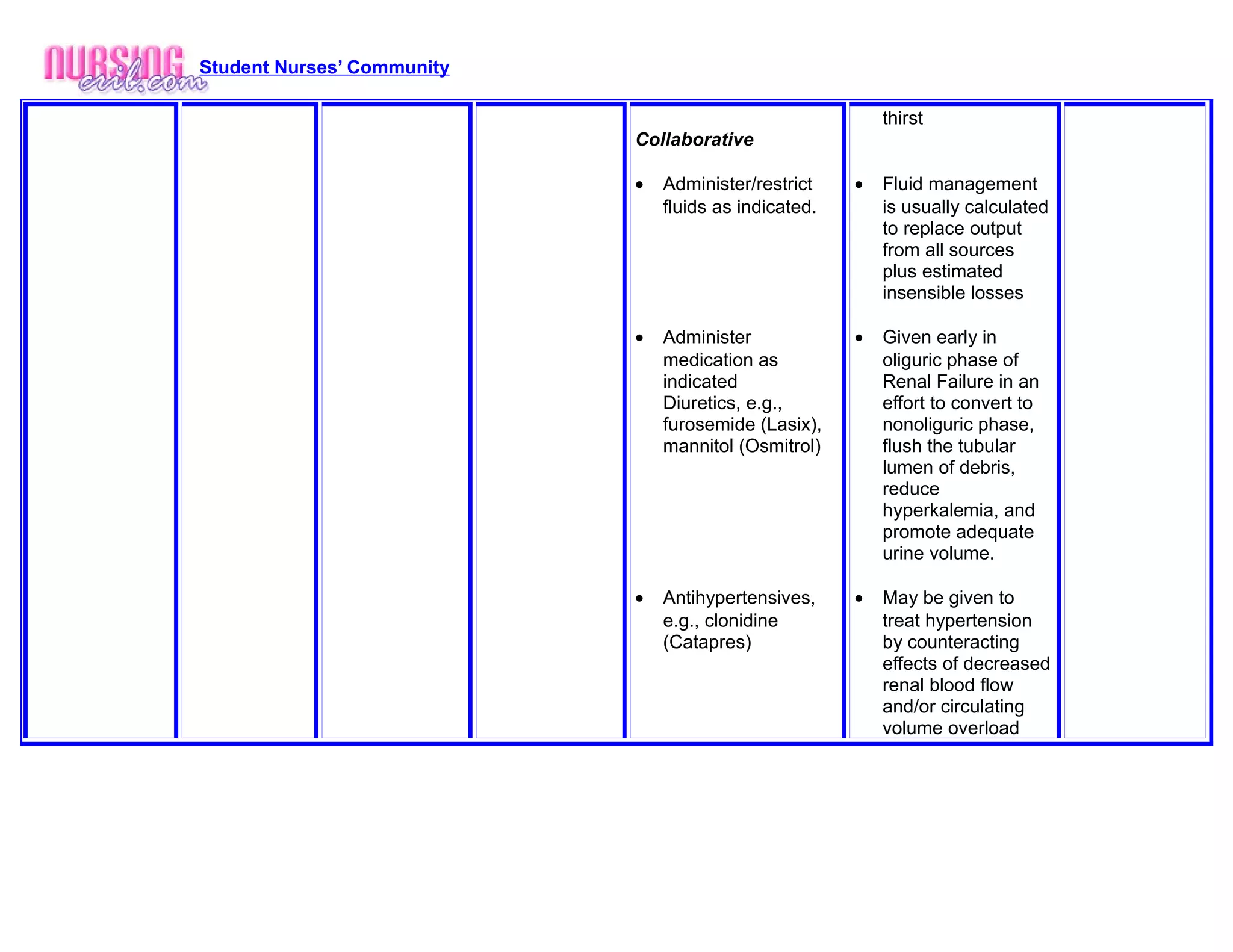
The nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing renal failure who presents with edema, fatigue, and weakness, and notes an assessment of fluid overload and compromised renal function. The plan includes monitoring intake and output, daily weighing, skin assessments for edema, oral fluid replacement within restrictions, and administering diuretics and antihypertensives as needed to manage fluid levels, reduce edema, and treat hypertension. The expected outcomes are appropriate urinary output, stable weight and vital signs, and resolution of edema.