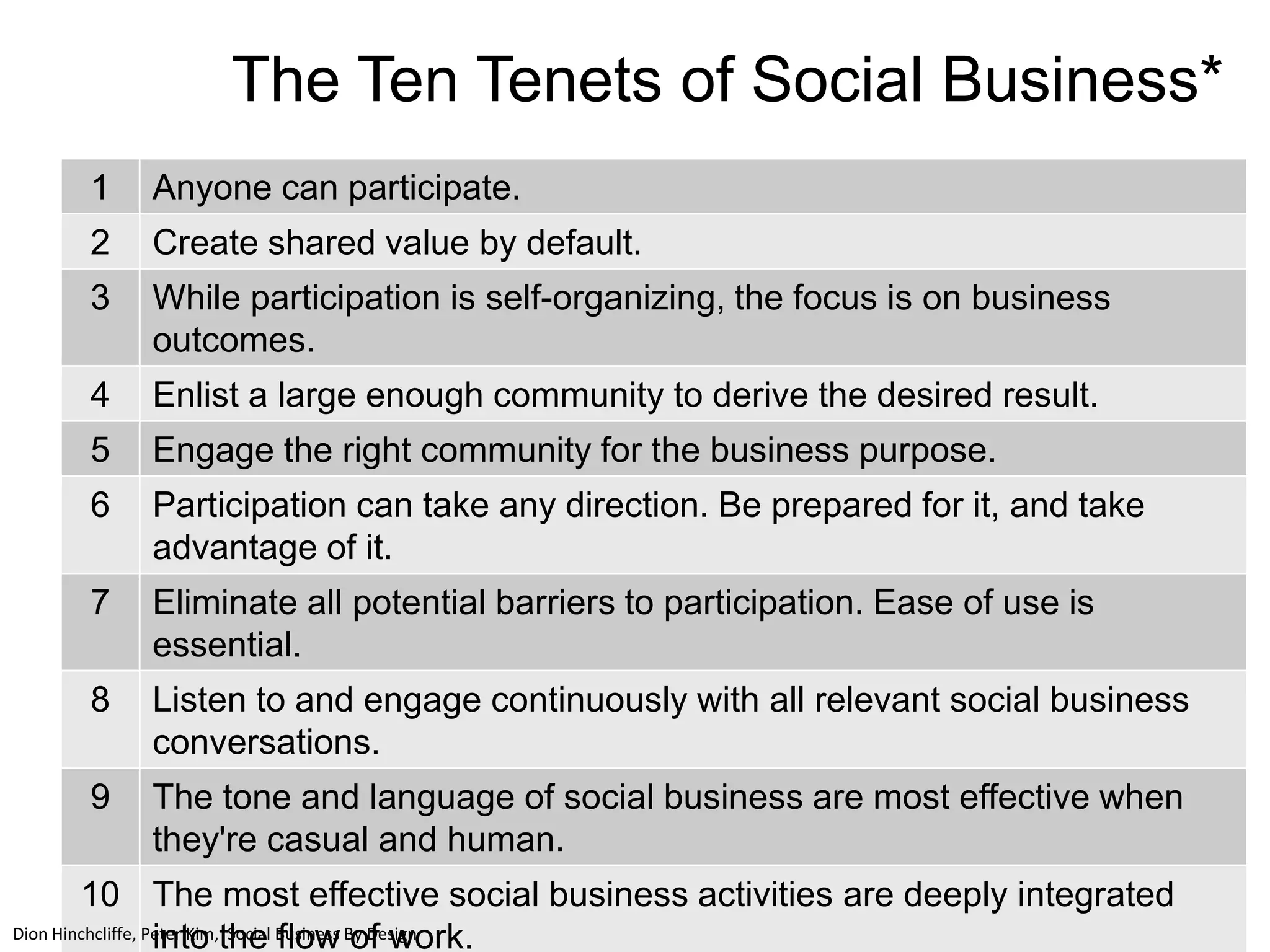
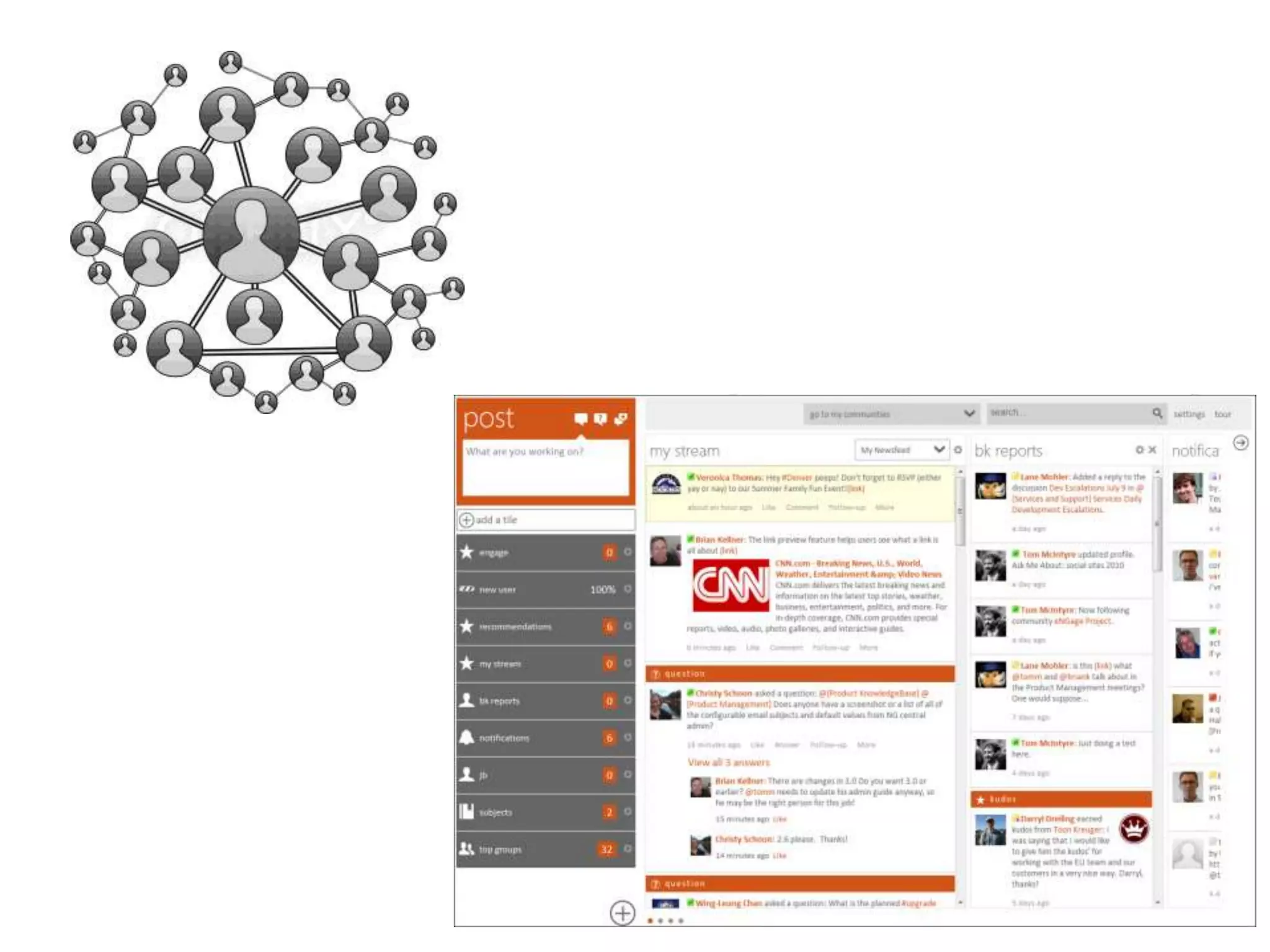
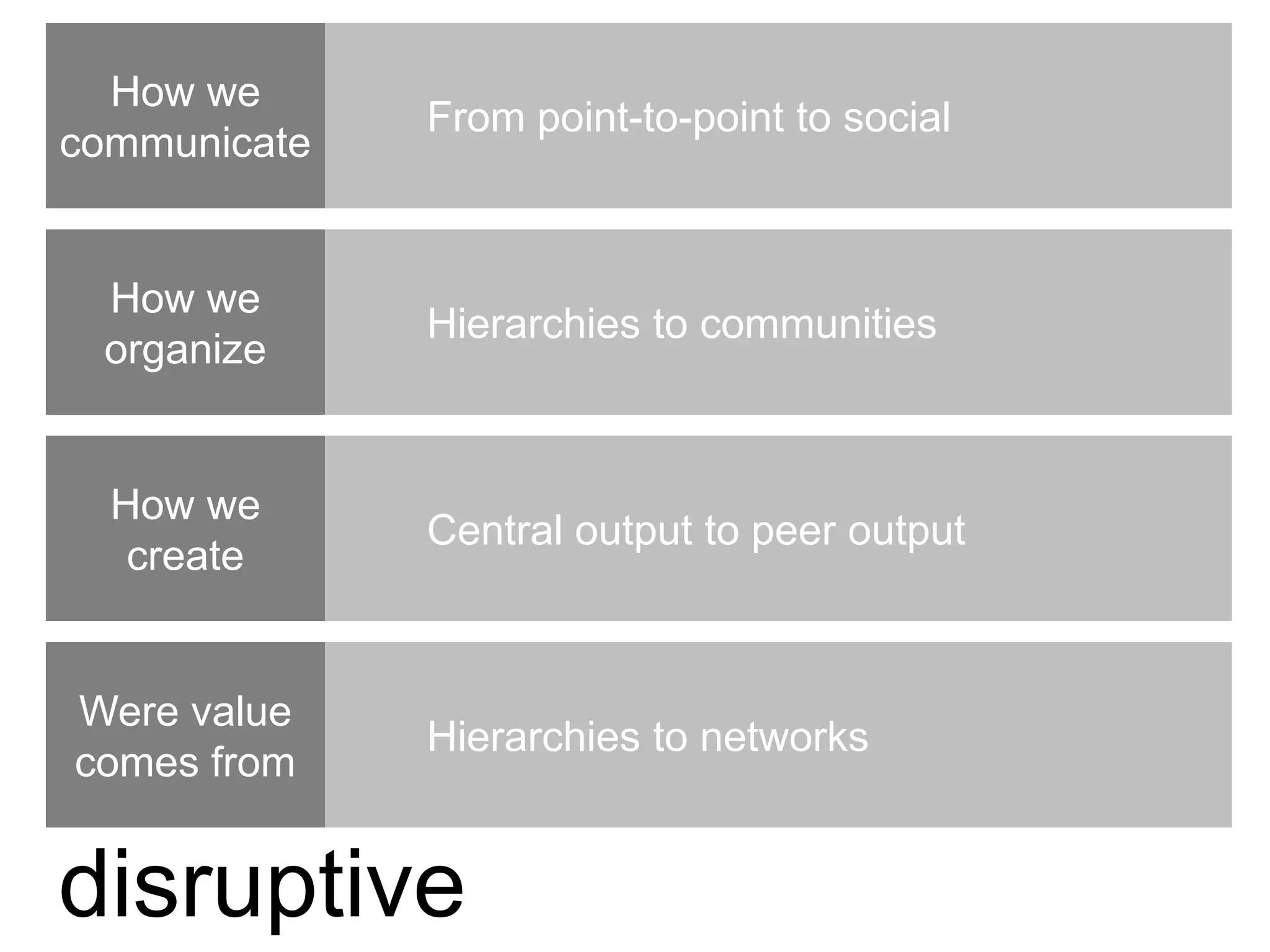
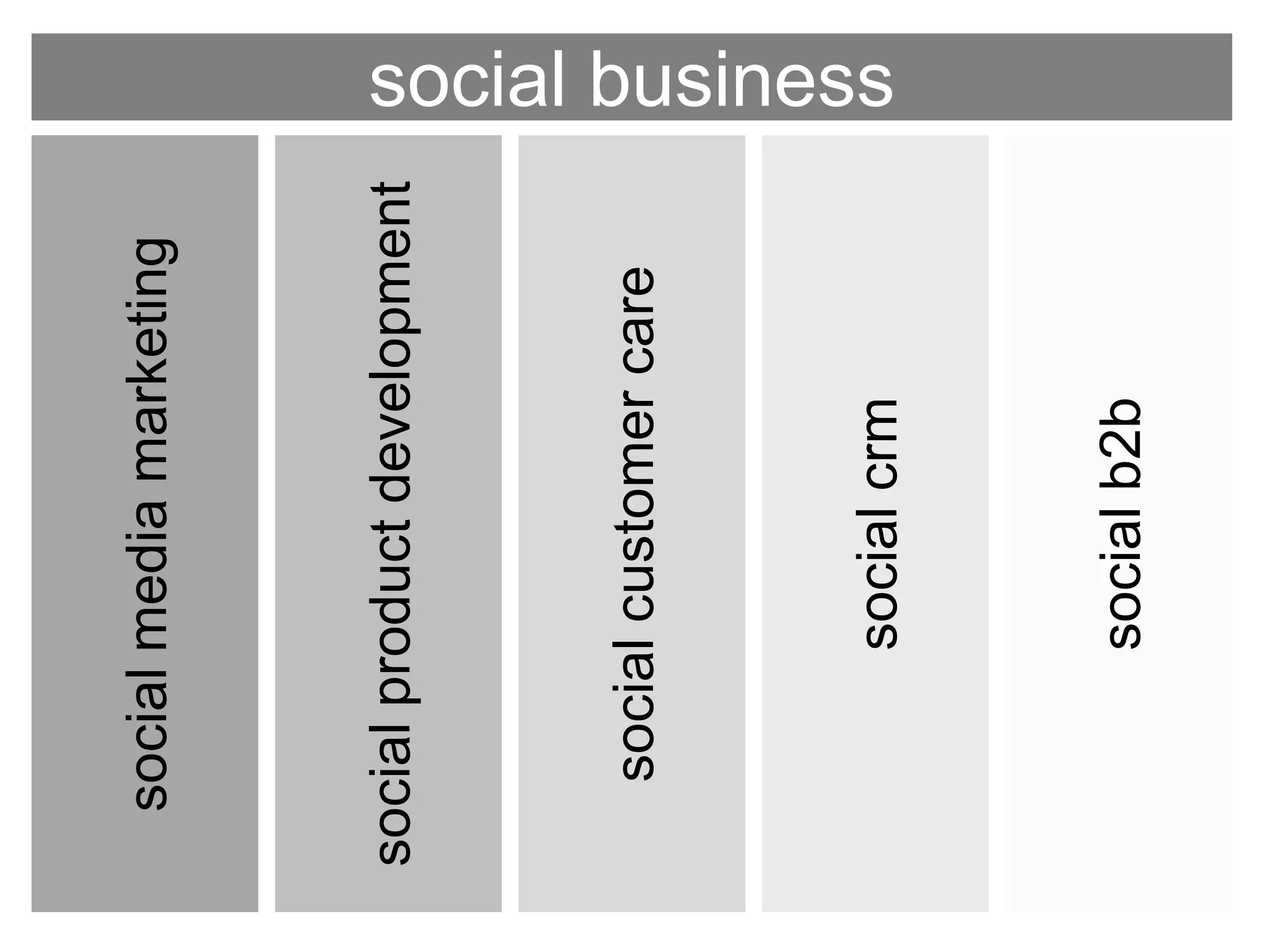
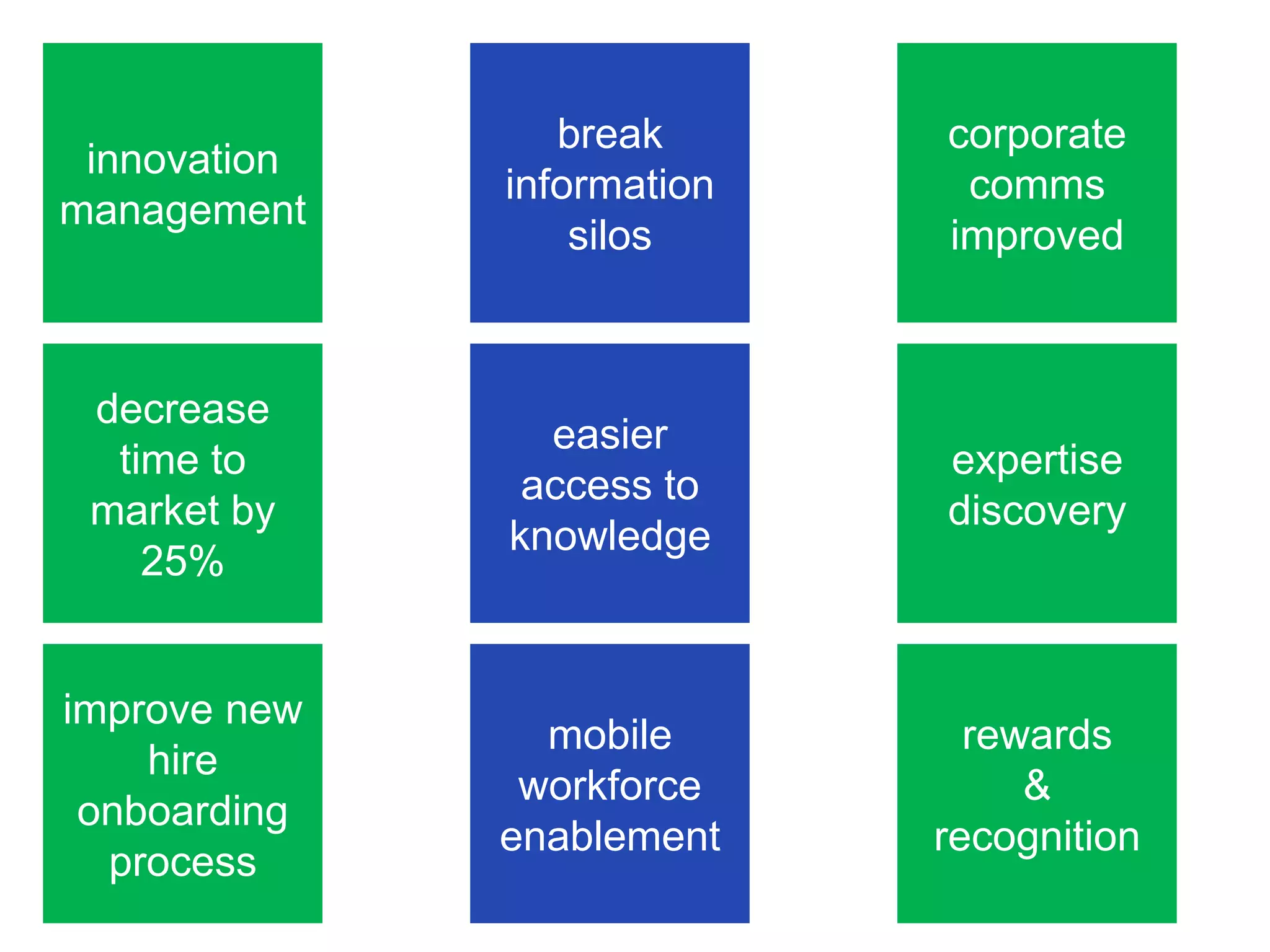
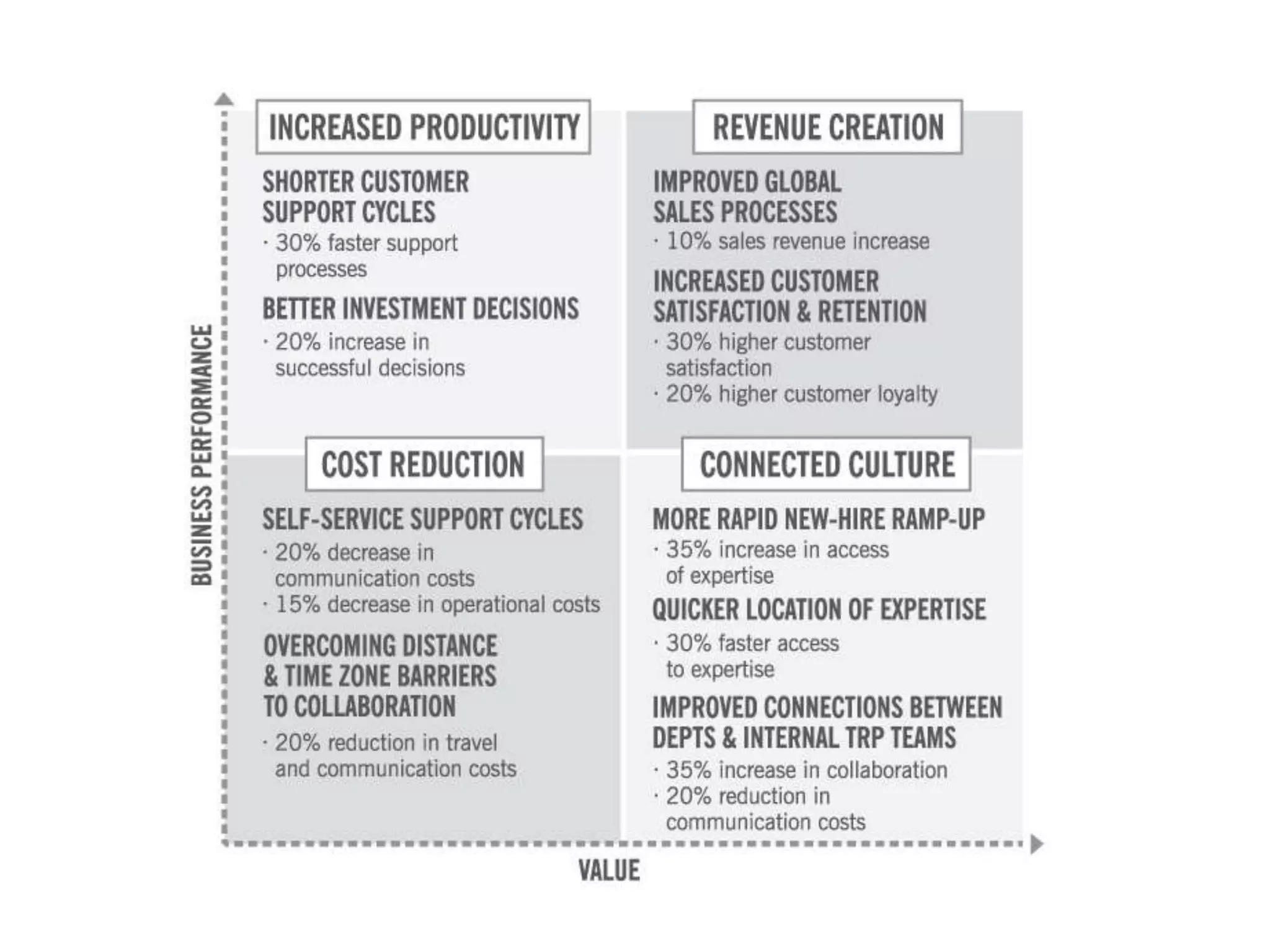
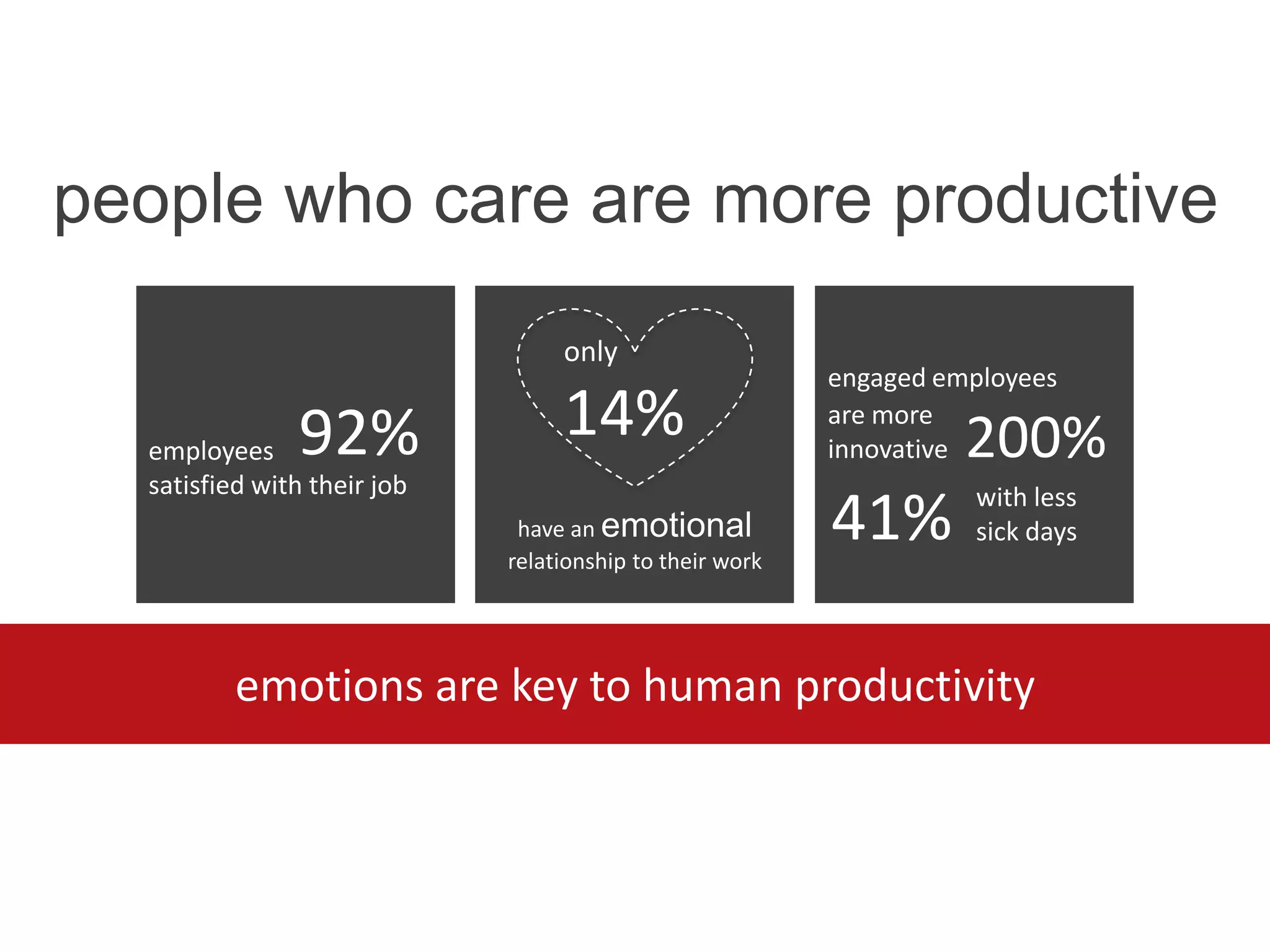
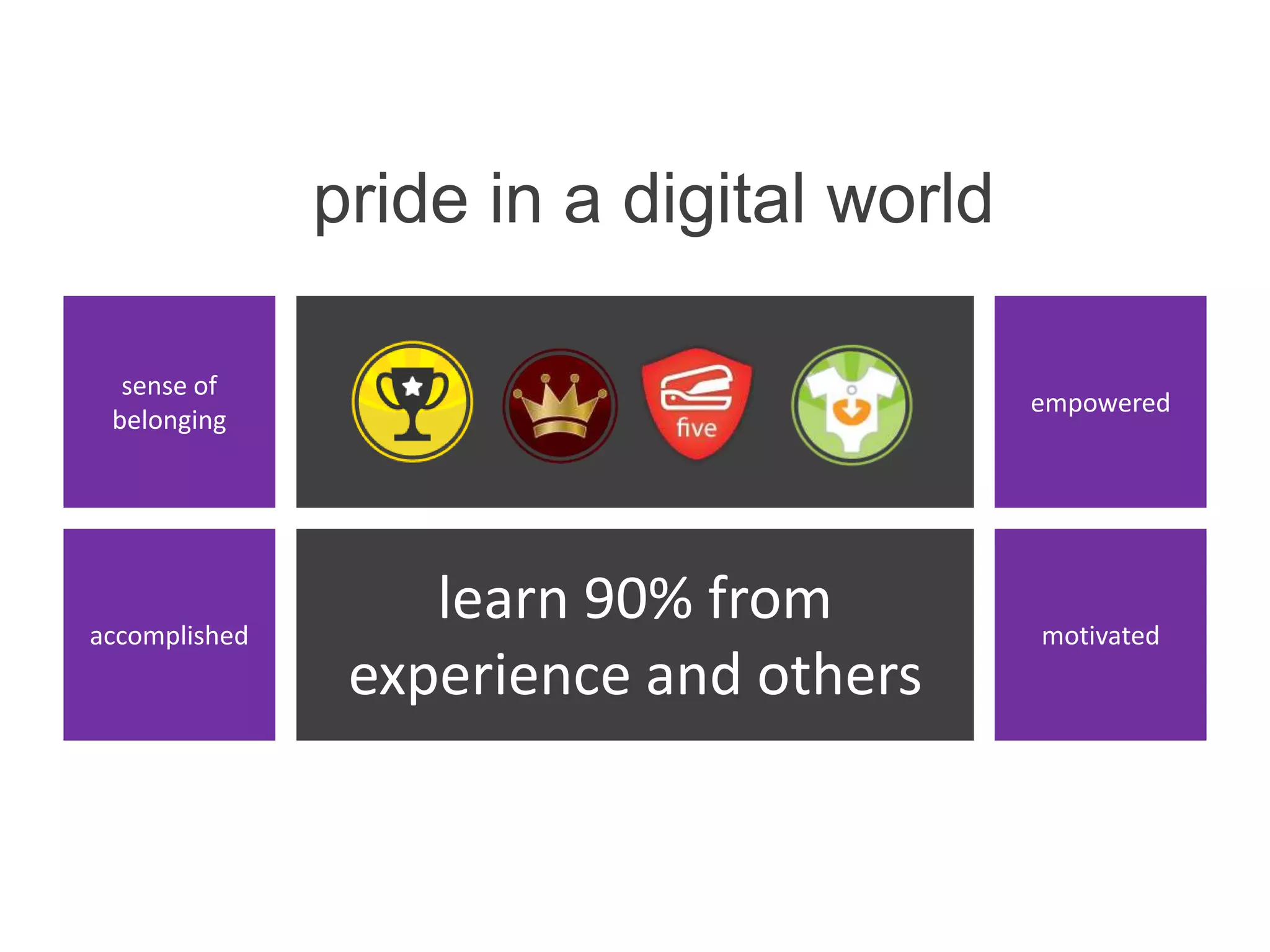
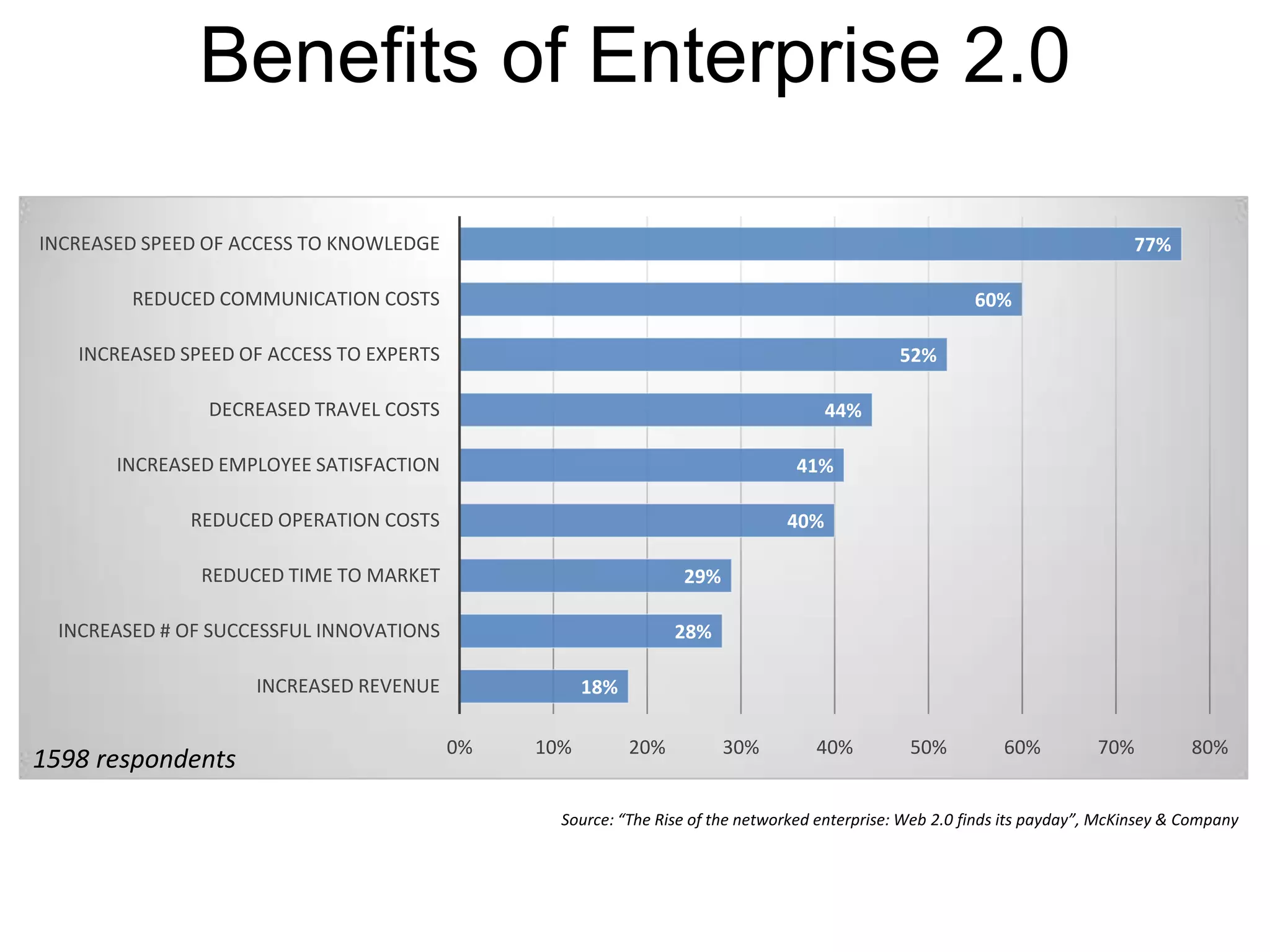
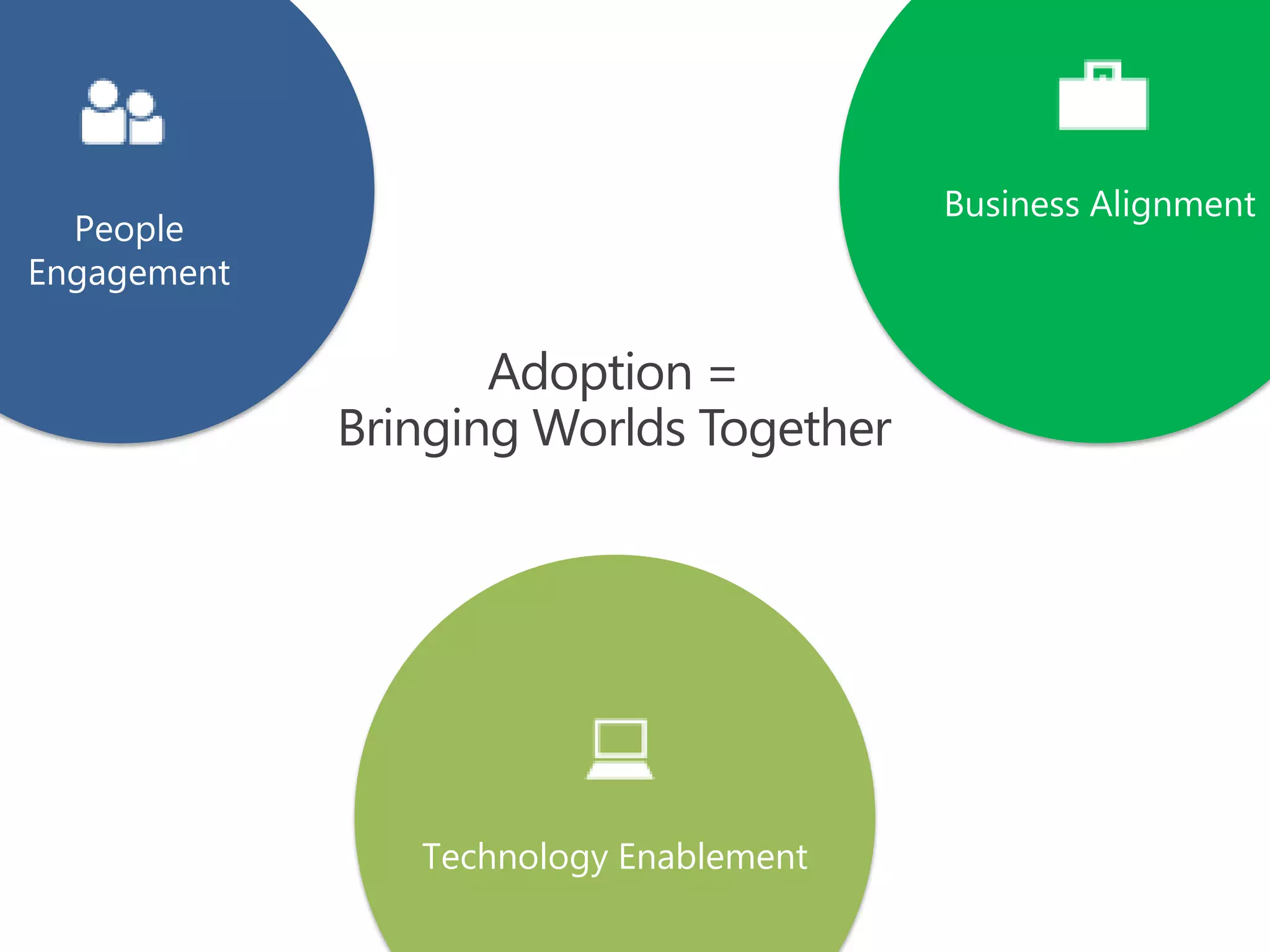
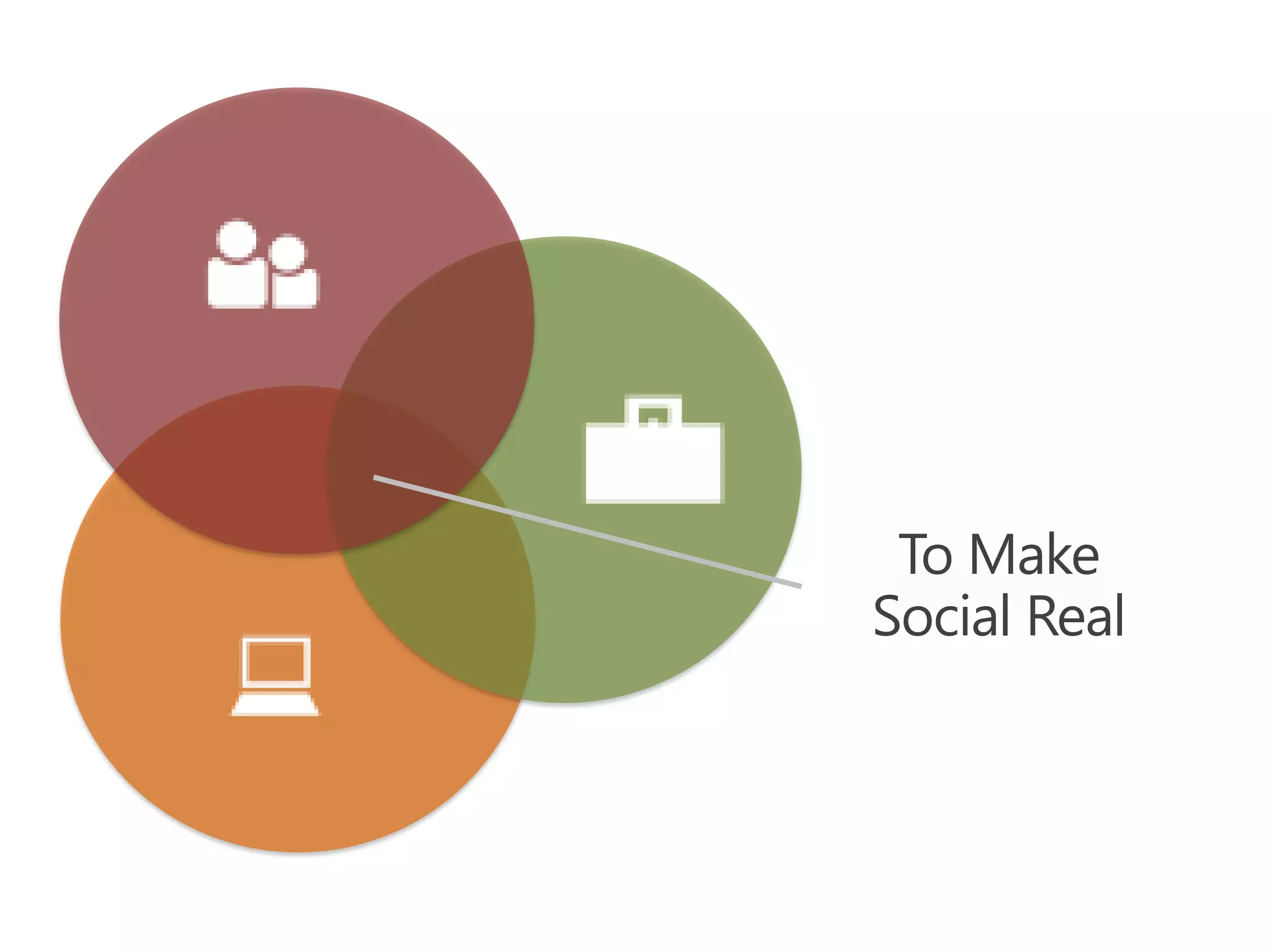
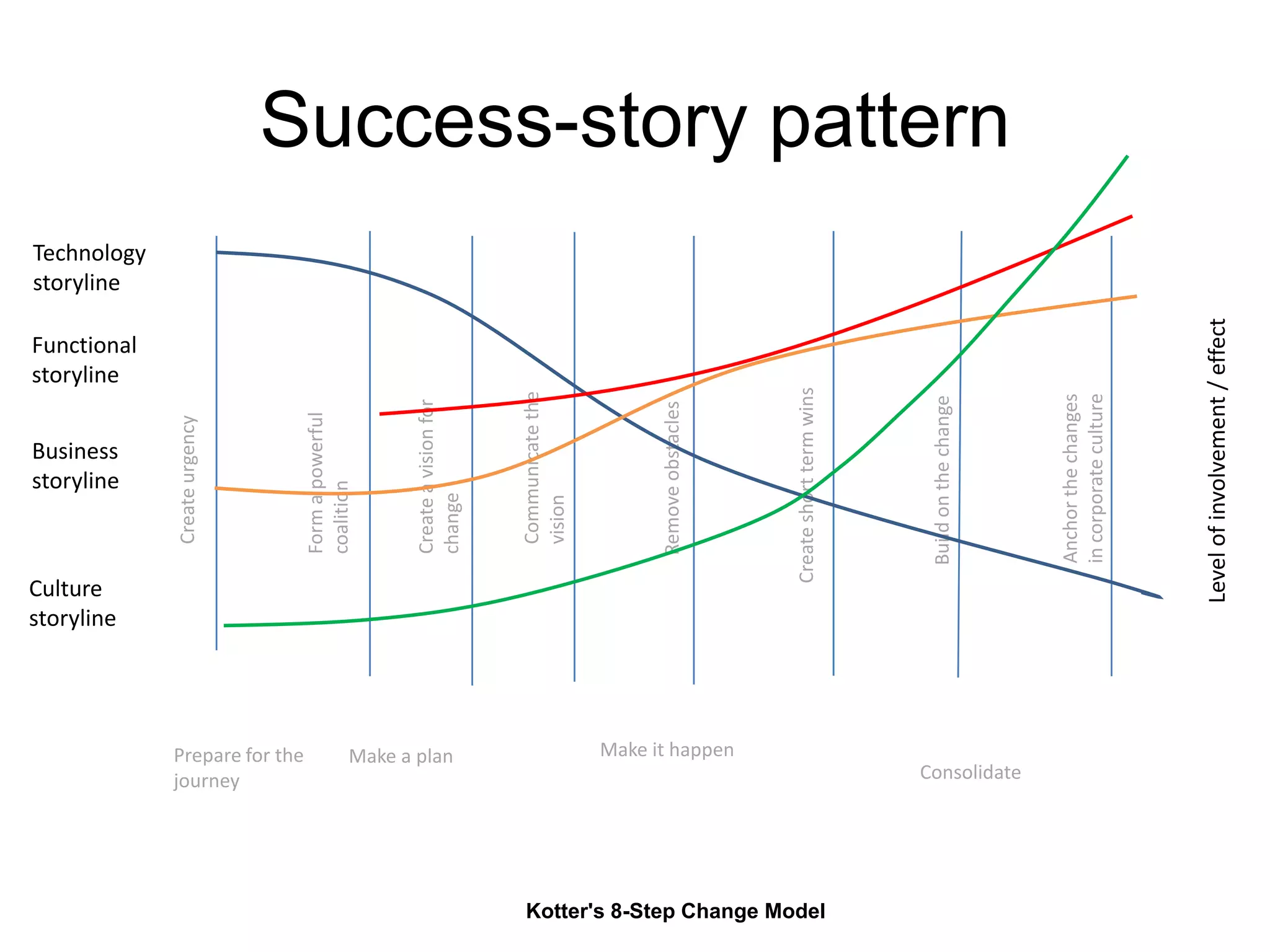
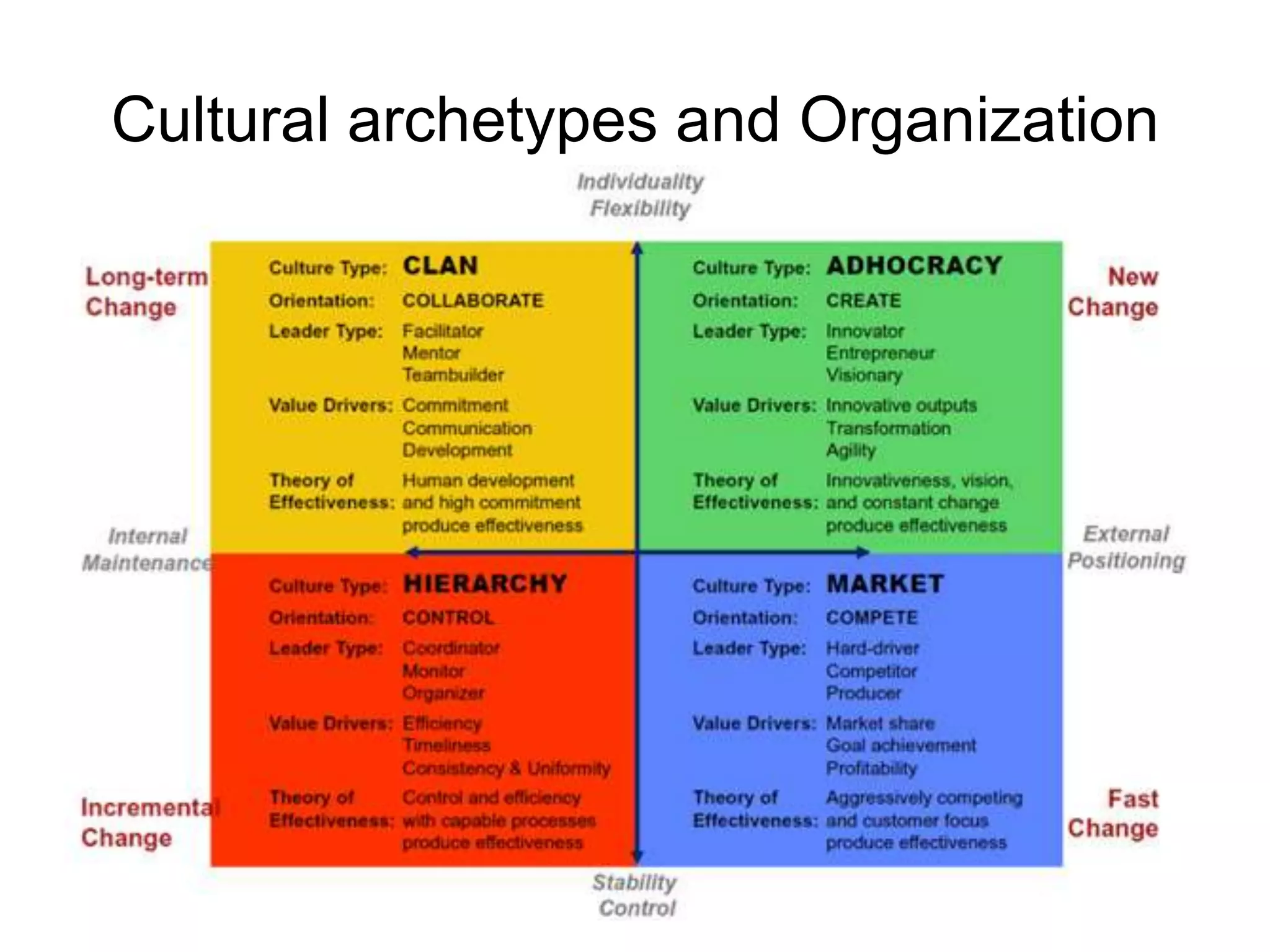
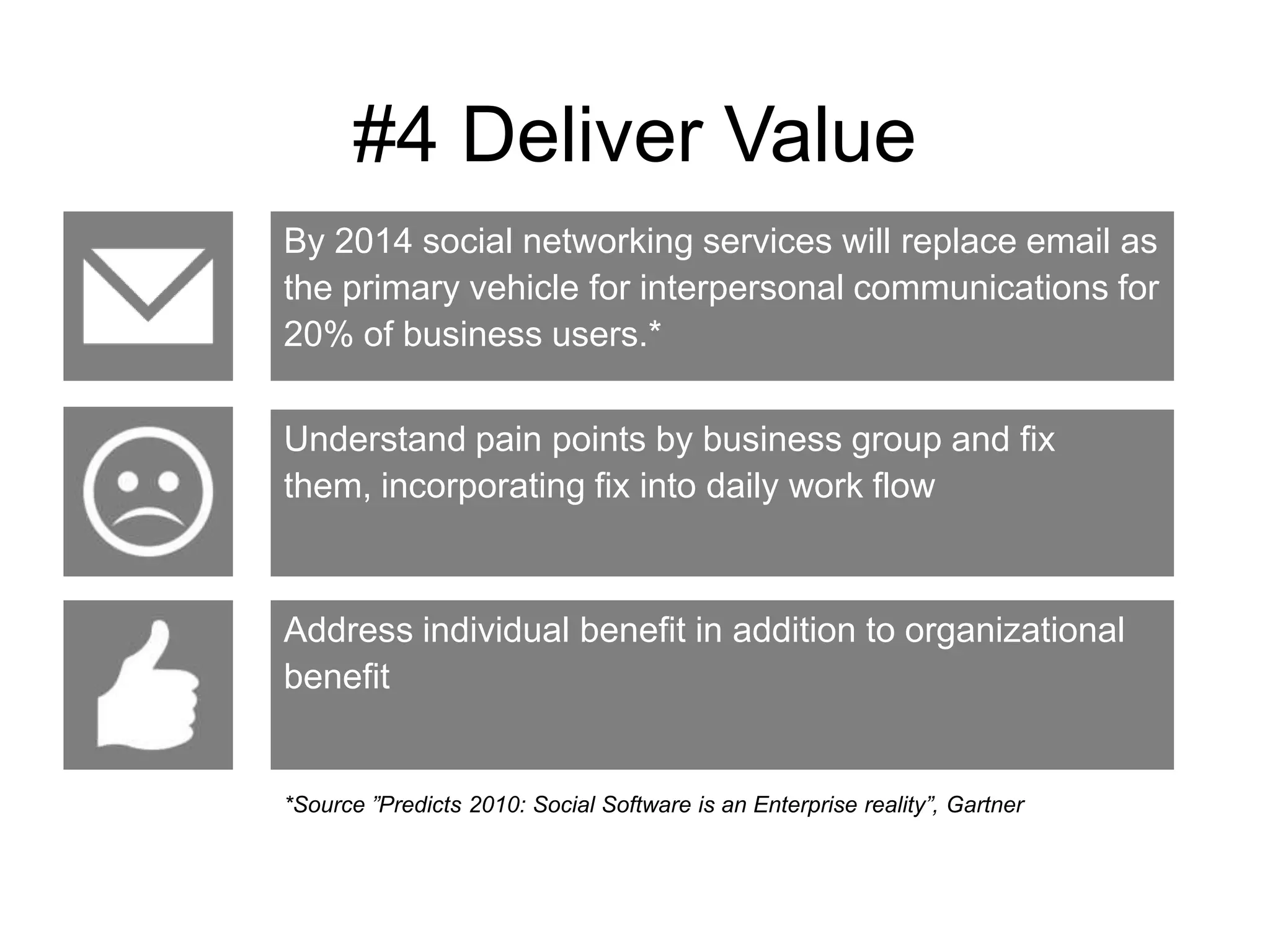
The document discusses the implementation and benefits of enterprise social networking solutions within businesses. It outlines key tenets for successful social business practices, emphasizing the importance of participation, community engagement, and cultural adaptation. Additionally, it highlights the positive impacts on employee satisfaction, innovation, and overall productivity.



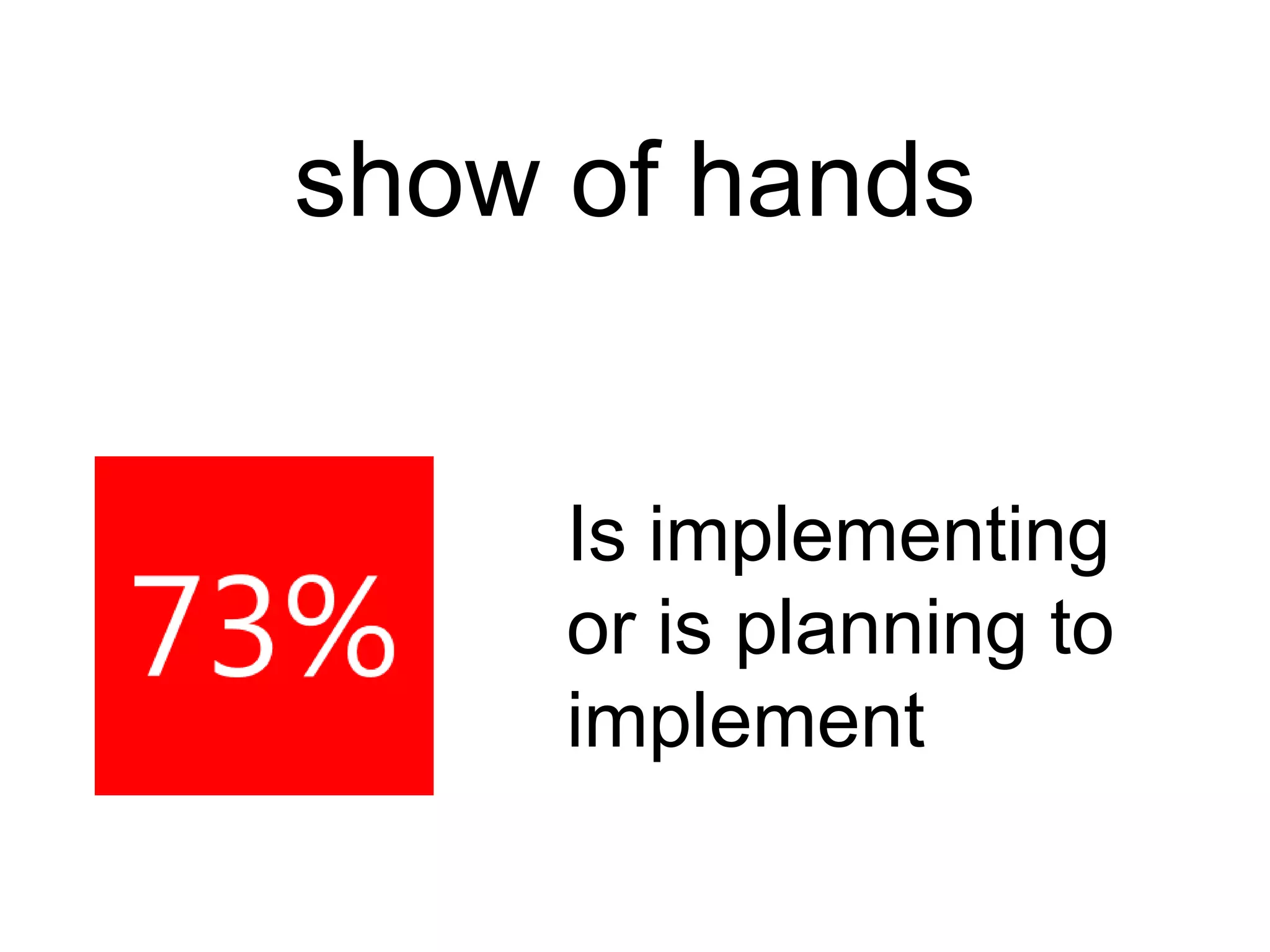





![social
business
[ working out loud ]
enterprise
social
networking
the
social
workplace
enterprise
2.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130415-spevo13-getsocialtalk-v2-130422061349-phpapp02/75/GetSocial-It-s-Good-For-You-SPEvo13-12-2048.jpg)