
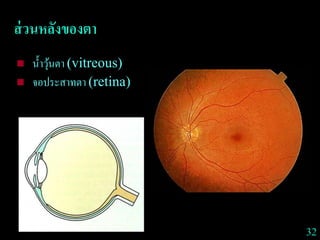
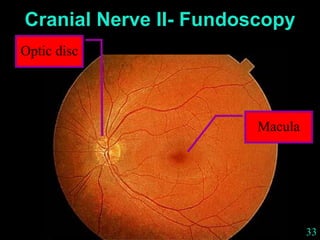
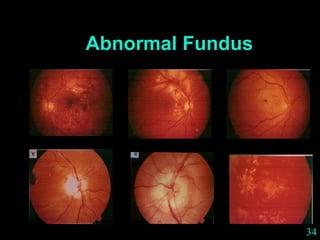
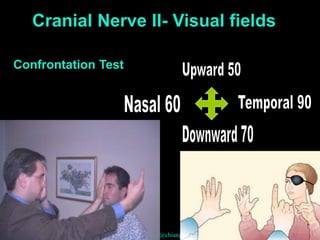
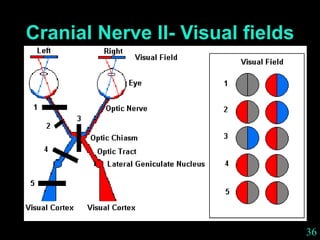
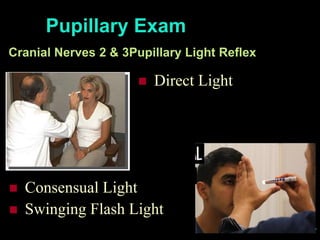
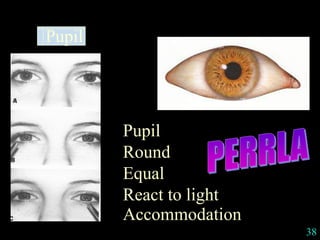
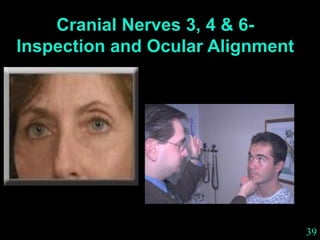
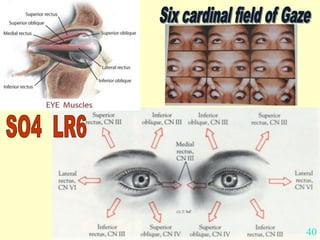
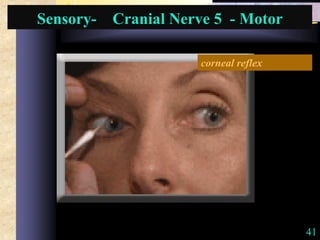
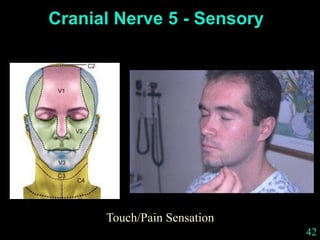
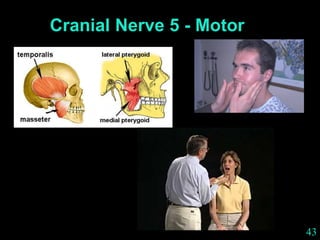
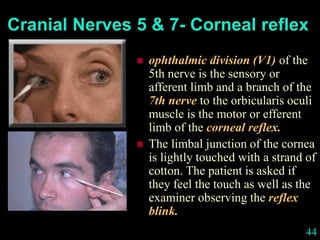
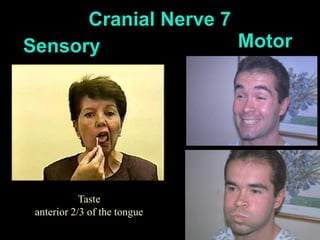
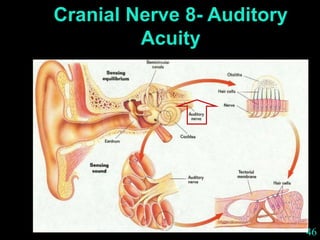
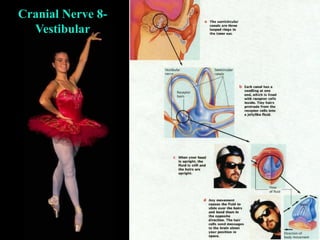
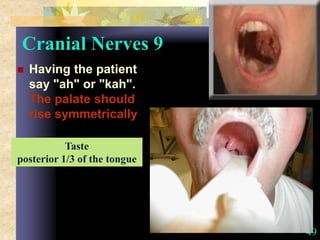
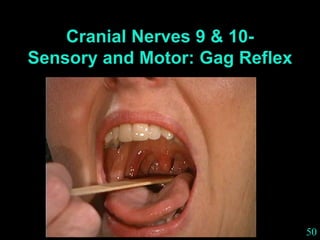
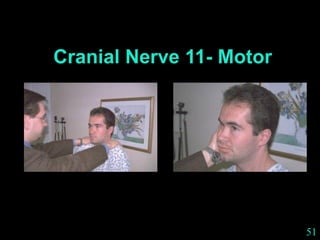
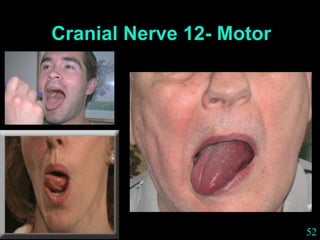
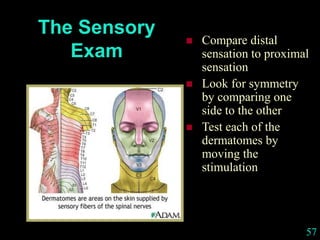
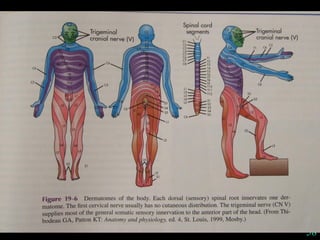
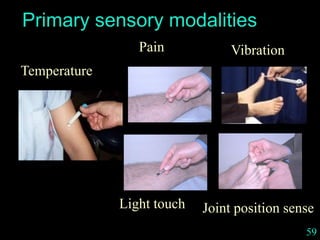
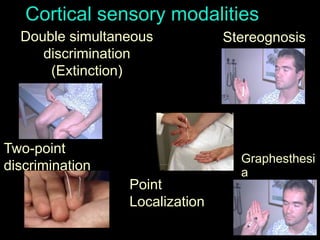
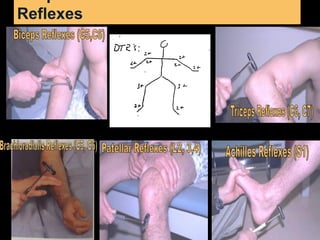
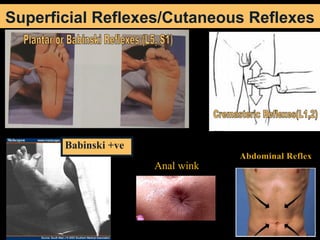
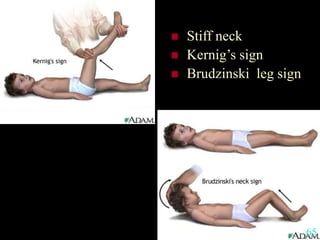
This document provides guidance on neurological assessment techniques. It outlines objectives such as describing how to take a neurological history and examine the nervous system. Assessment areas covered include cerebral and cerebellar function, cranial nerves, motor and sensory systems, and reflexes. Specific examination techniques are described for testing things like vision, hearing, sensation, and coordination. Common neurological symptoms are also listed. The goal is to equip health professionals with the skills to properly evaluate patients for potential neurological conditions.