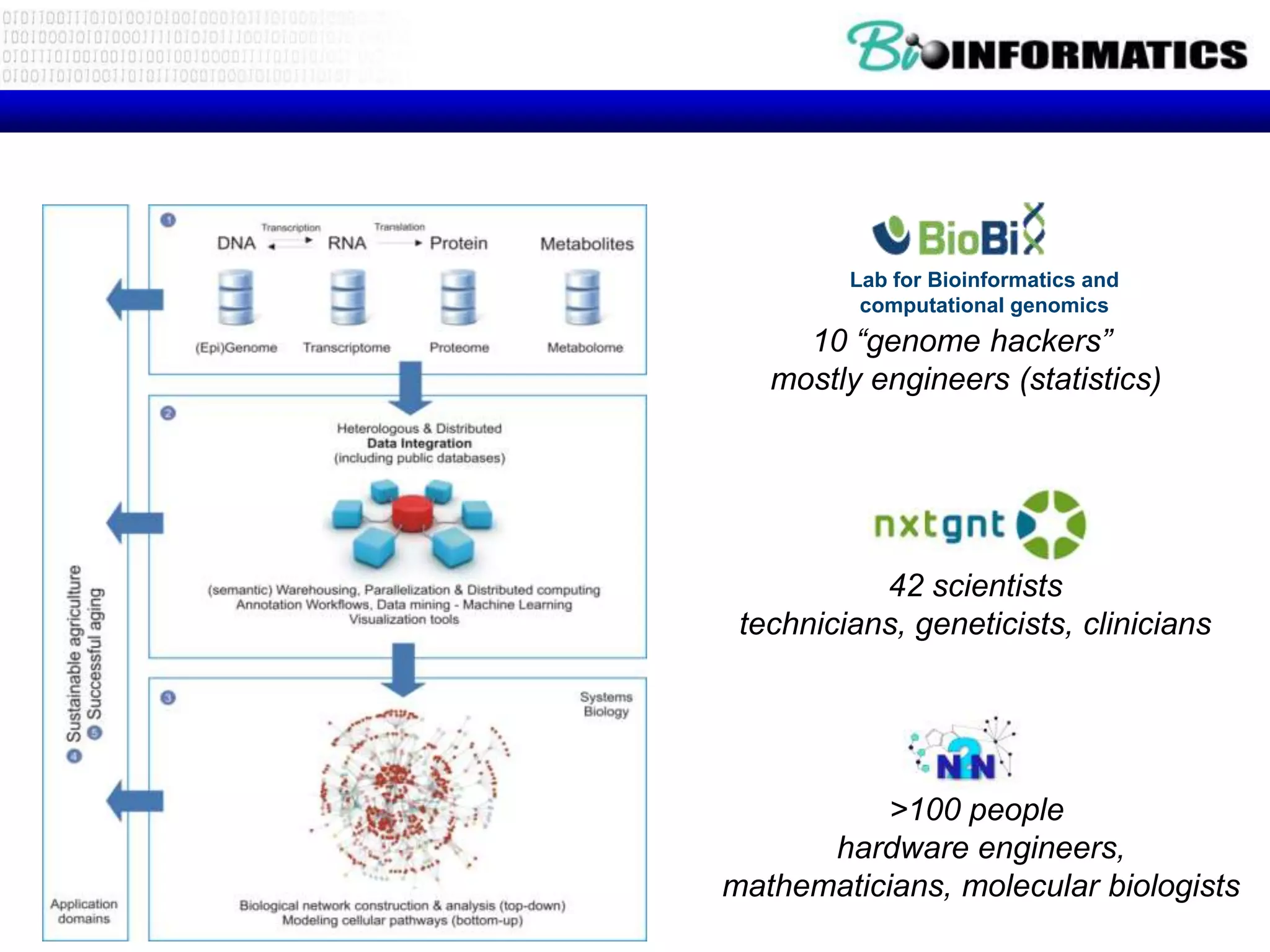
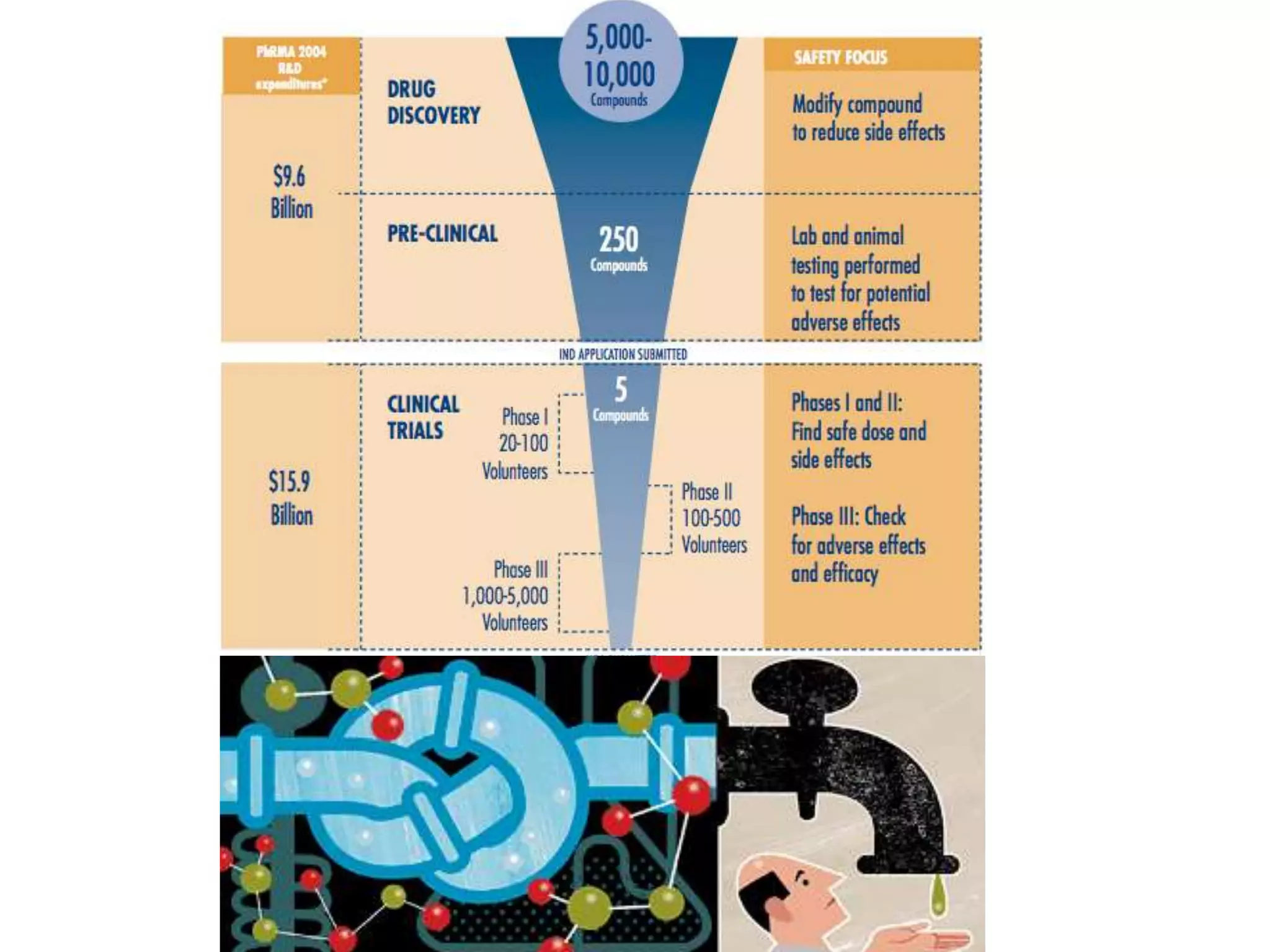
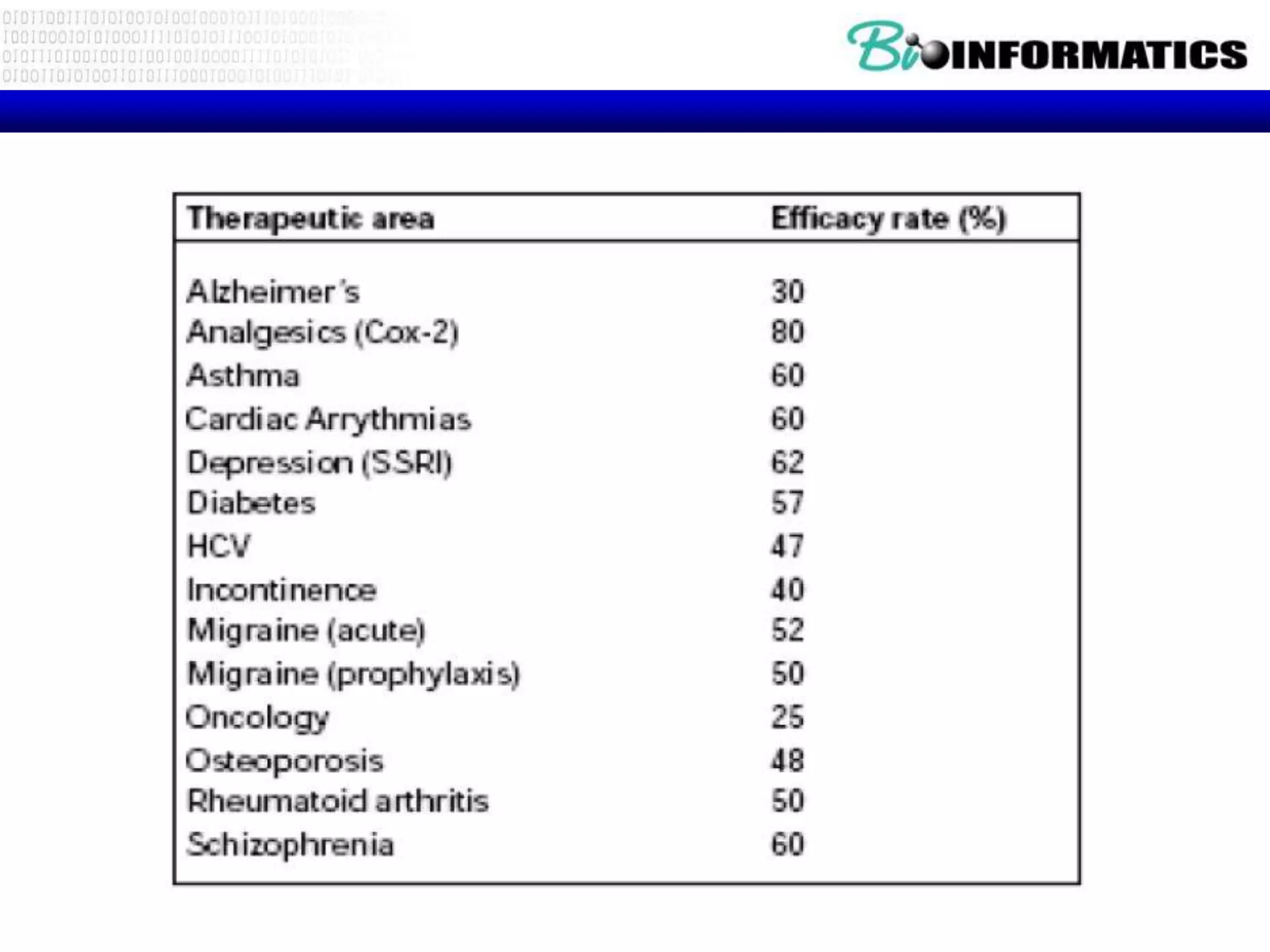
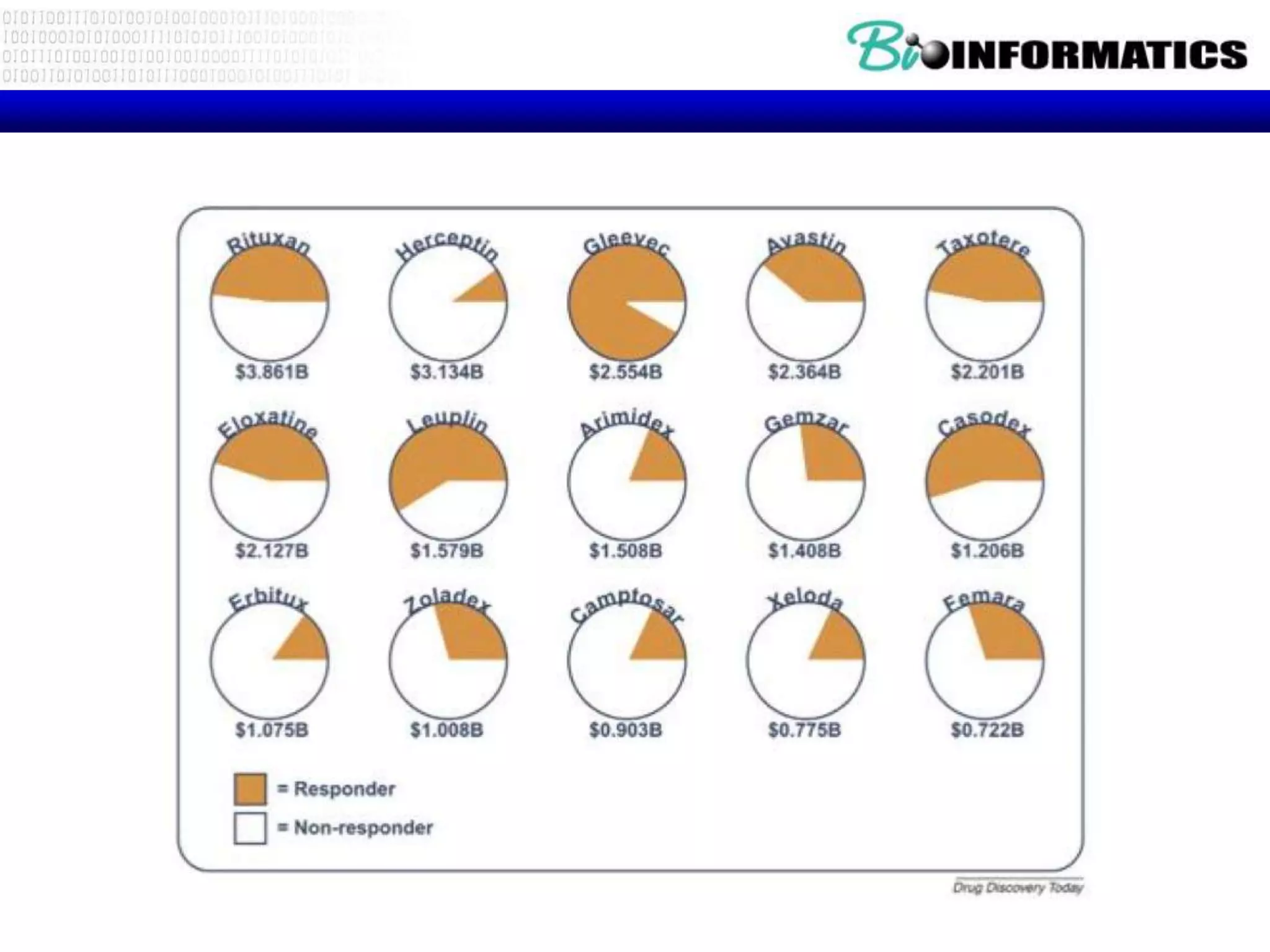
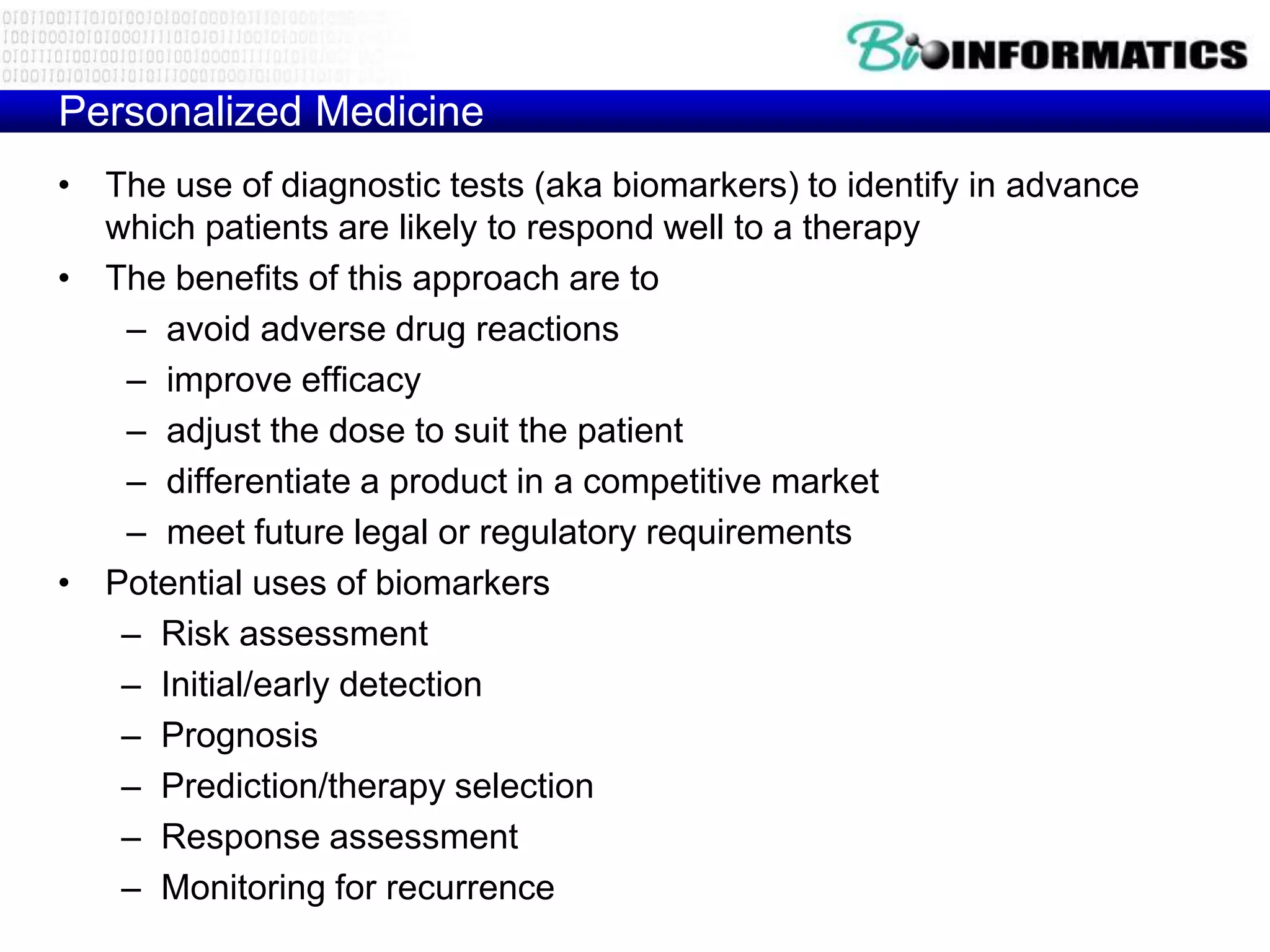
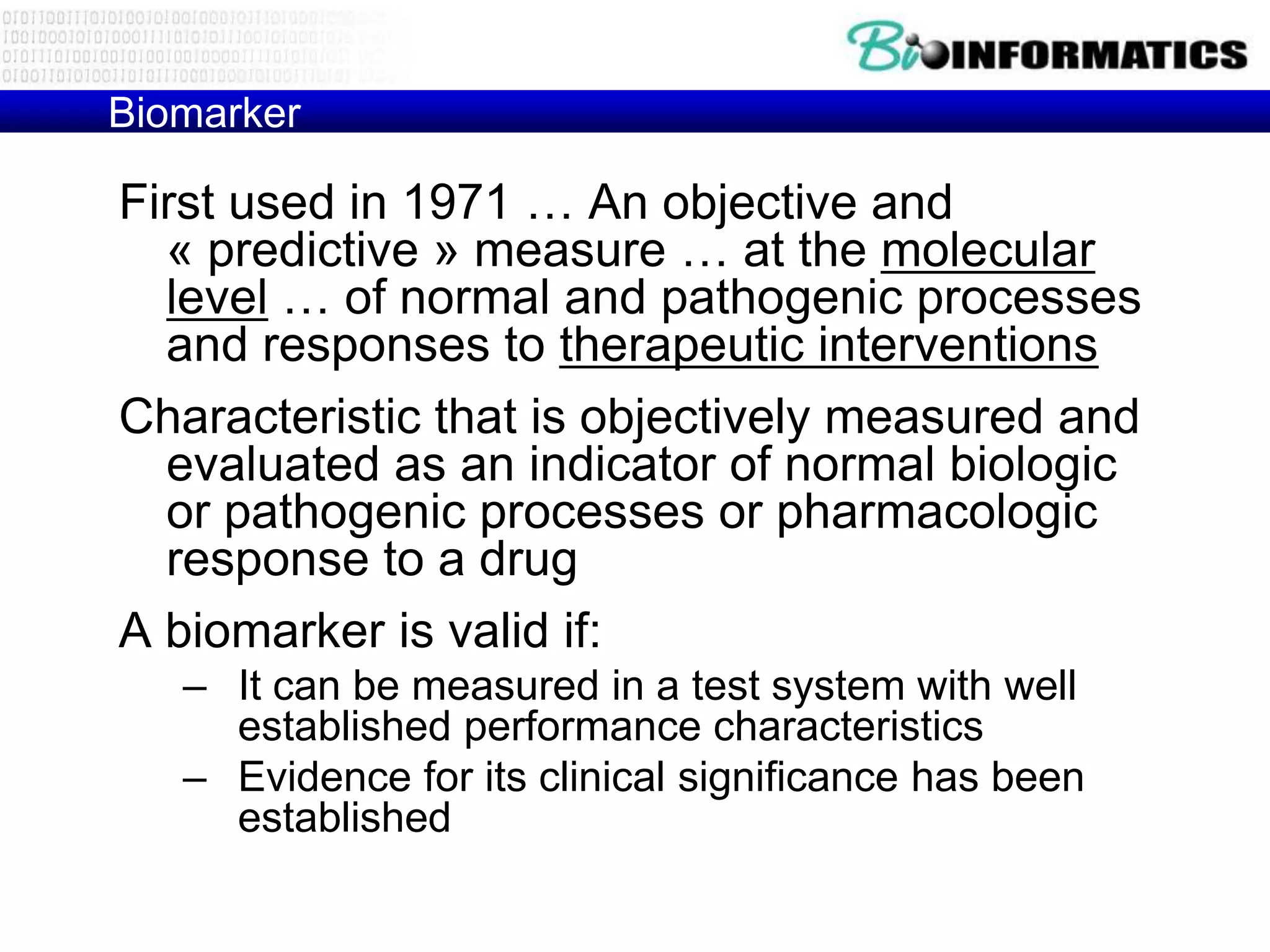
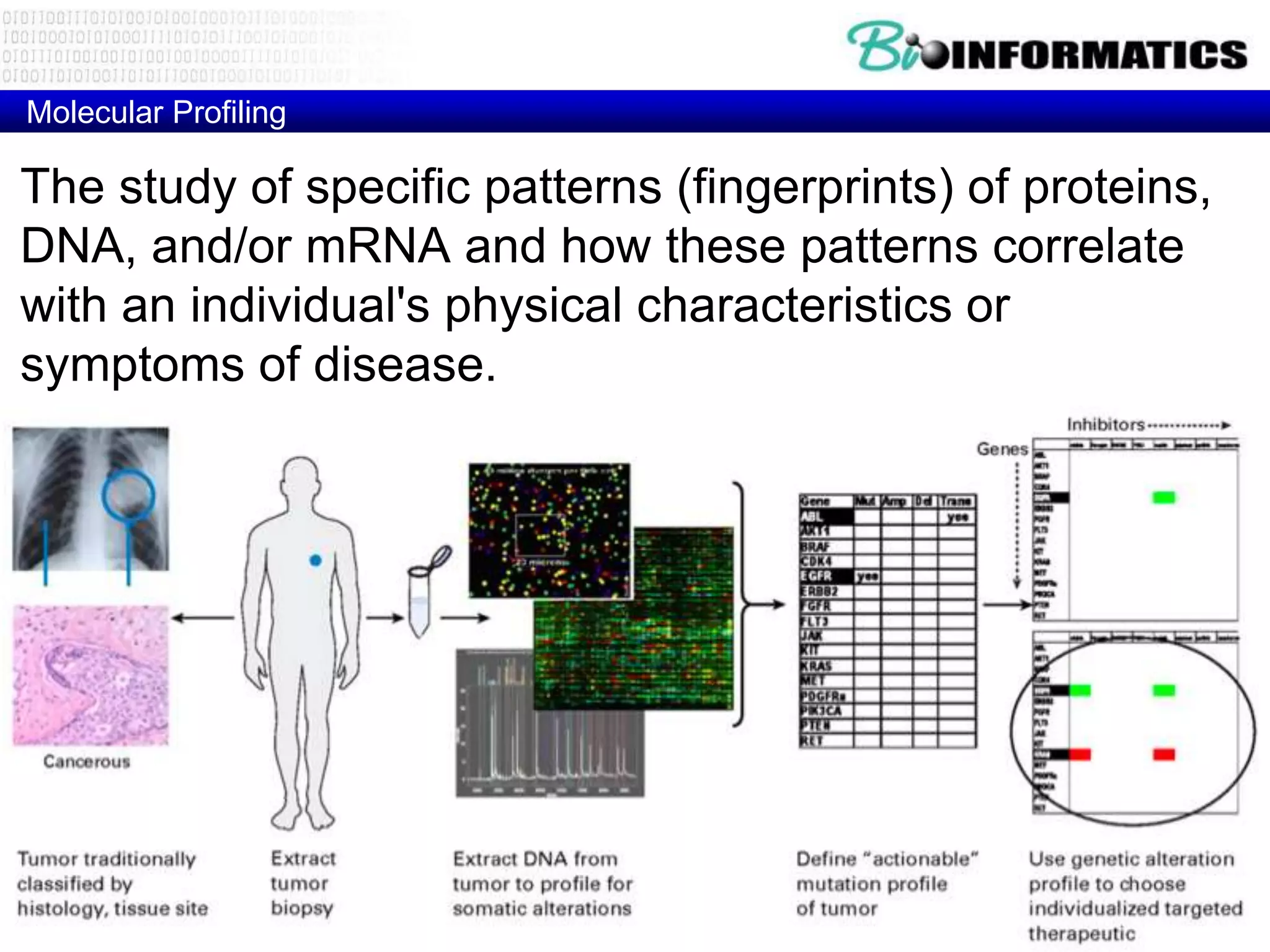
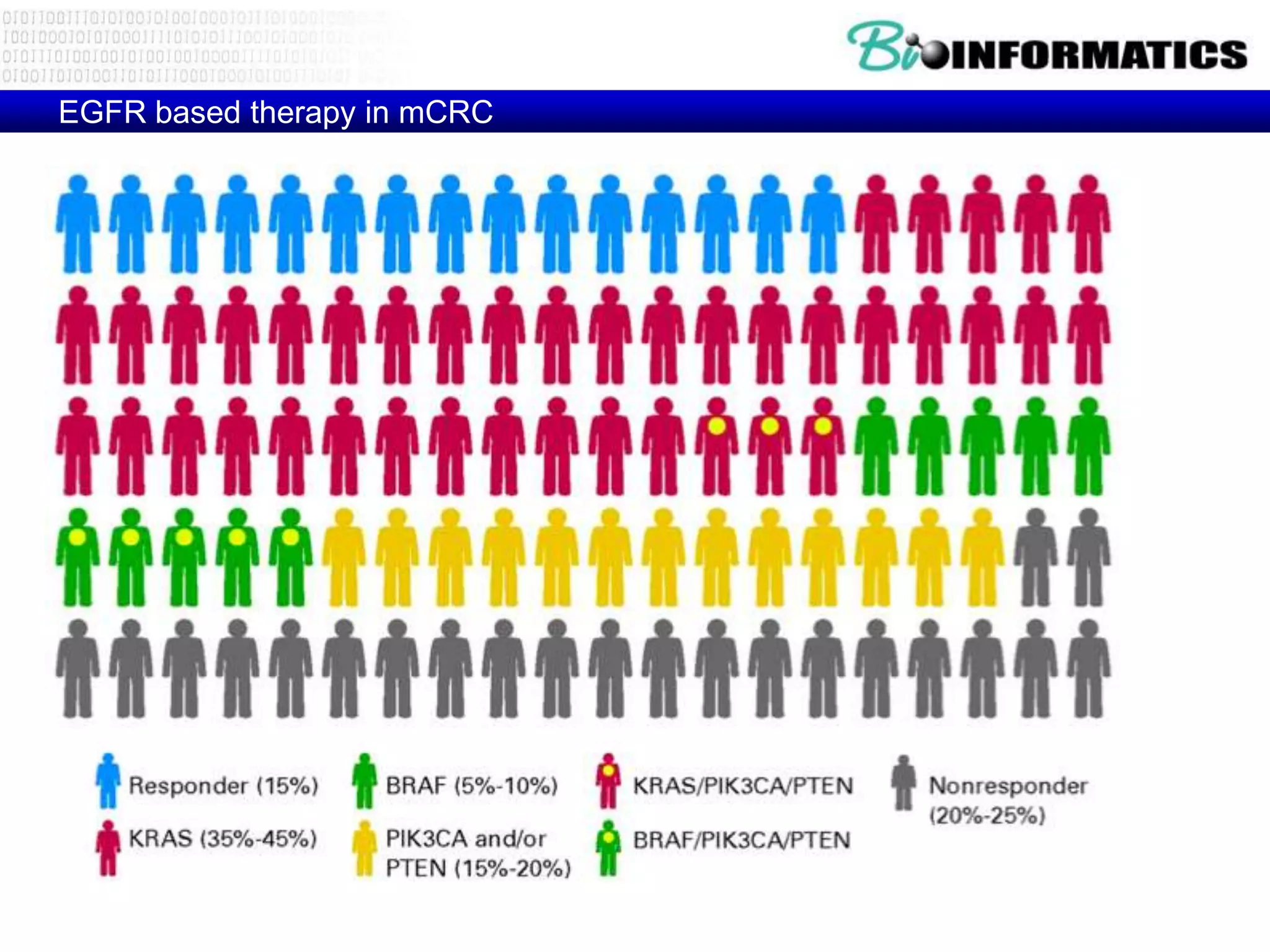
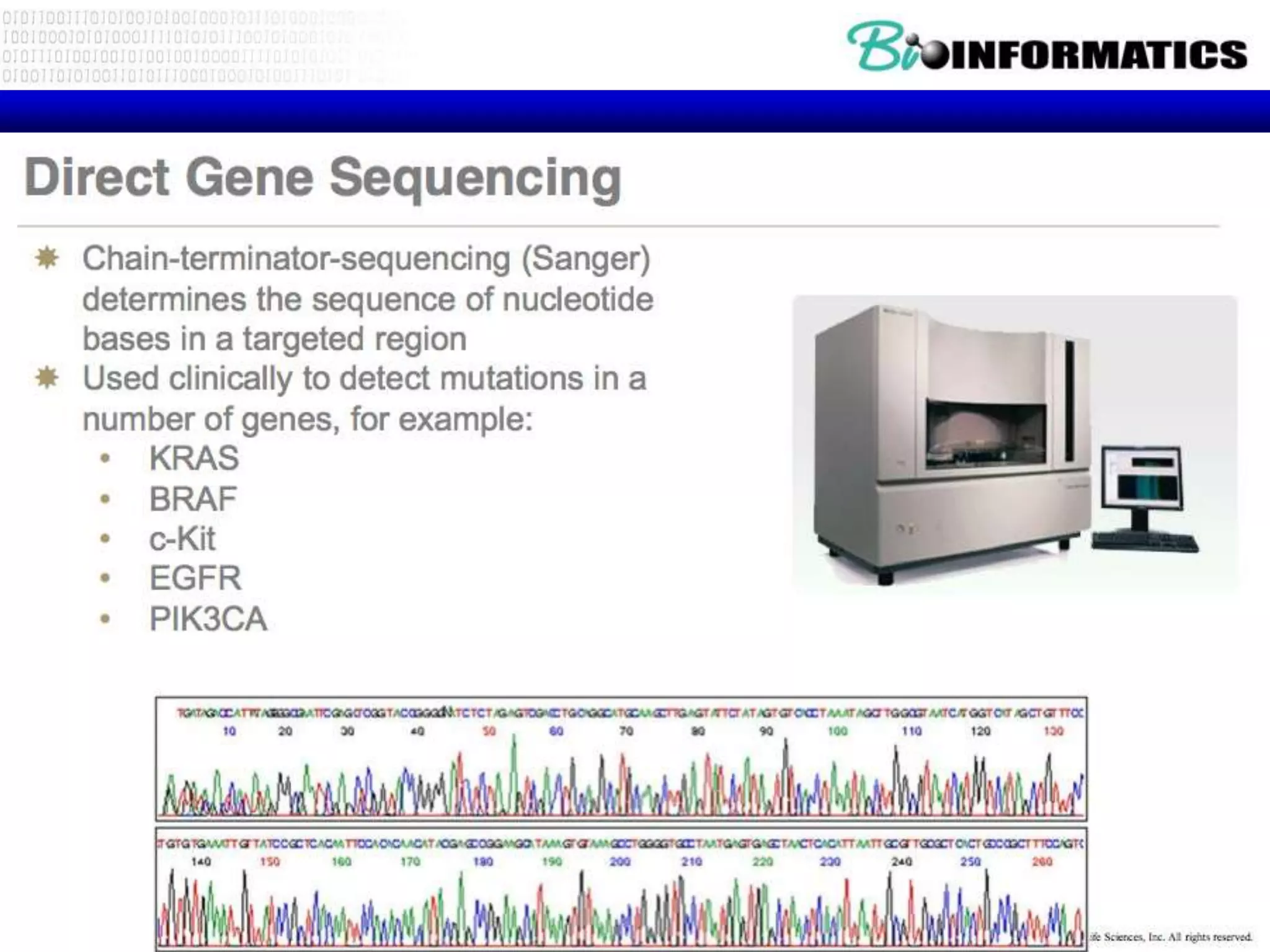
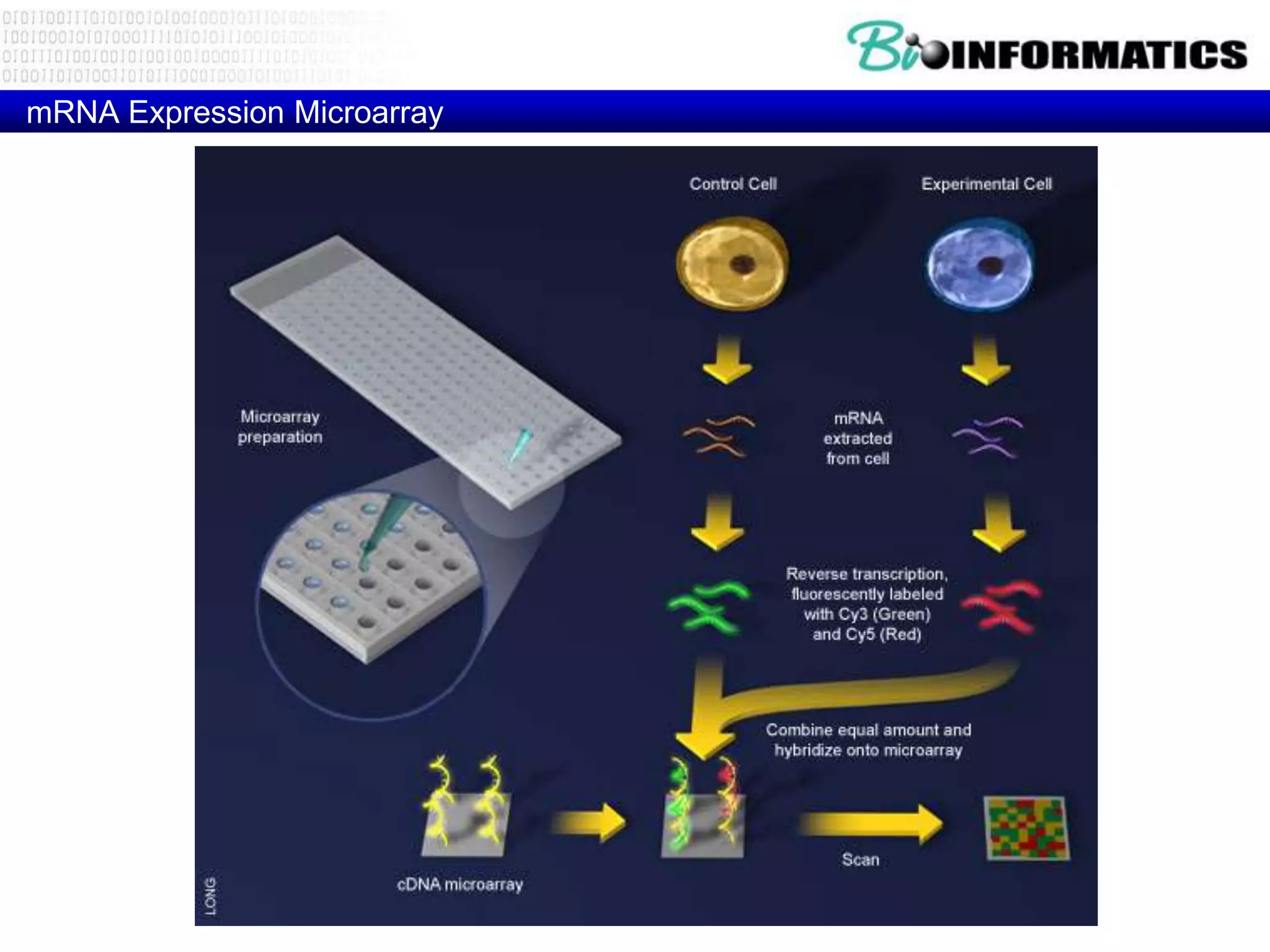
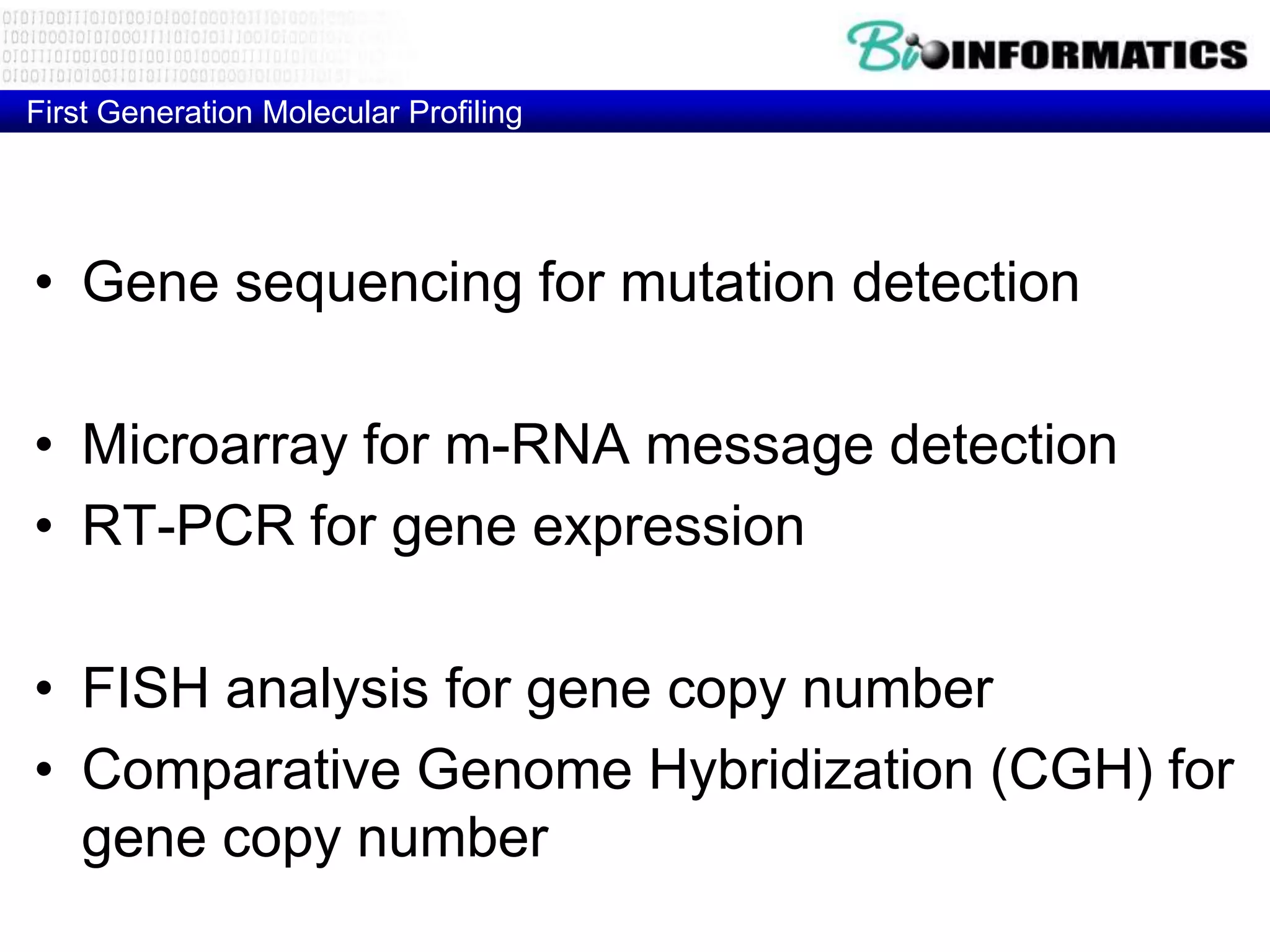
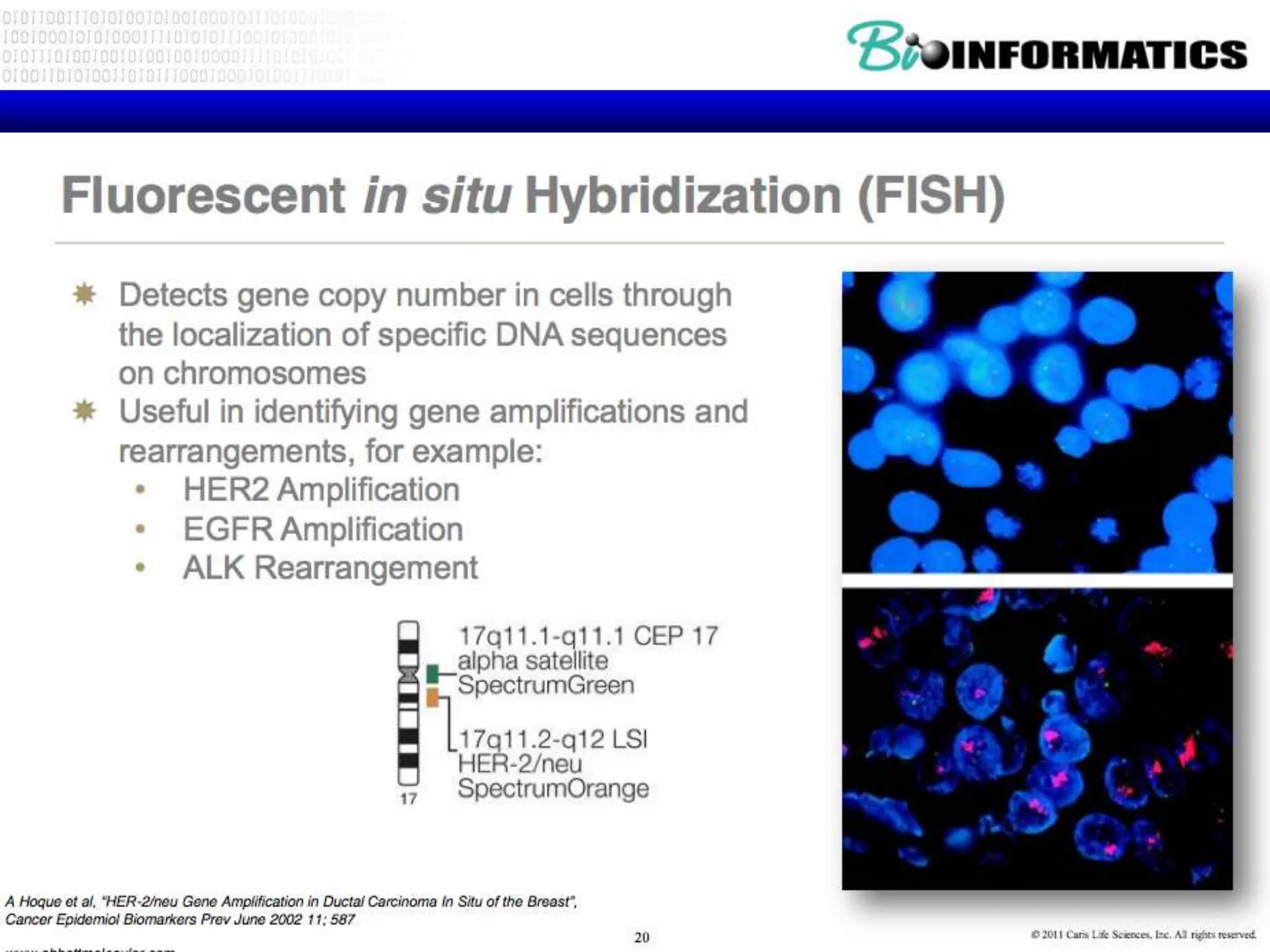
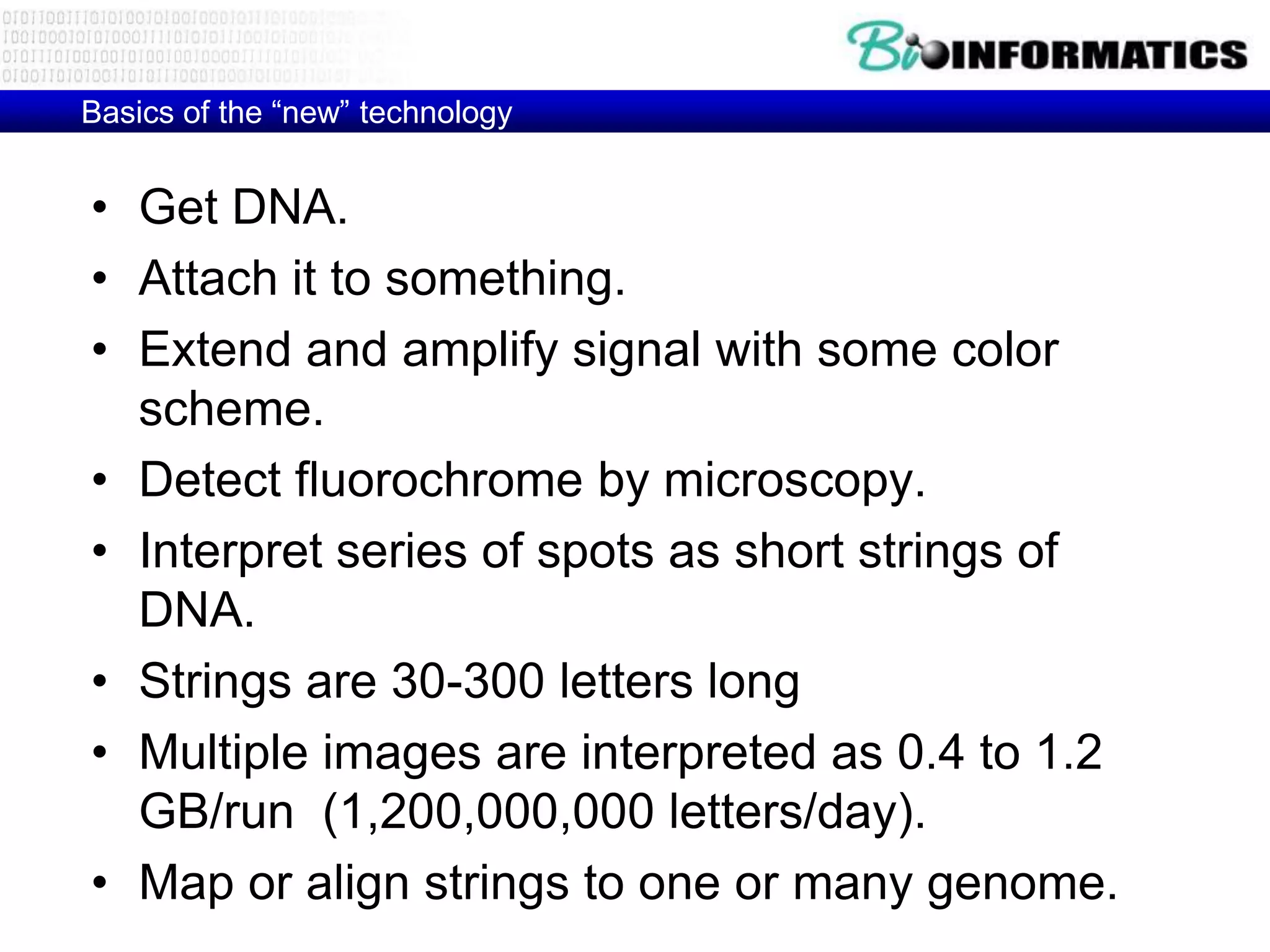
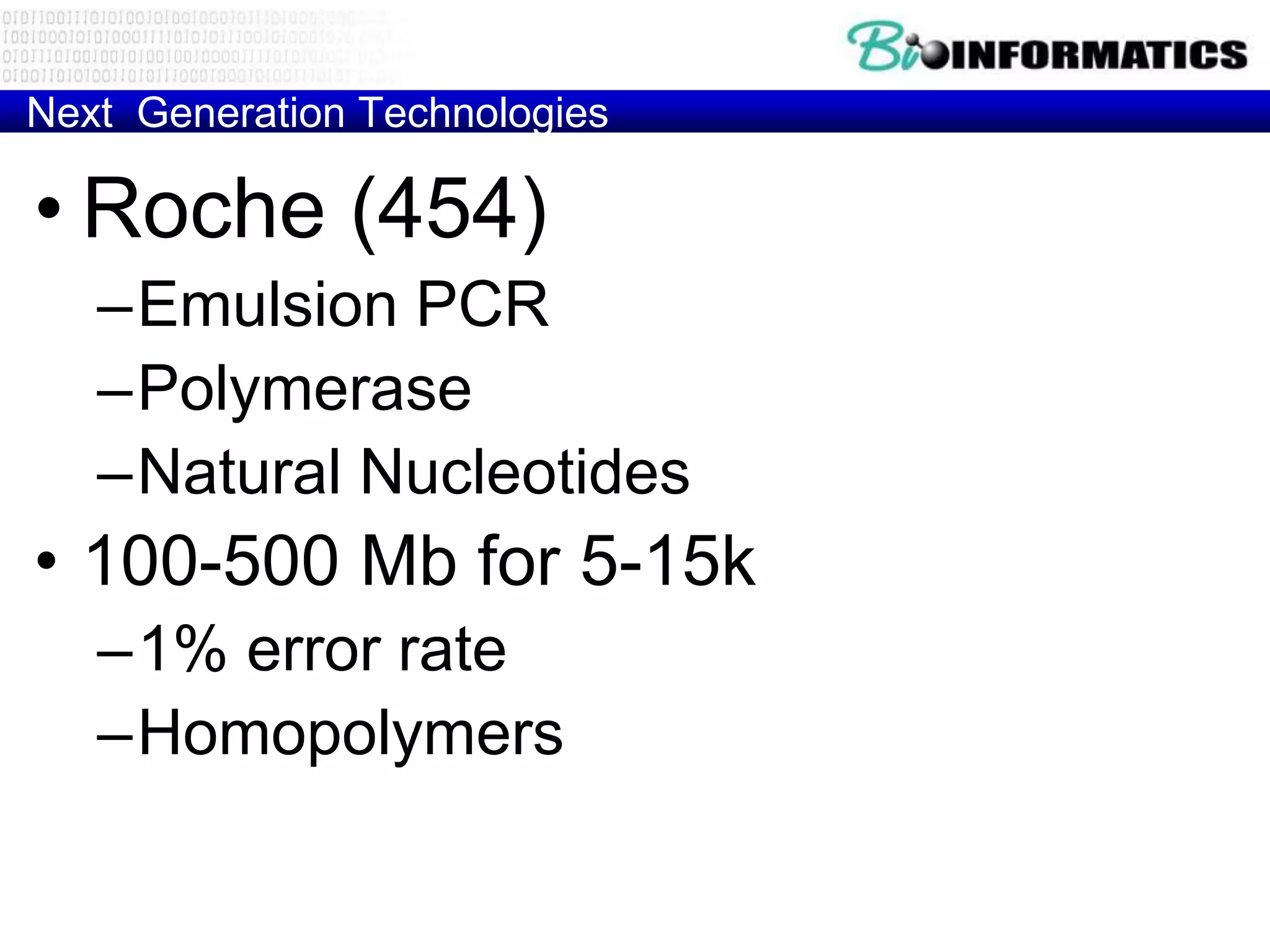
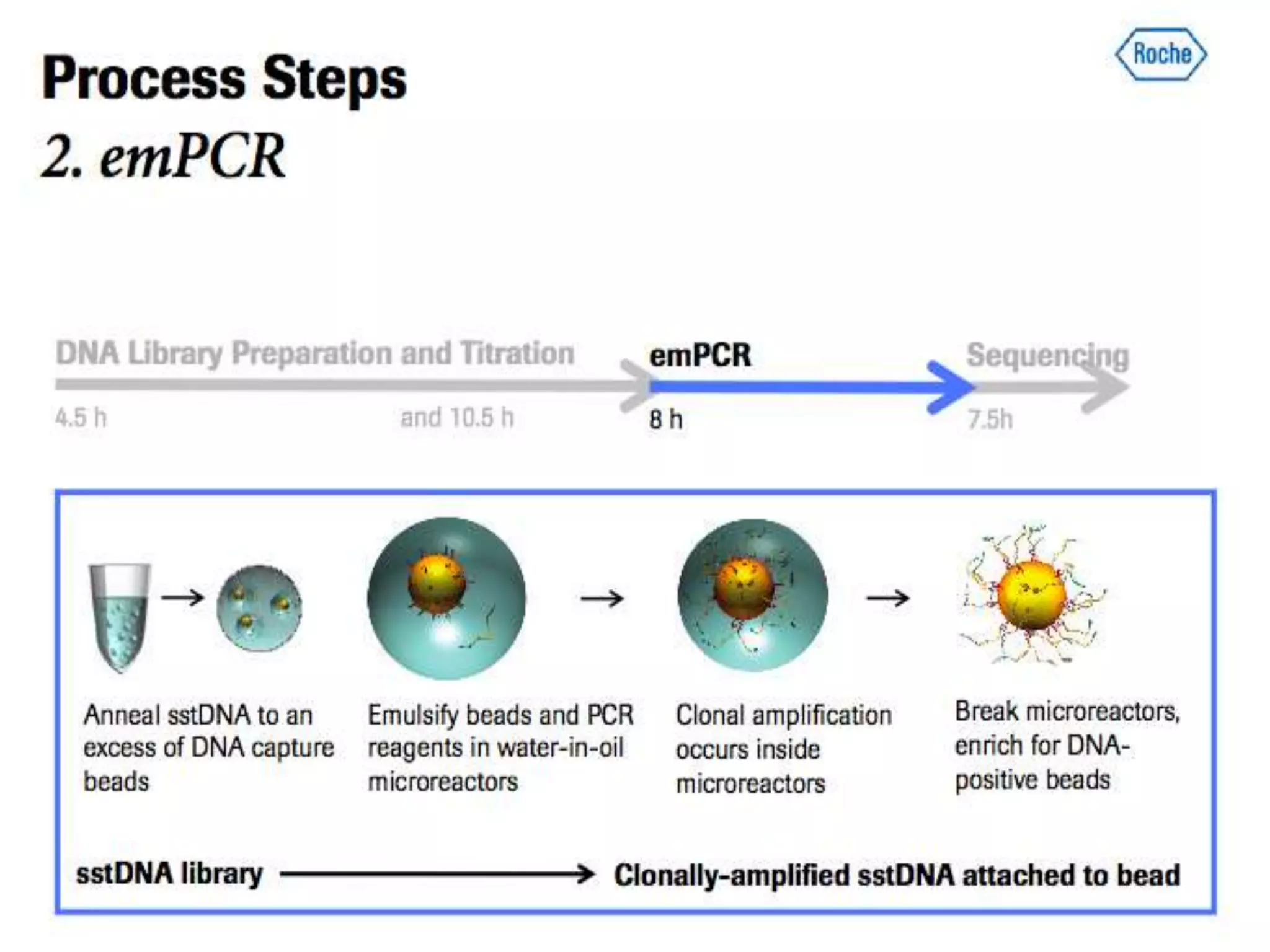
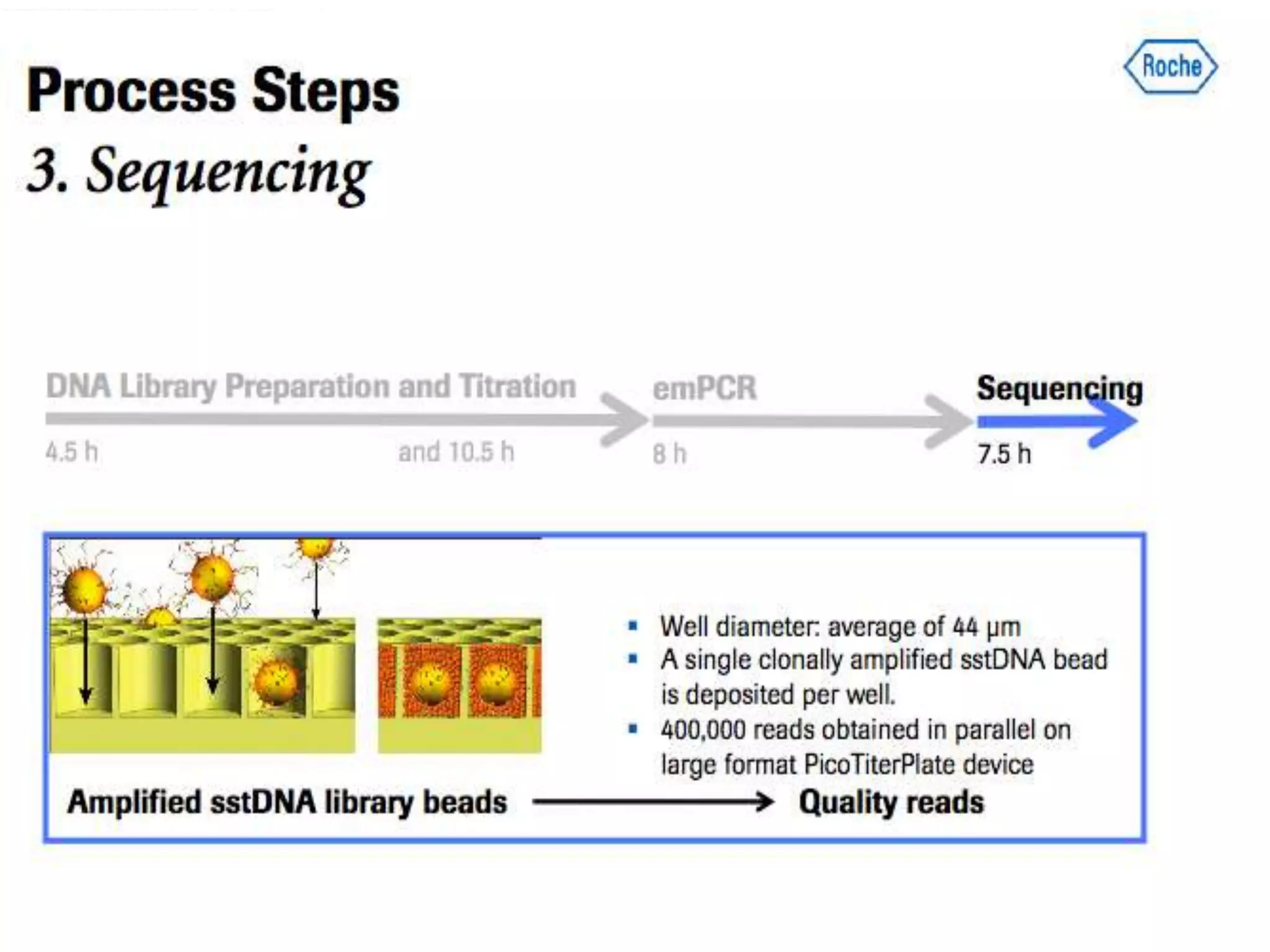
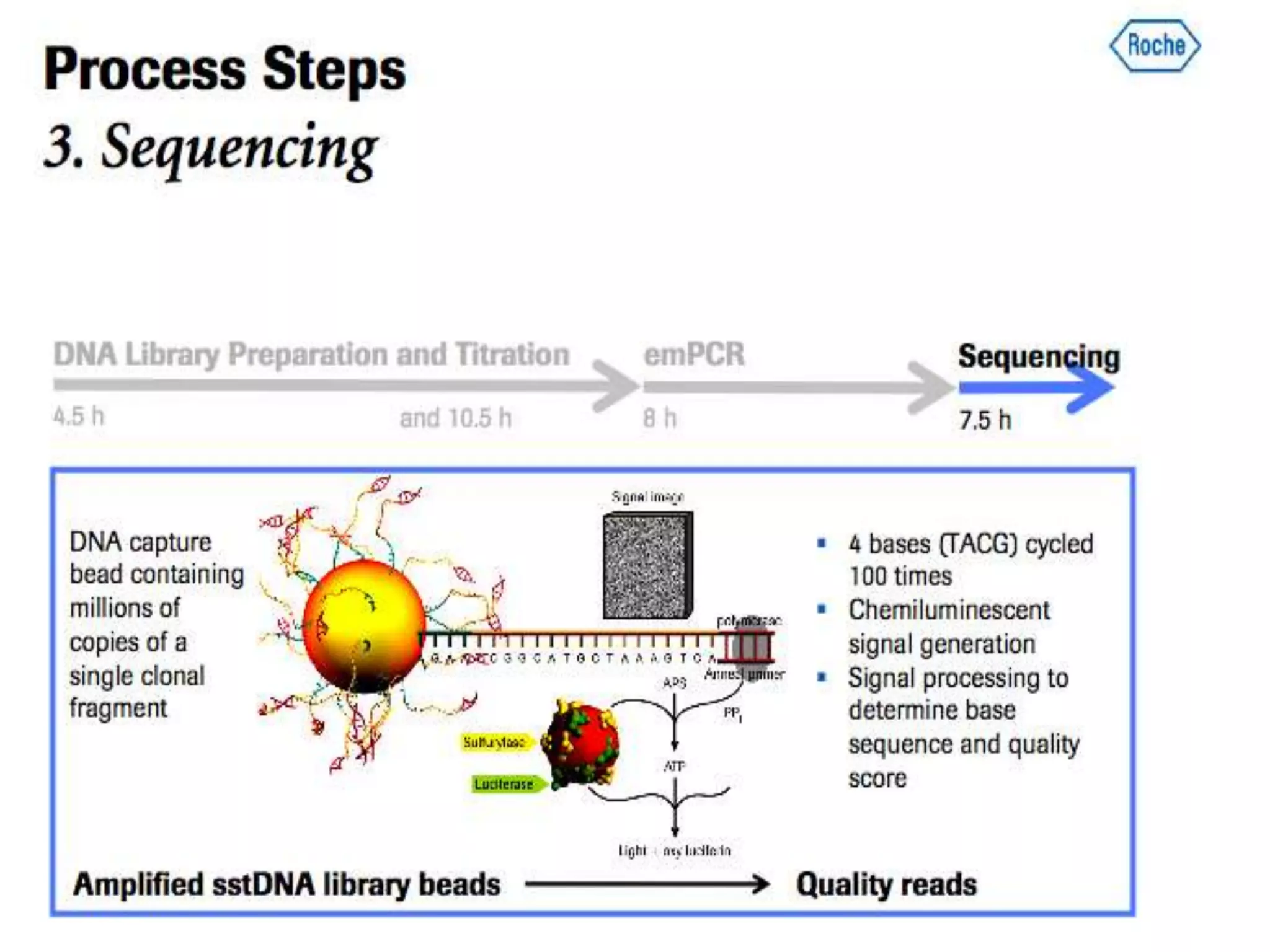
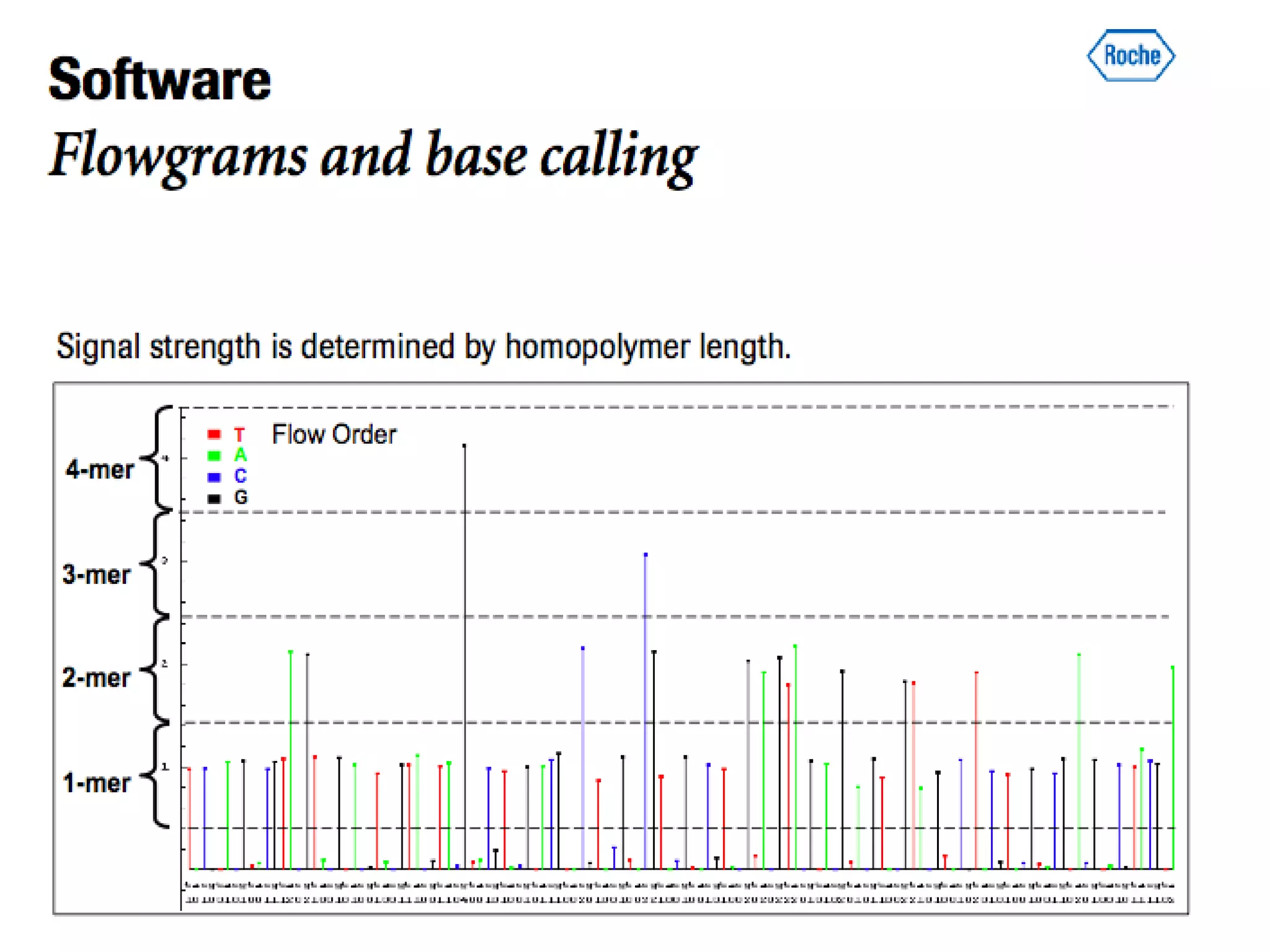
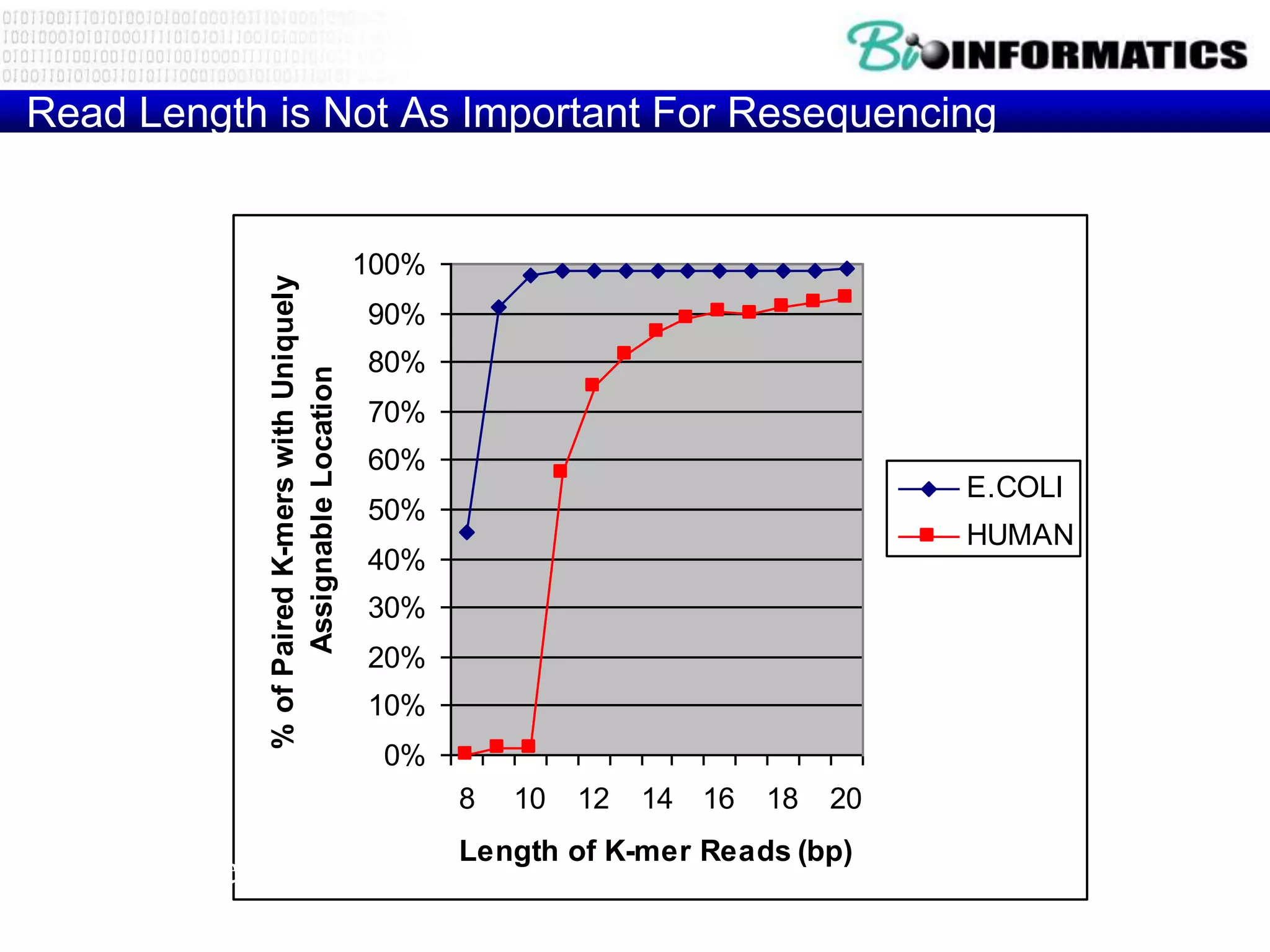
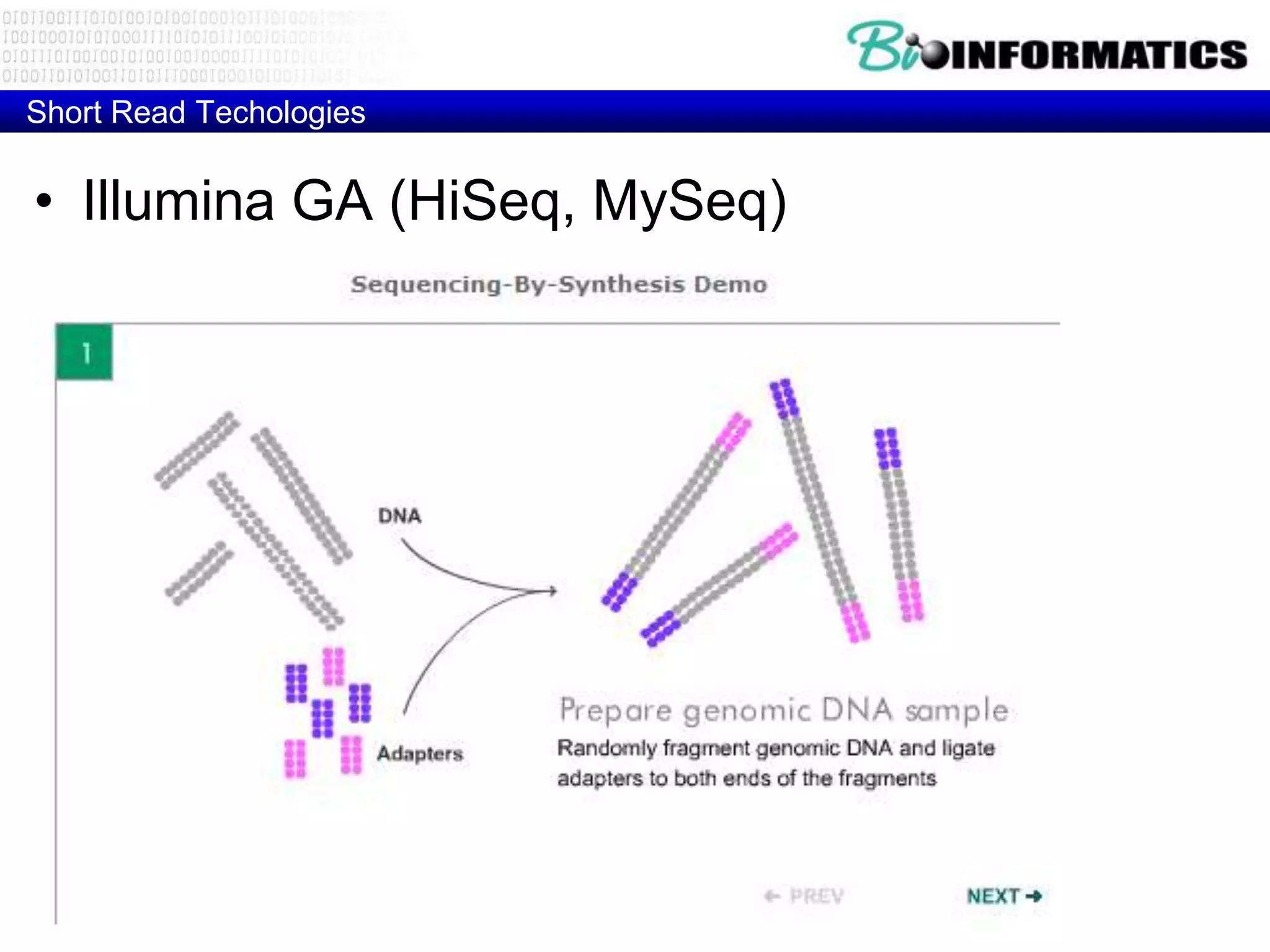
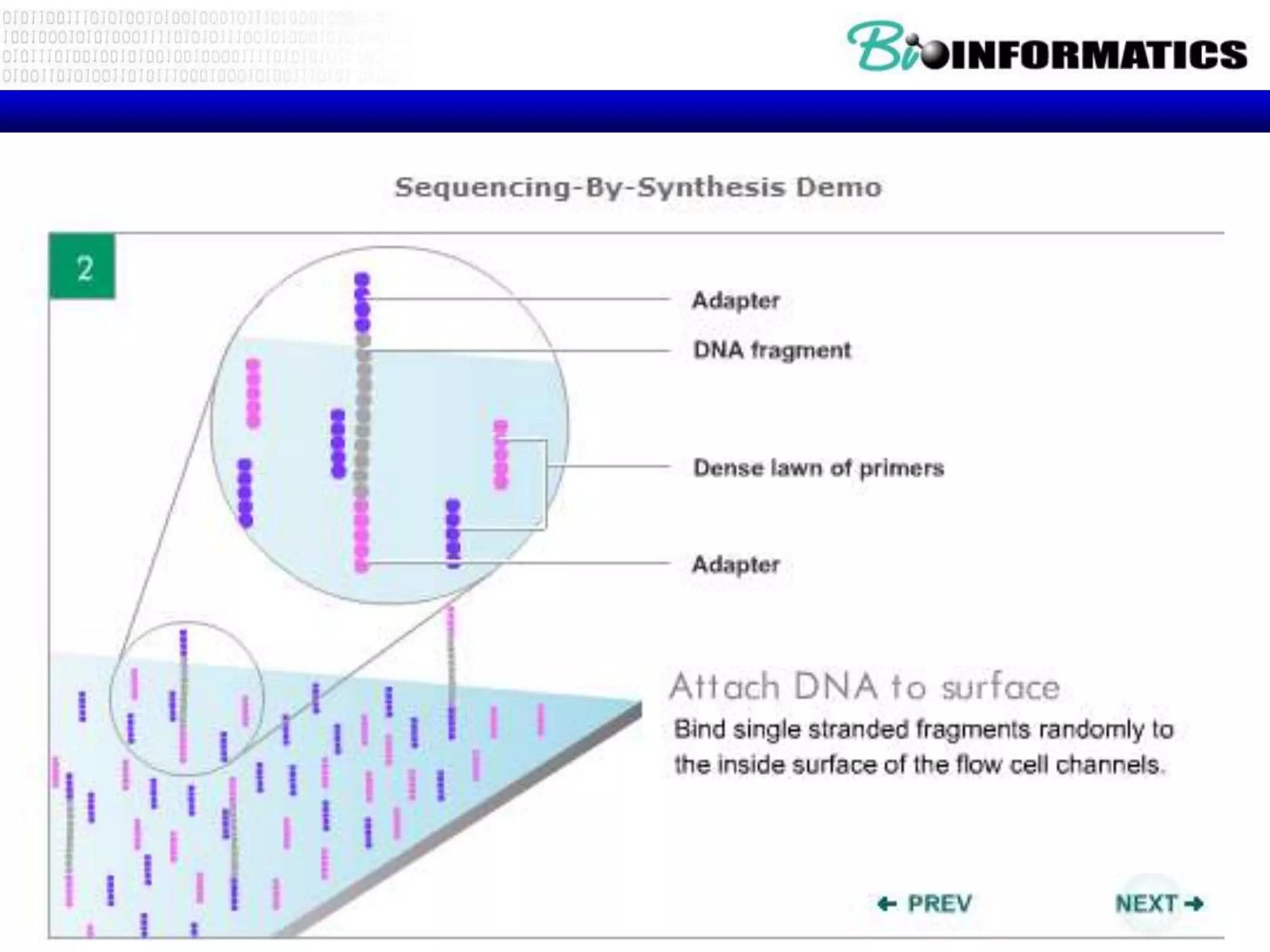
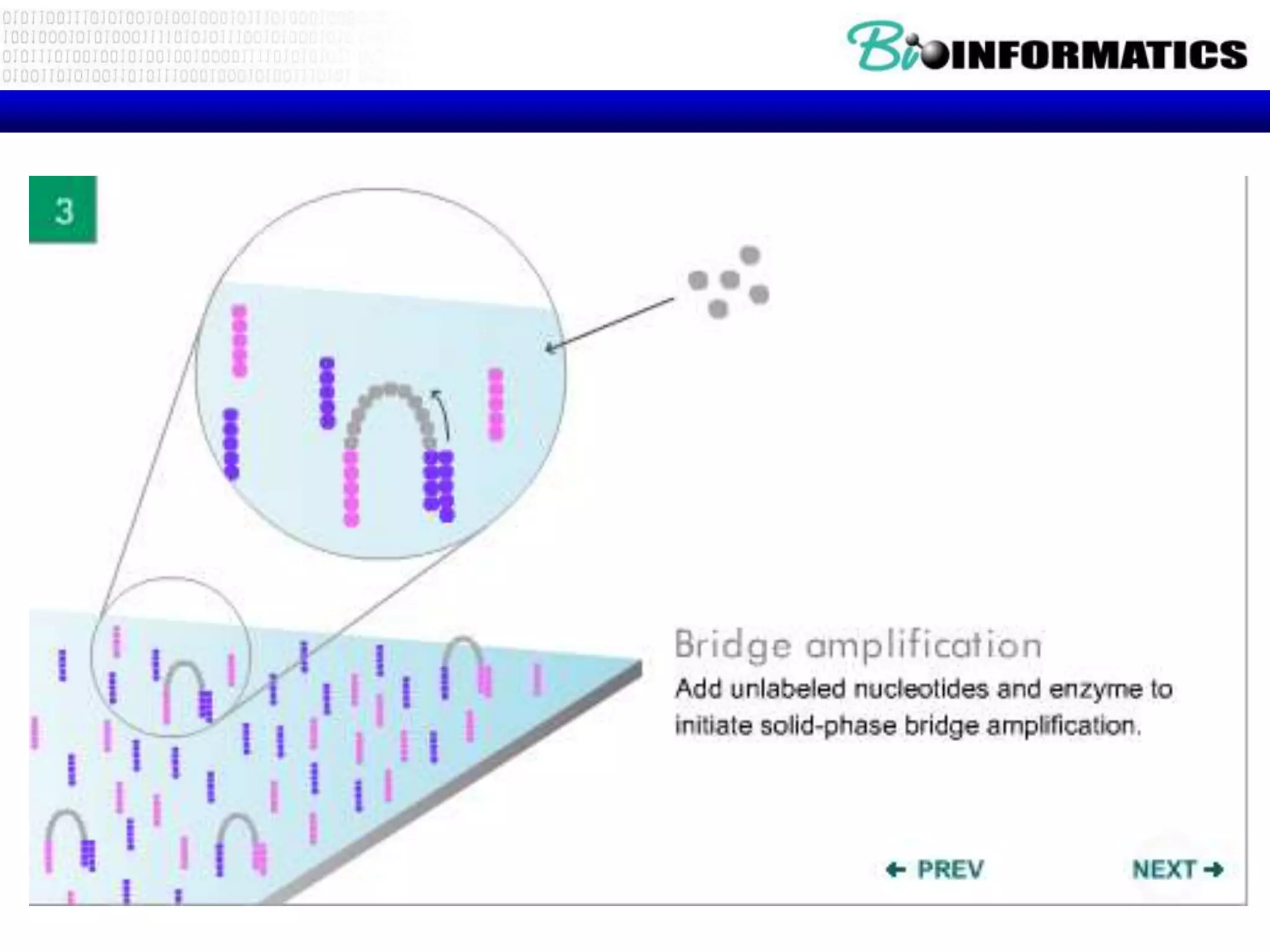
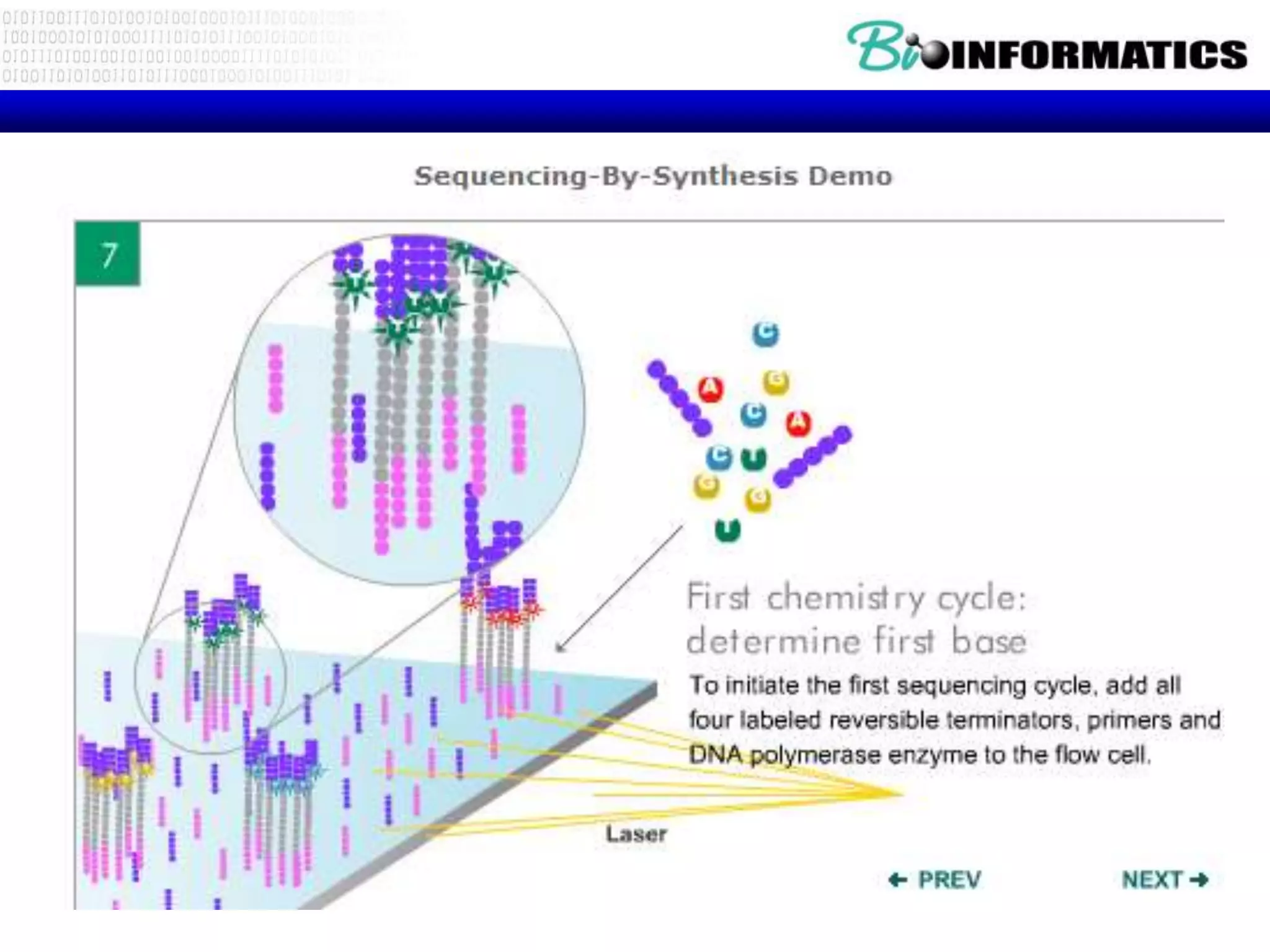
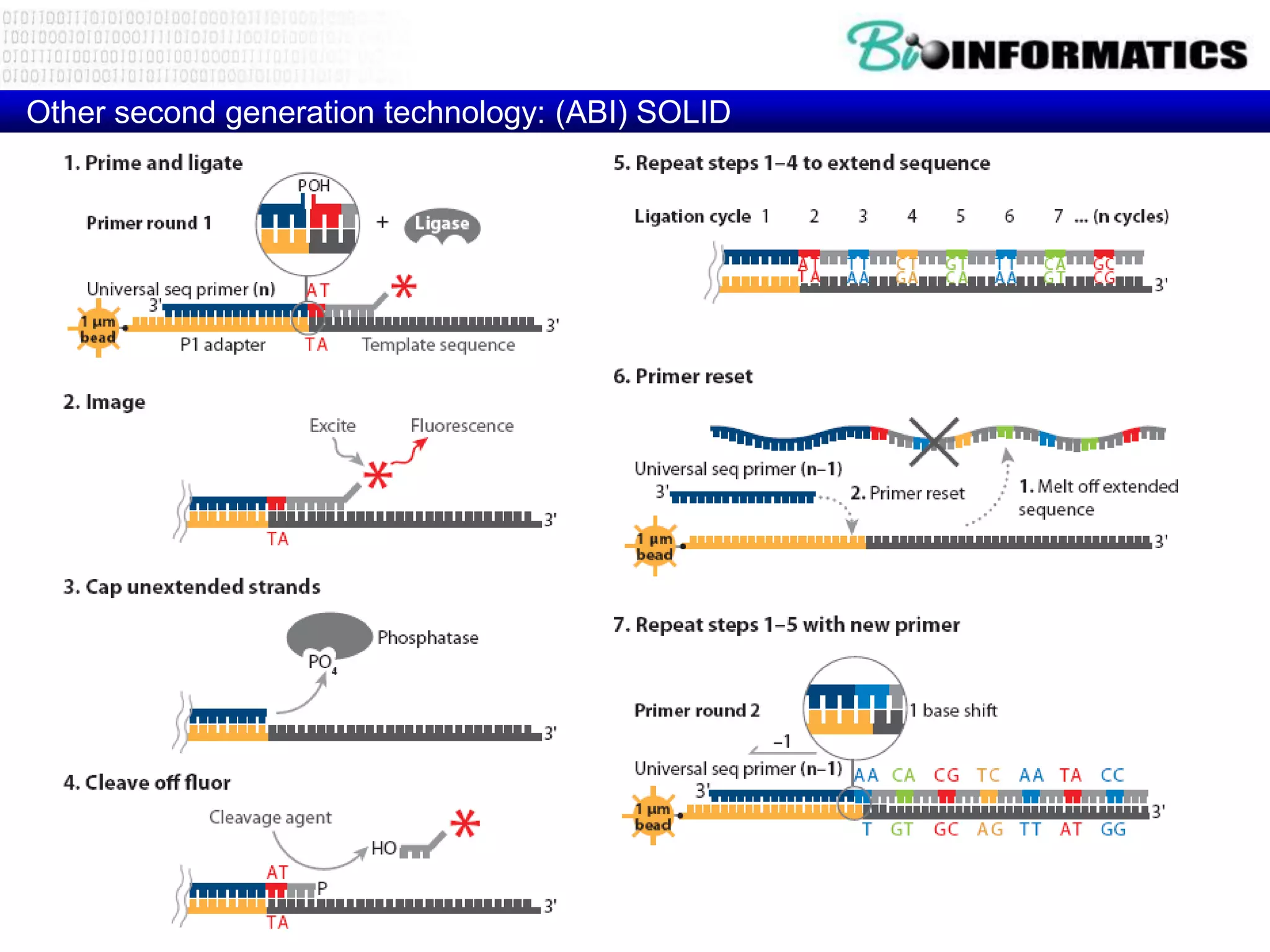
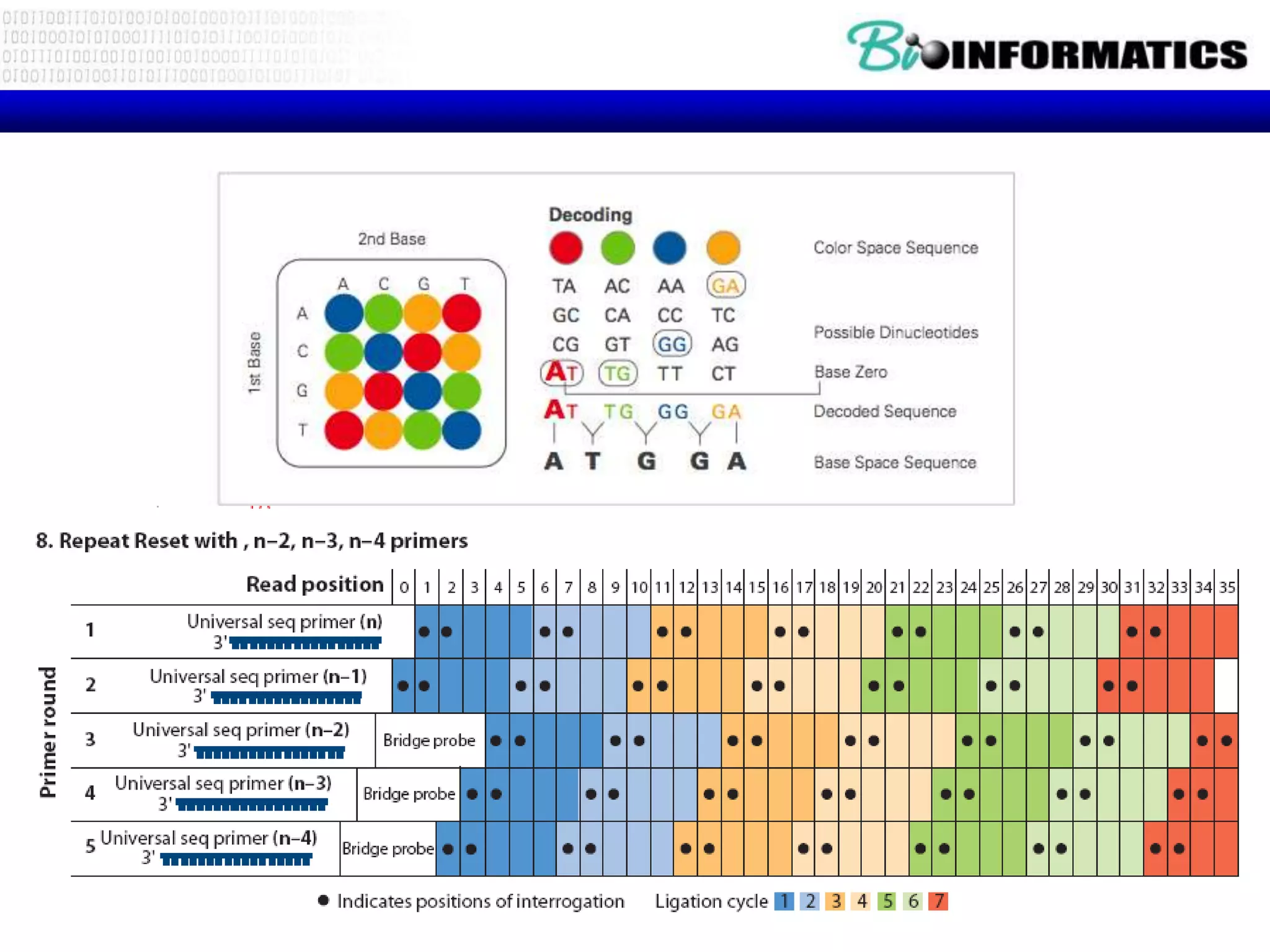
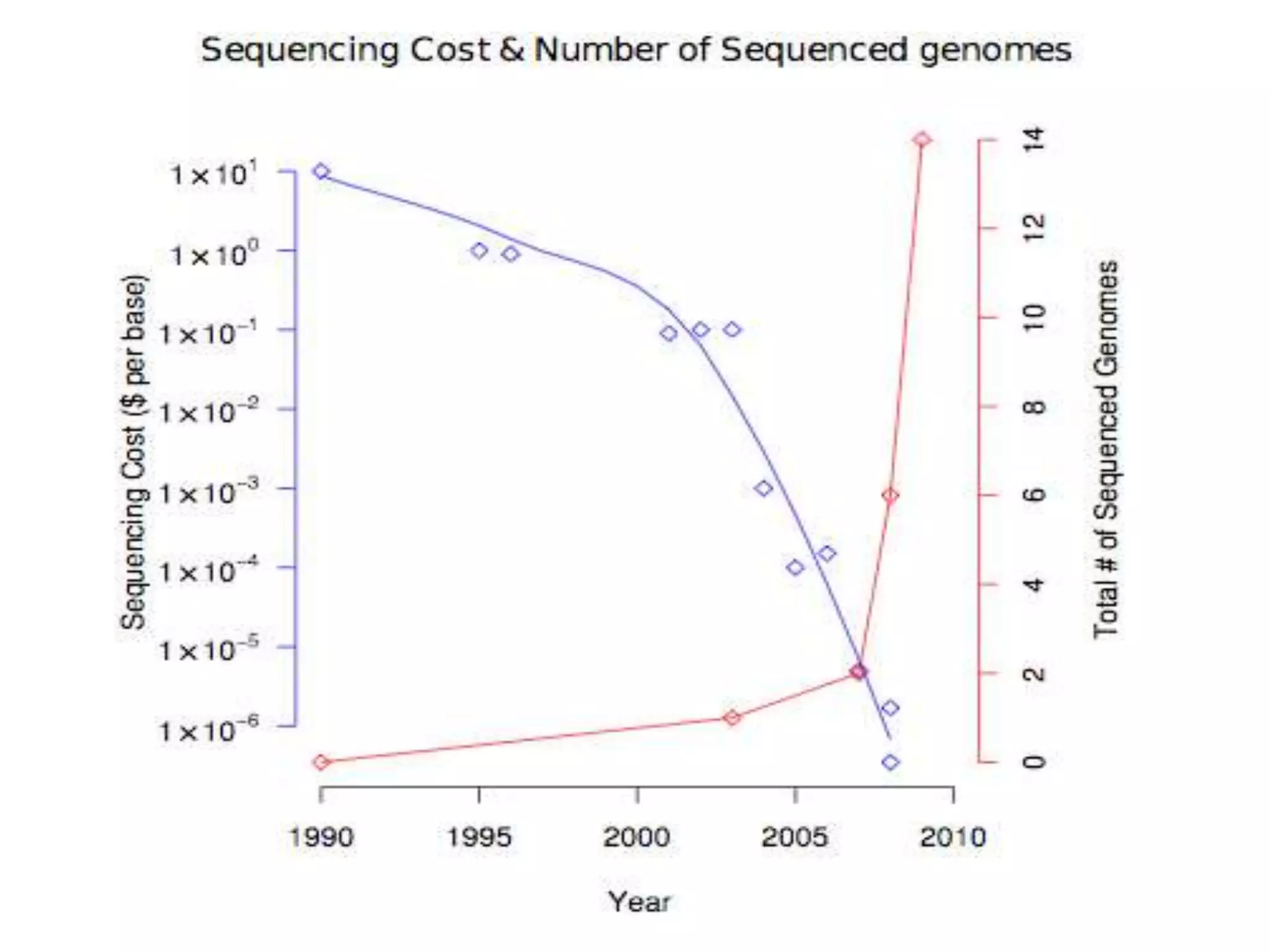
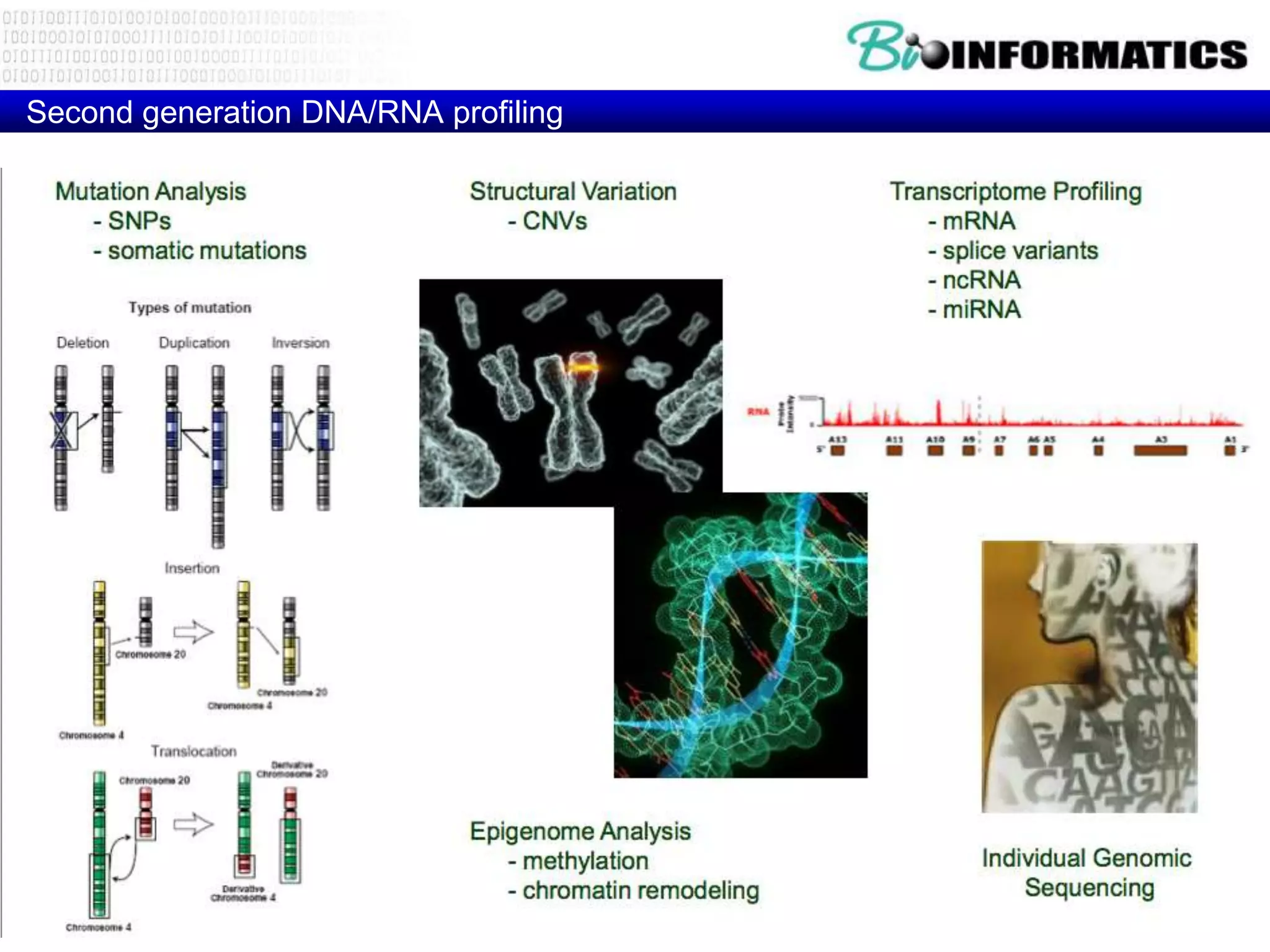
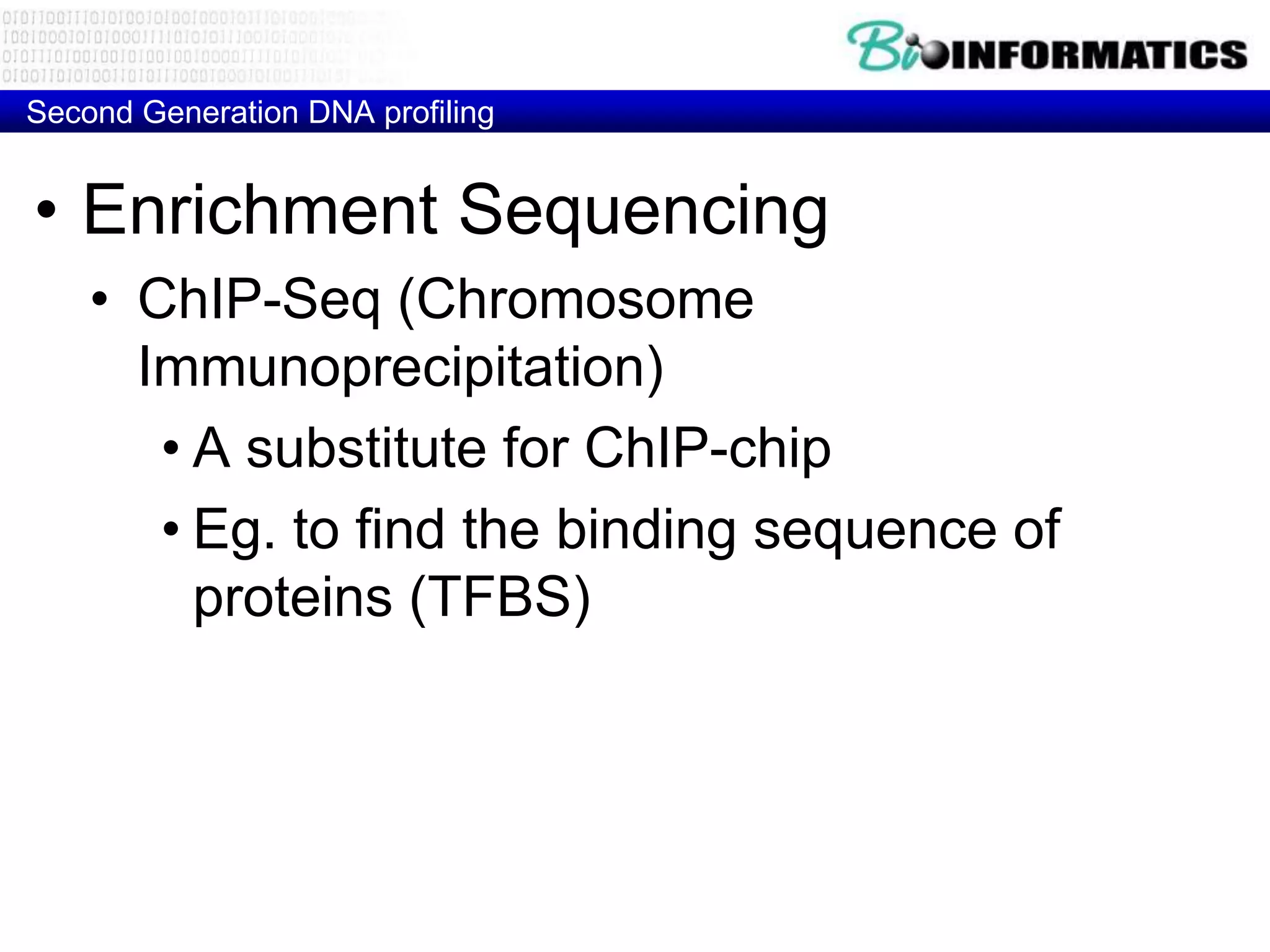
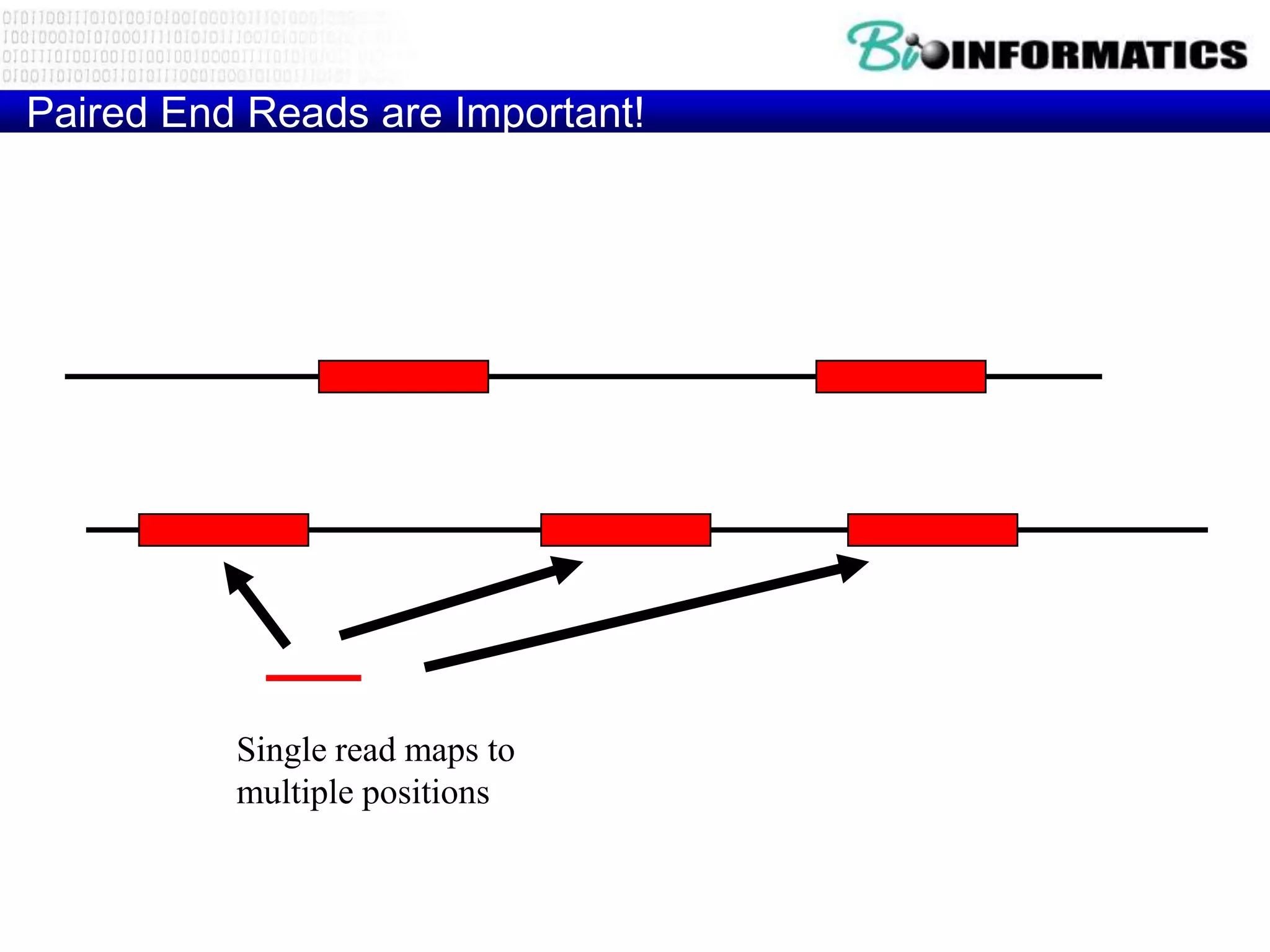
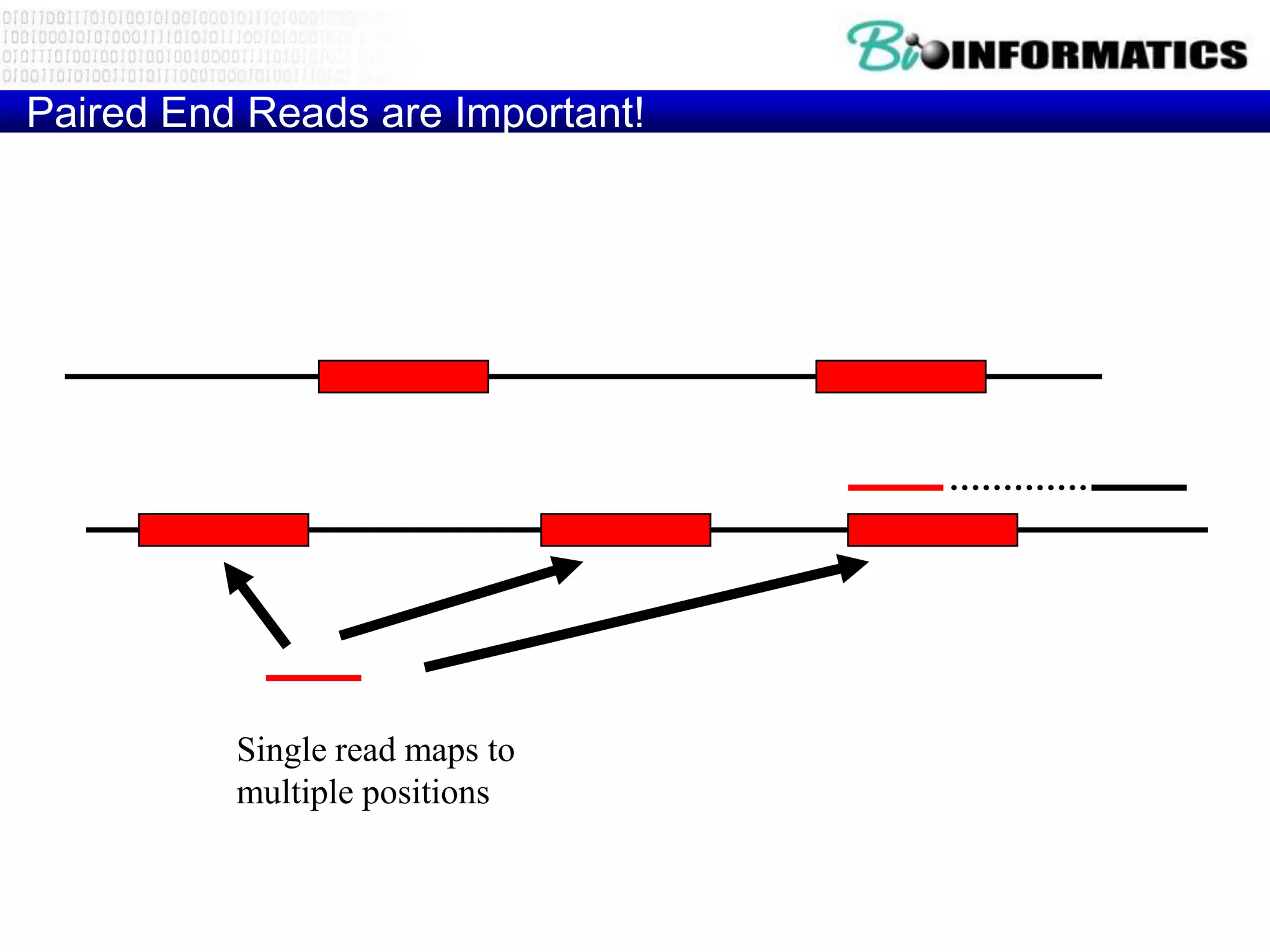
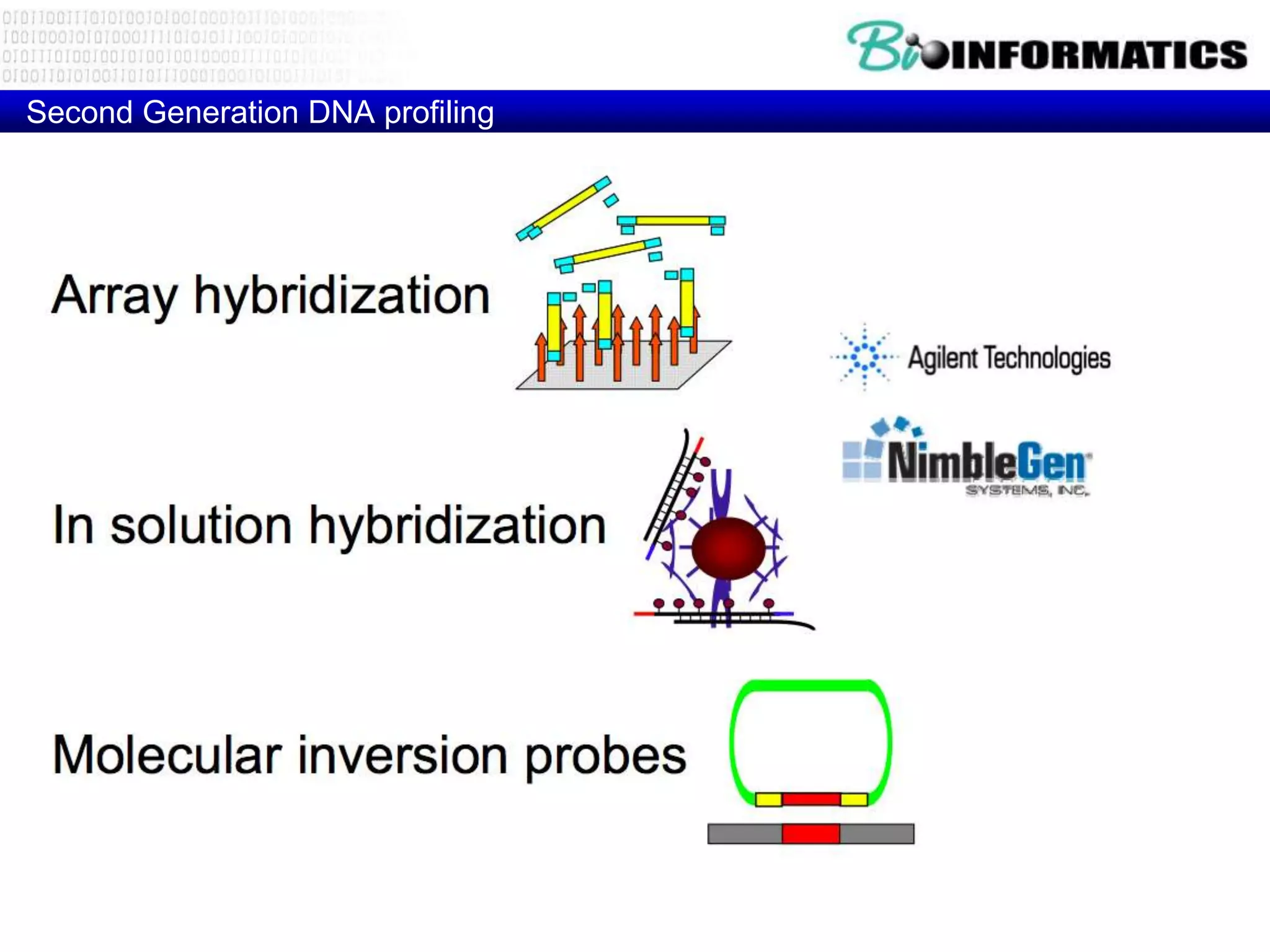
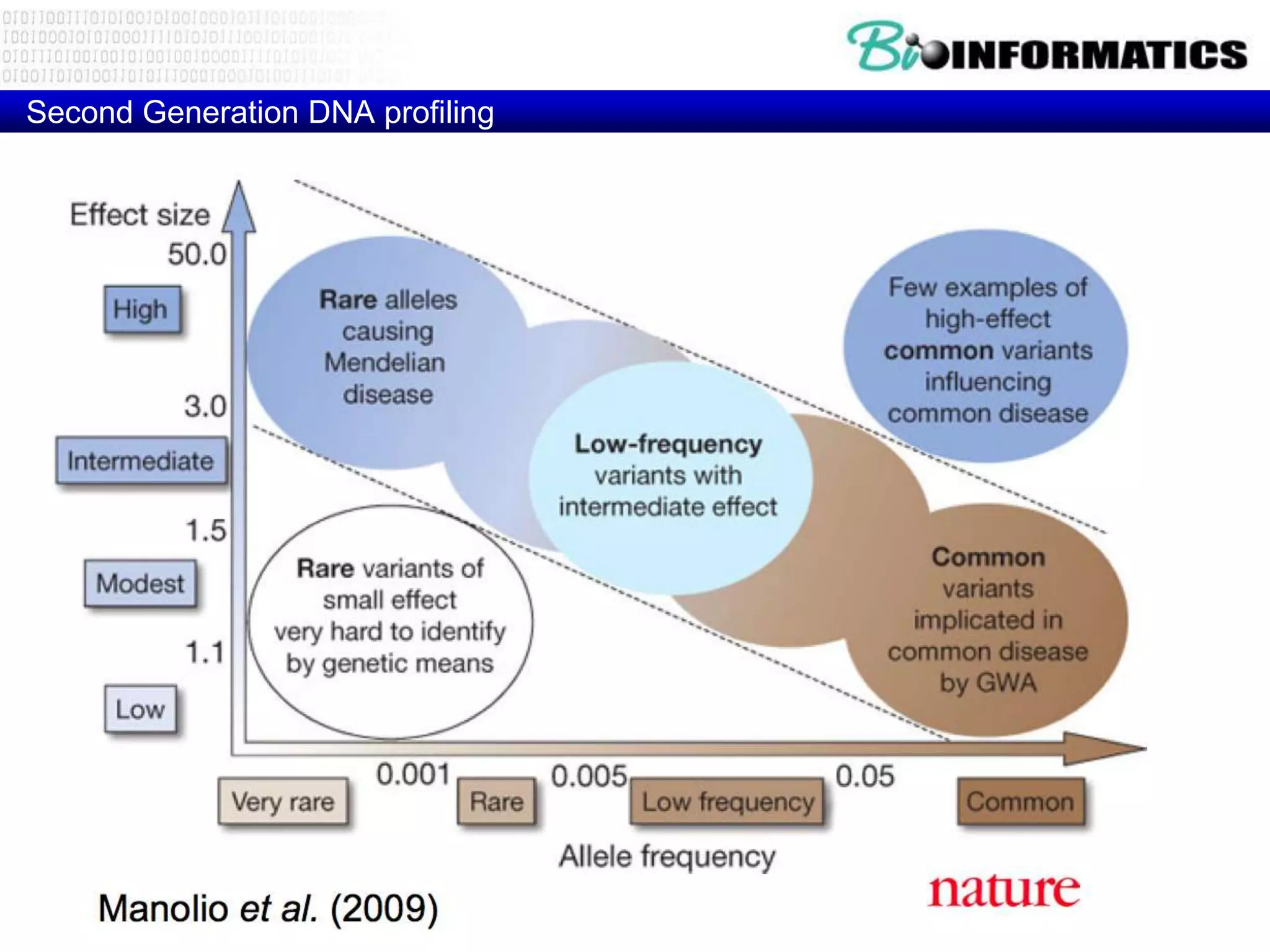
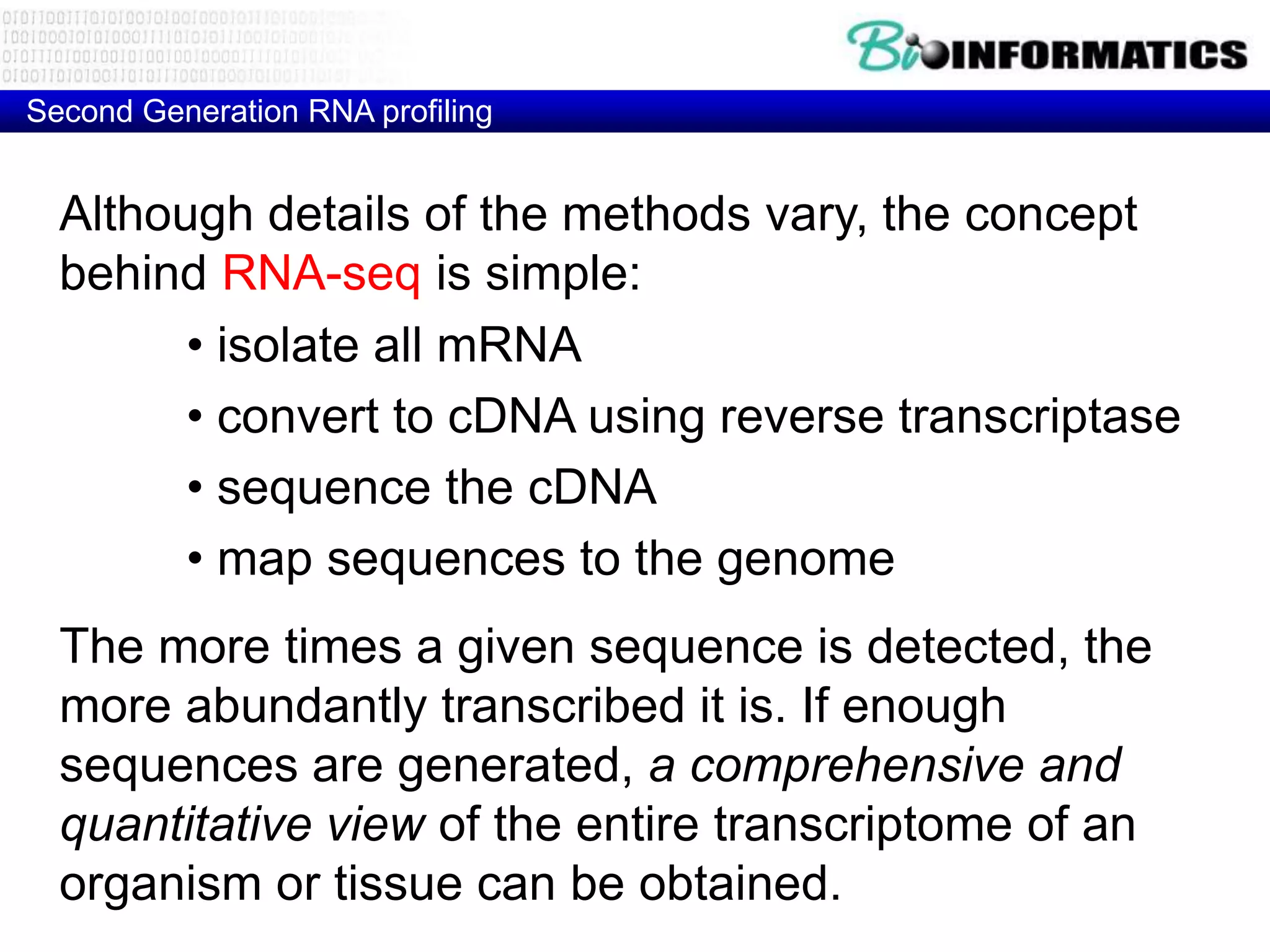
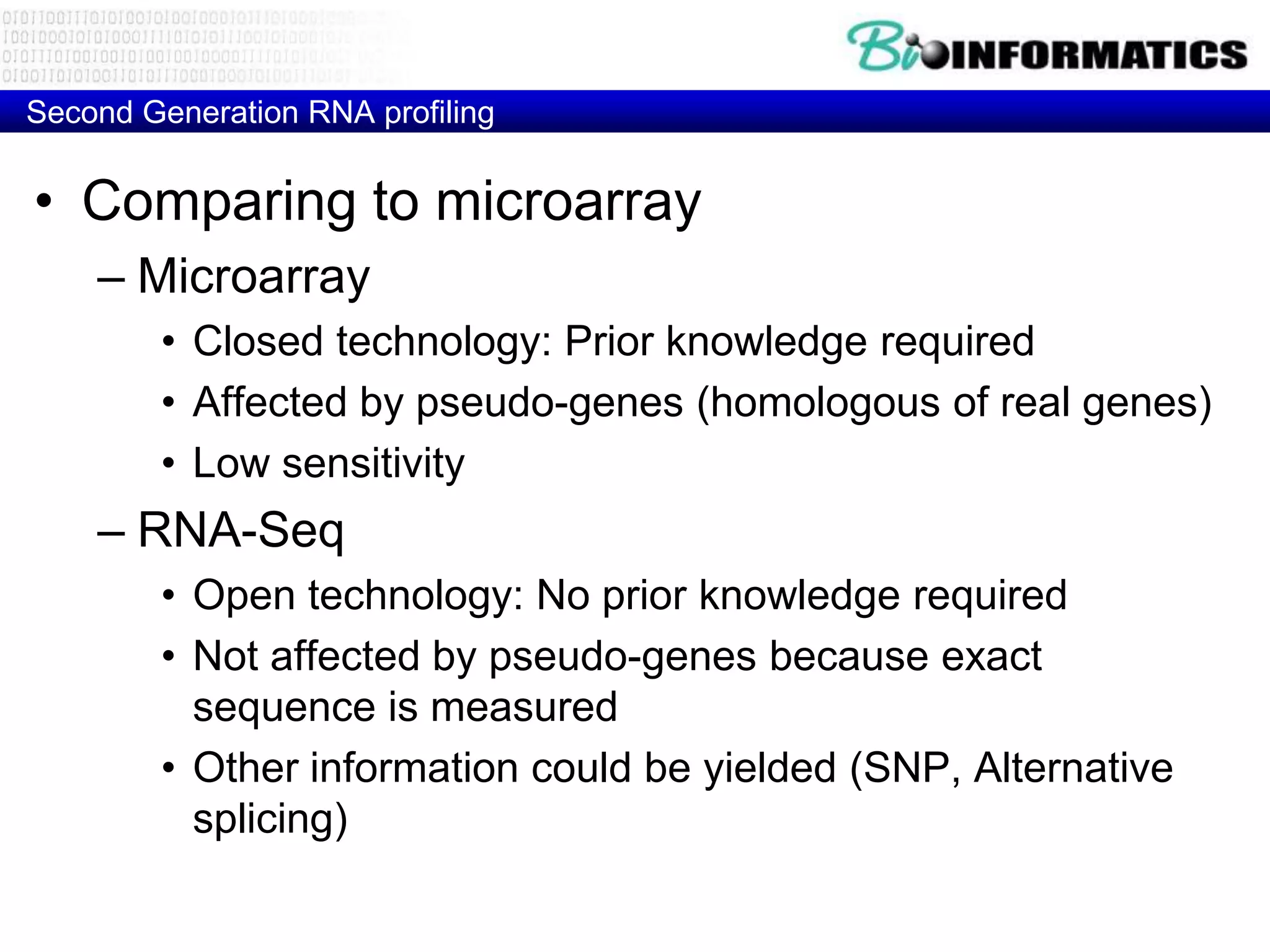
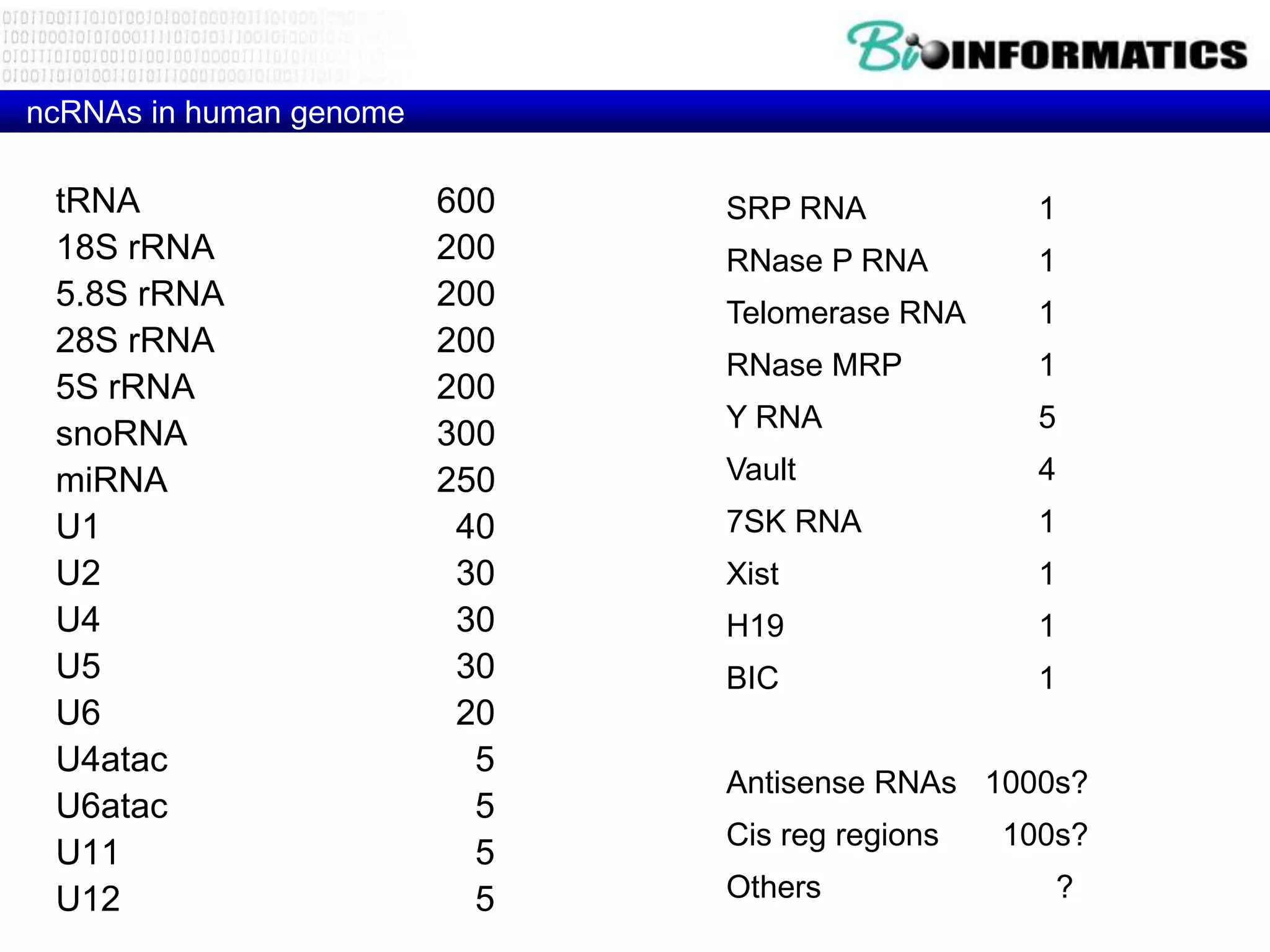
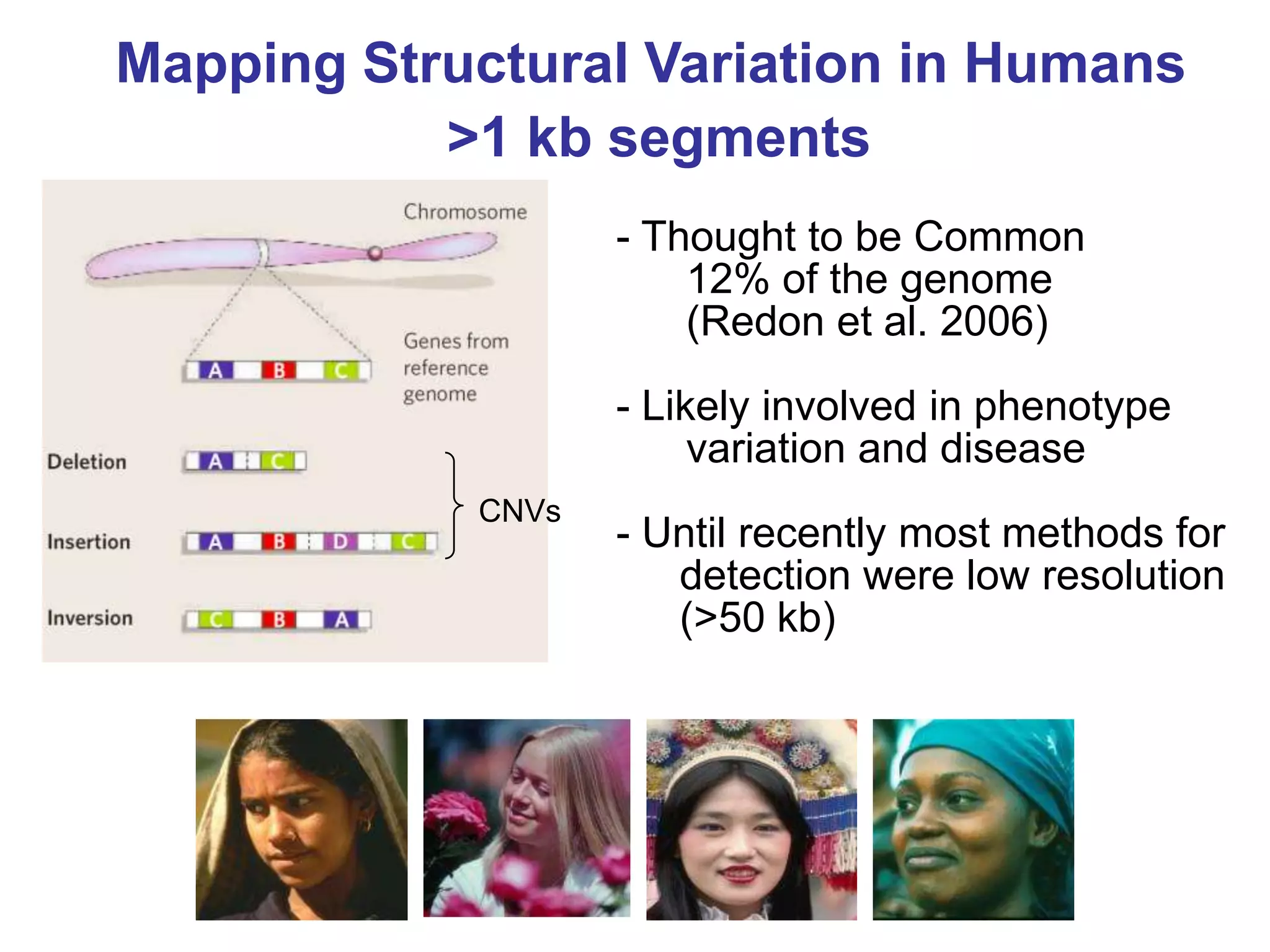
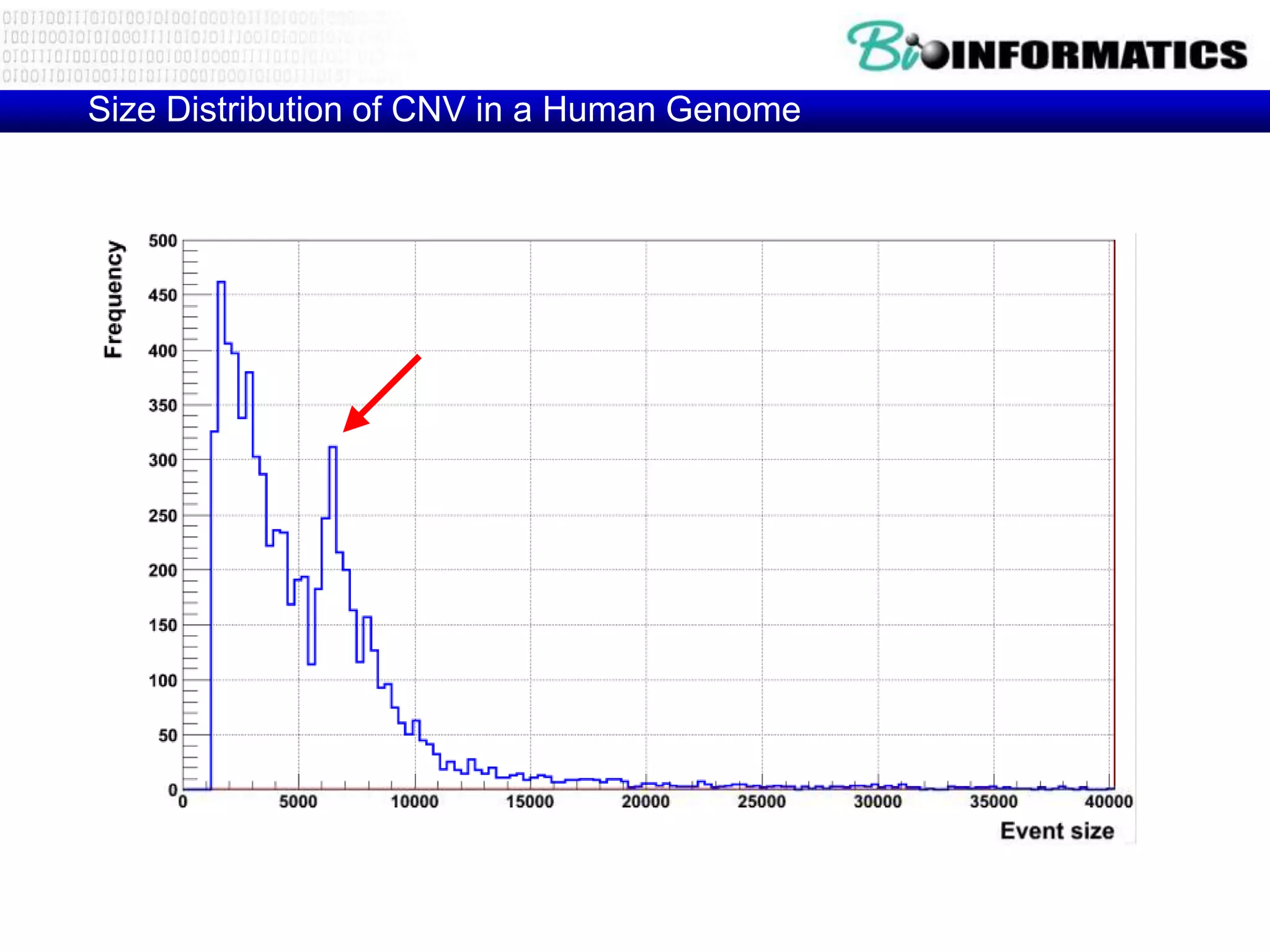
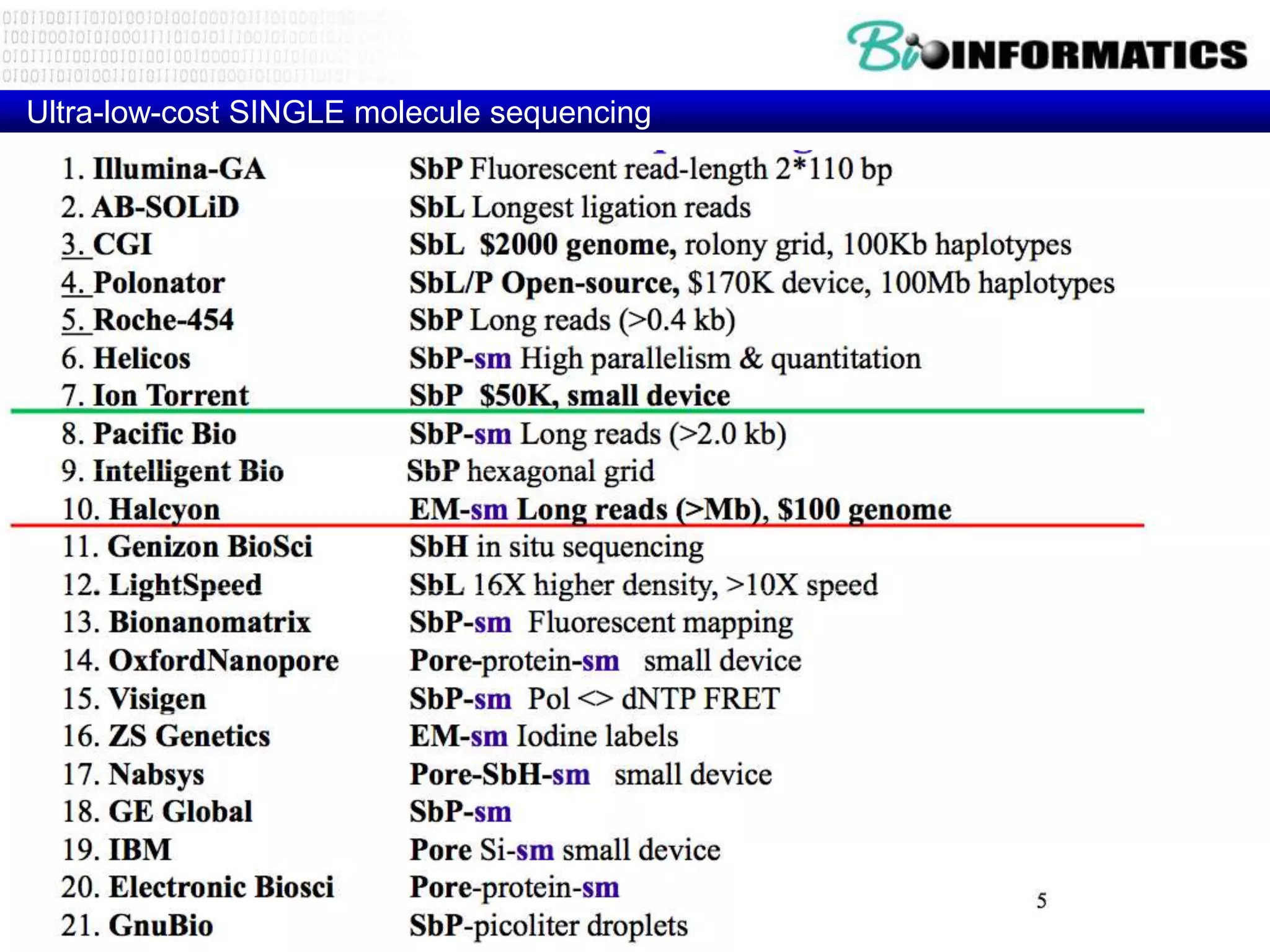
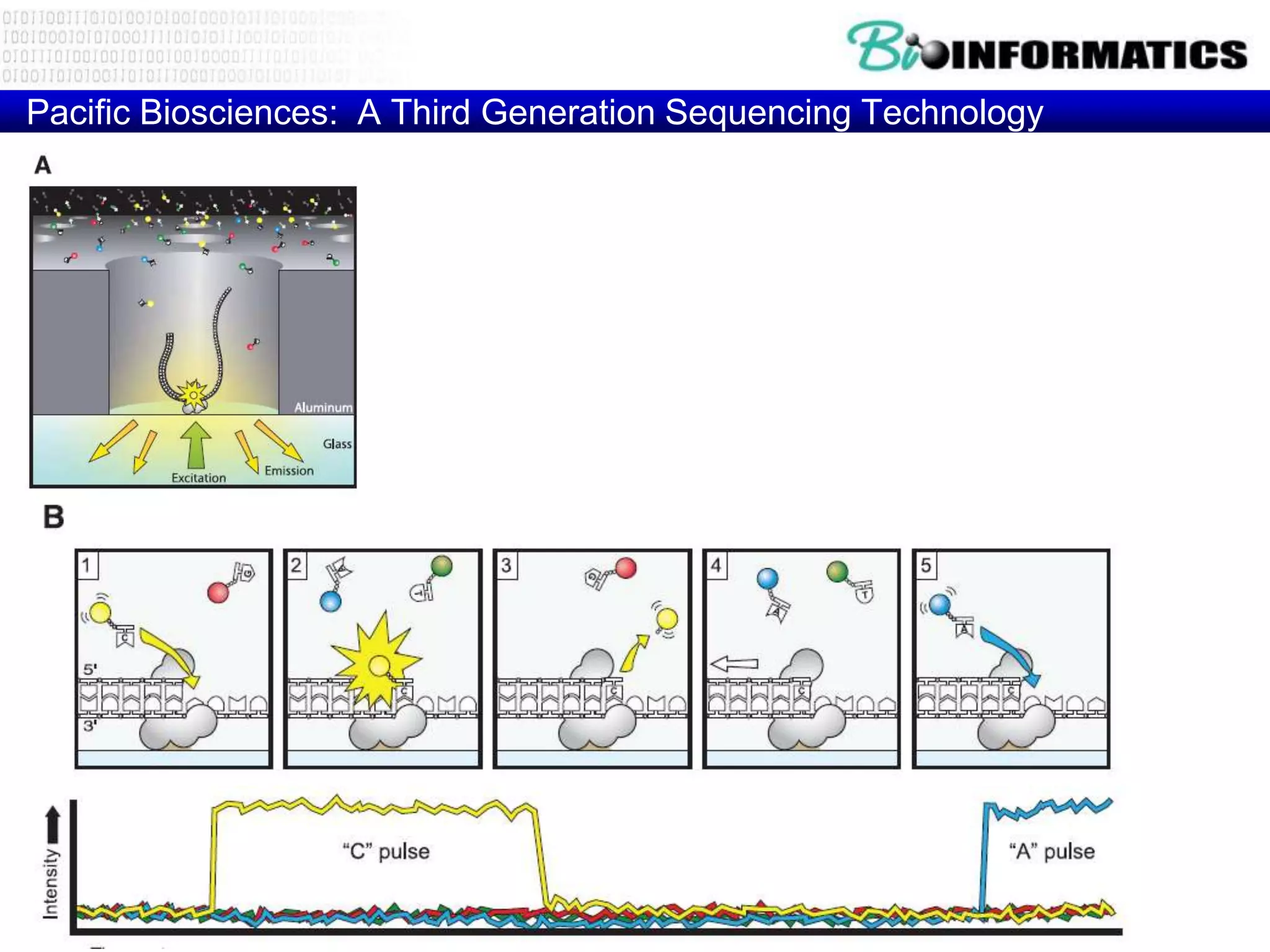
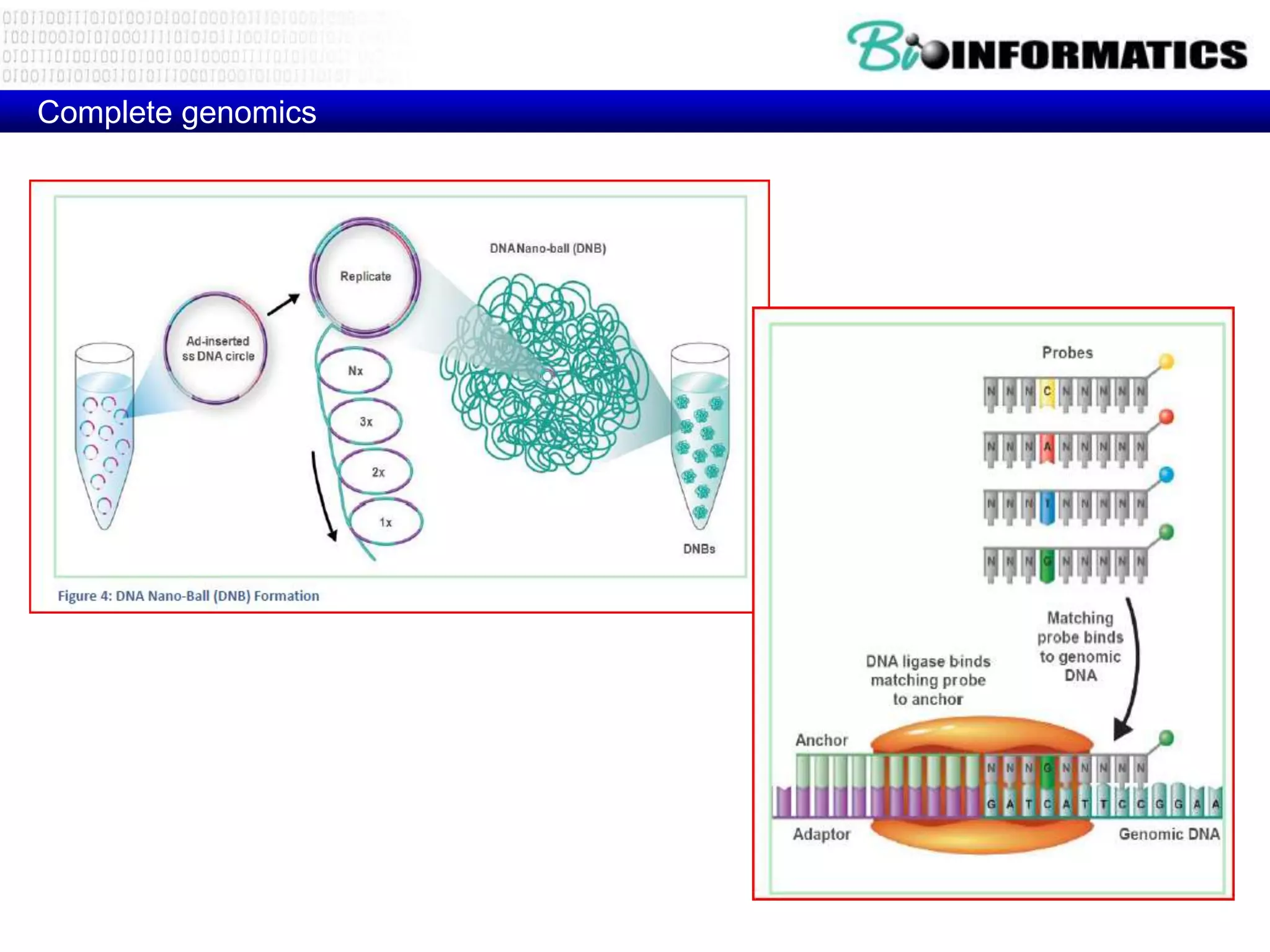
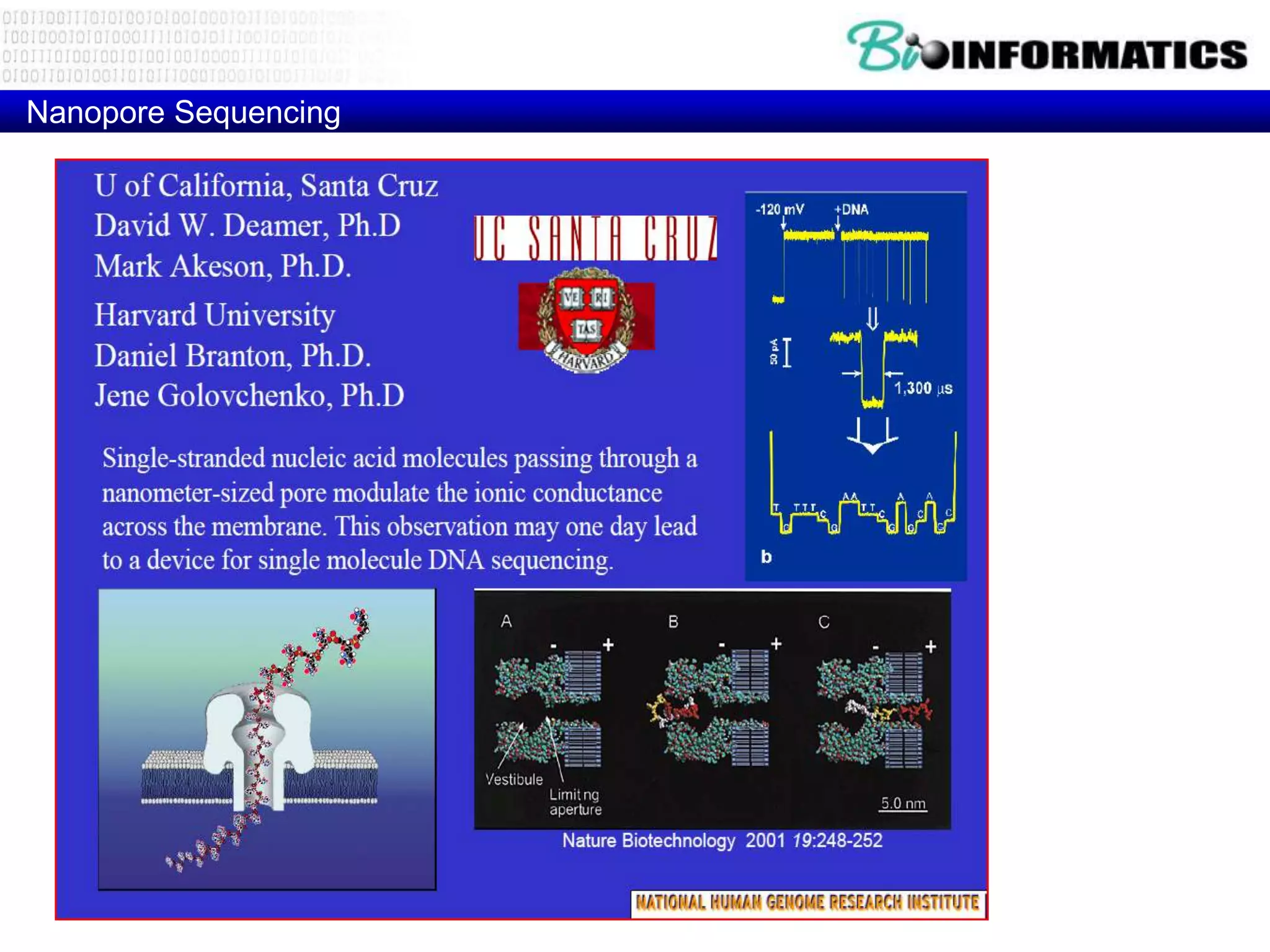
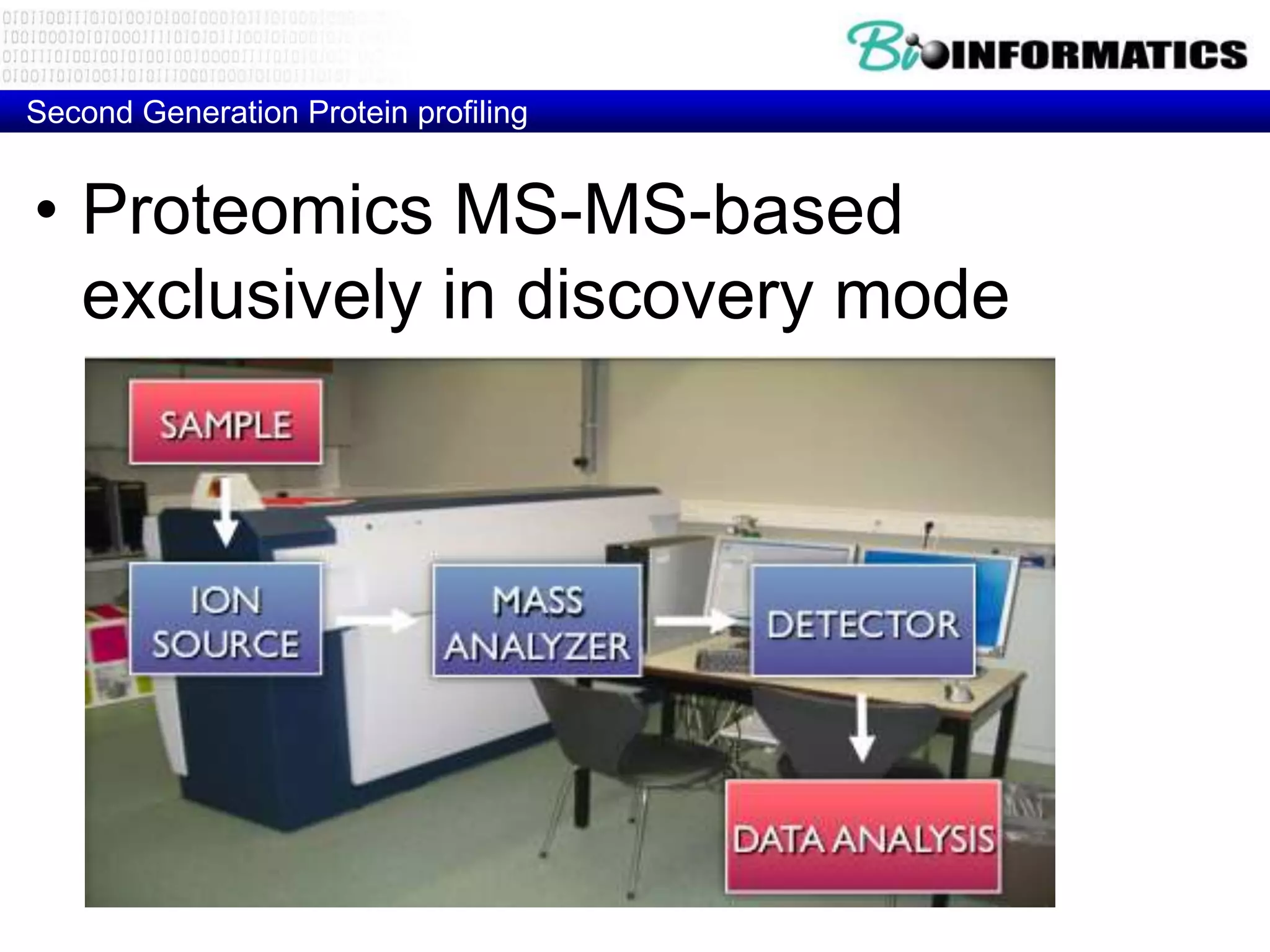
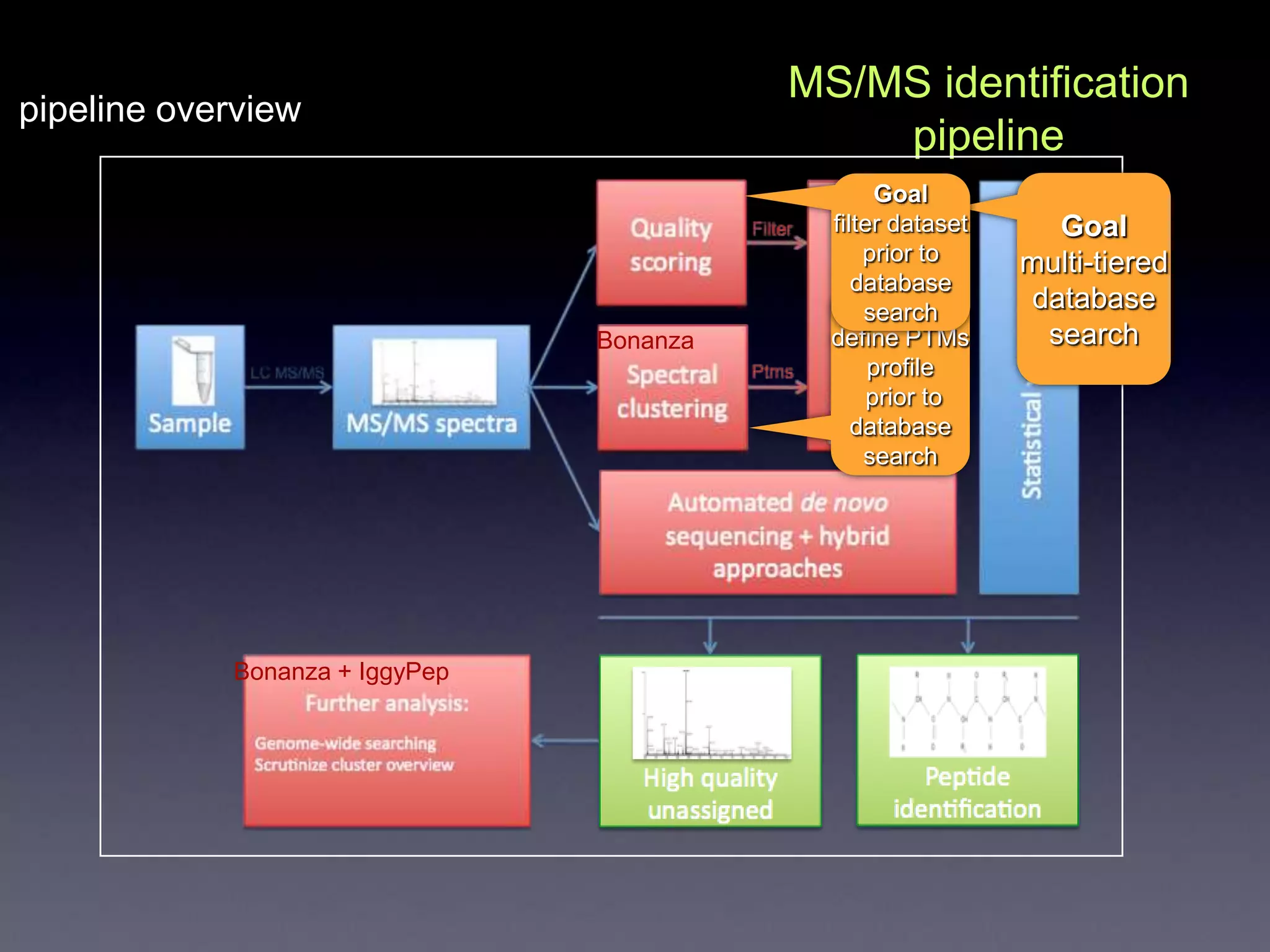
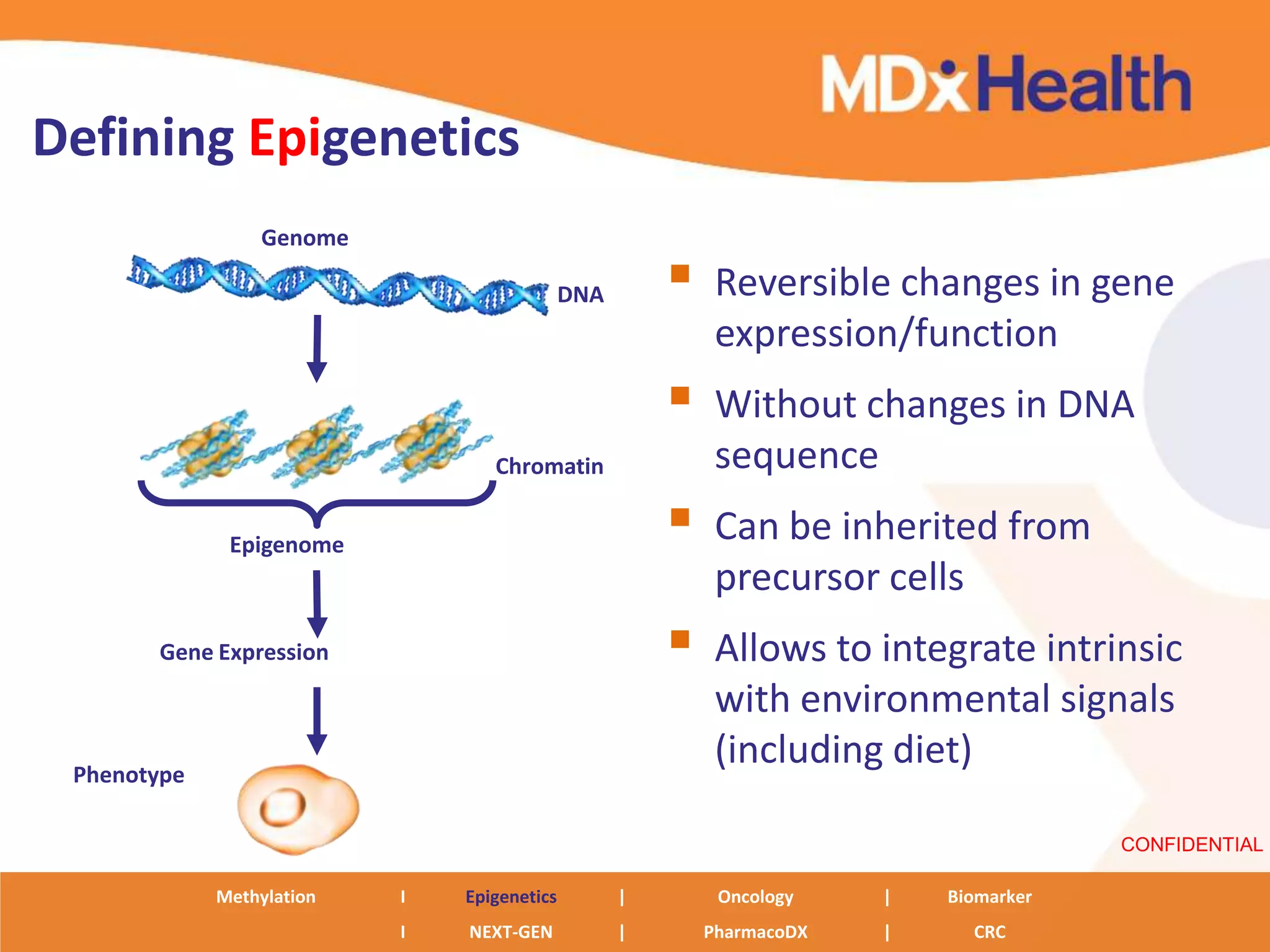
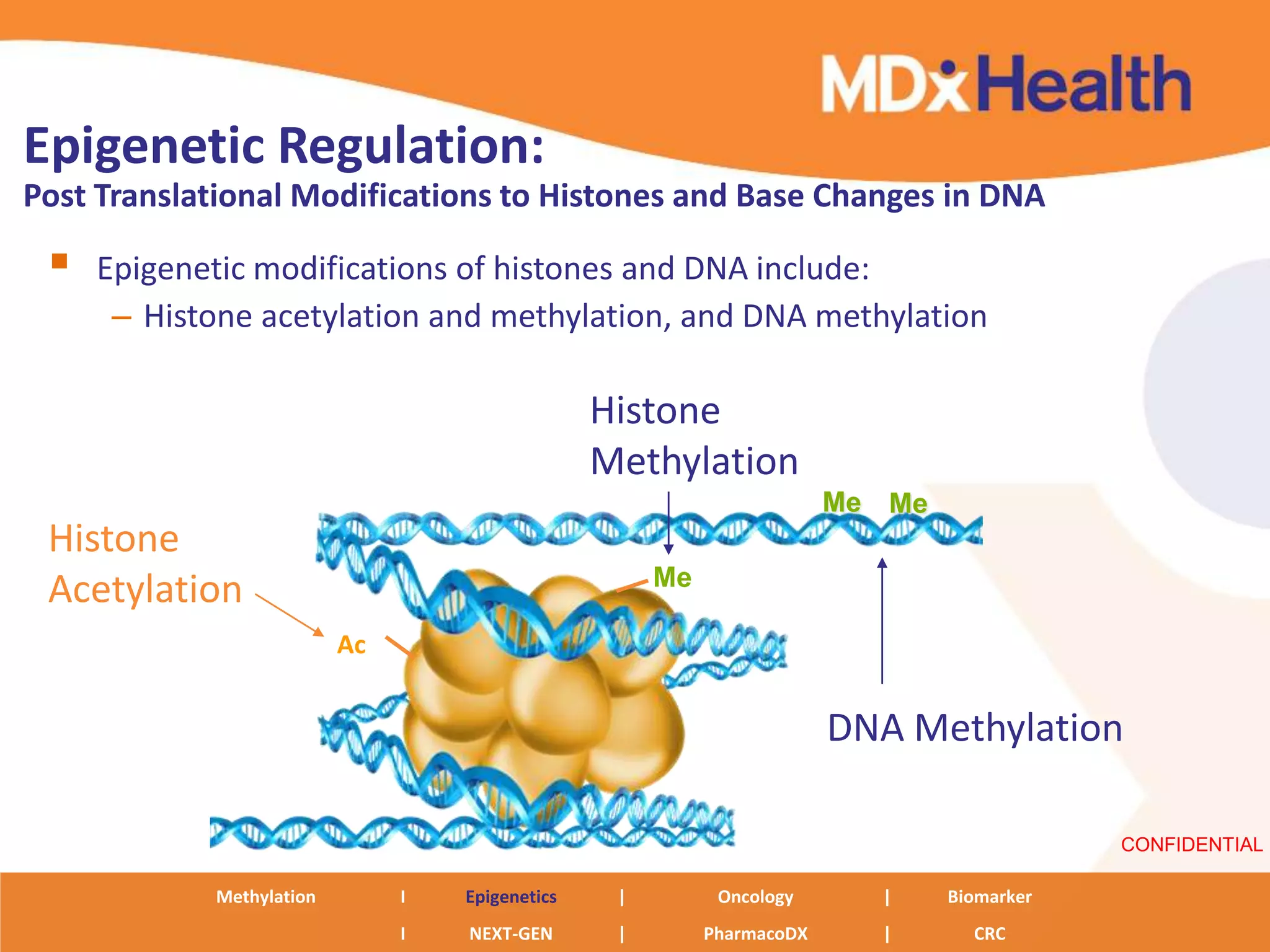
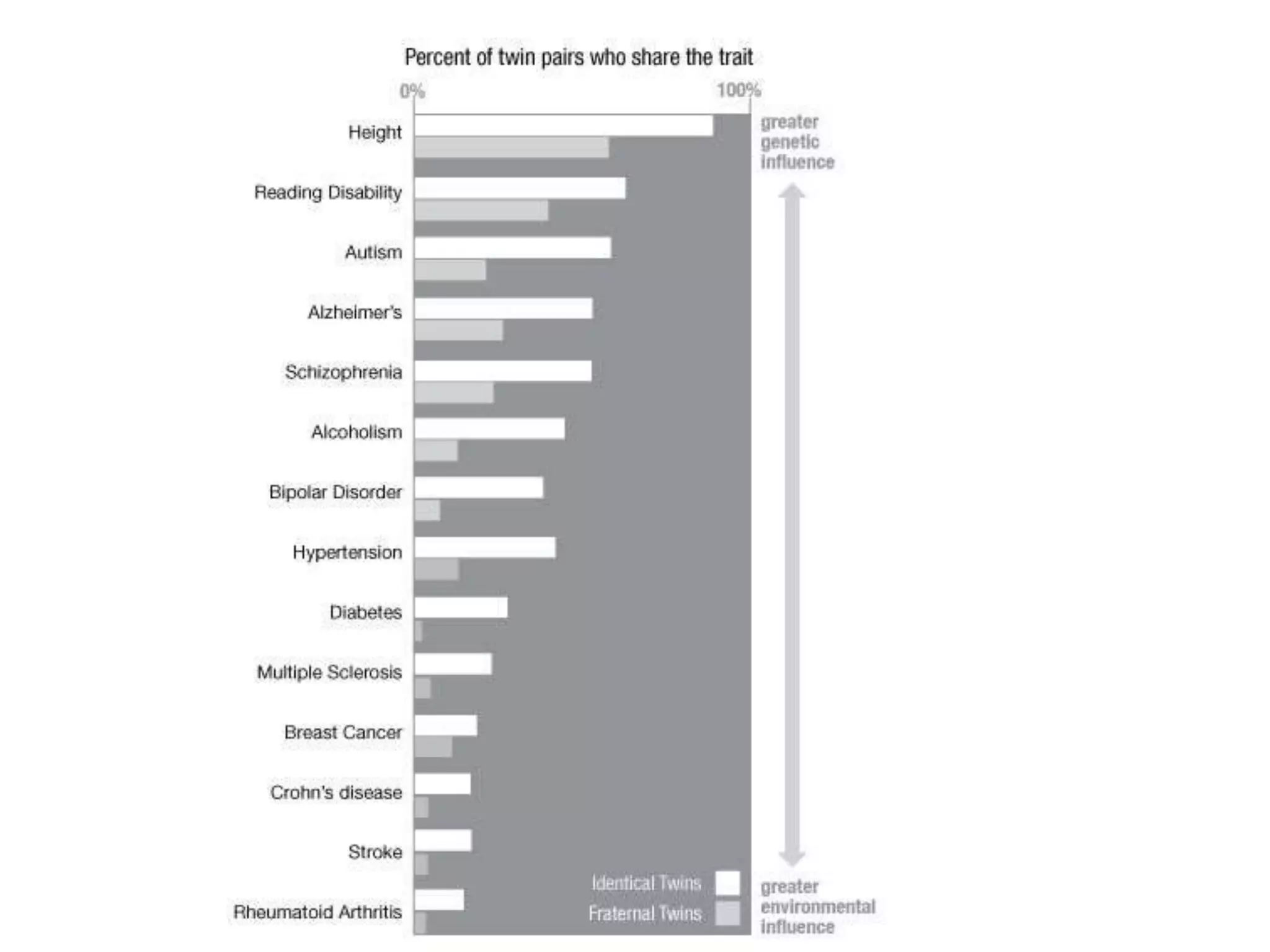
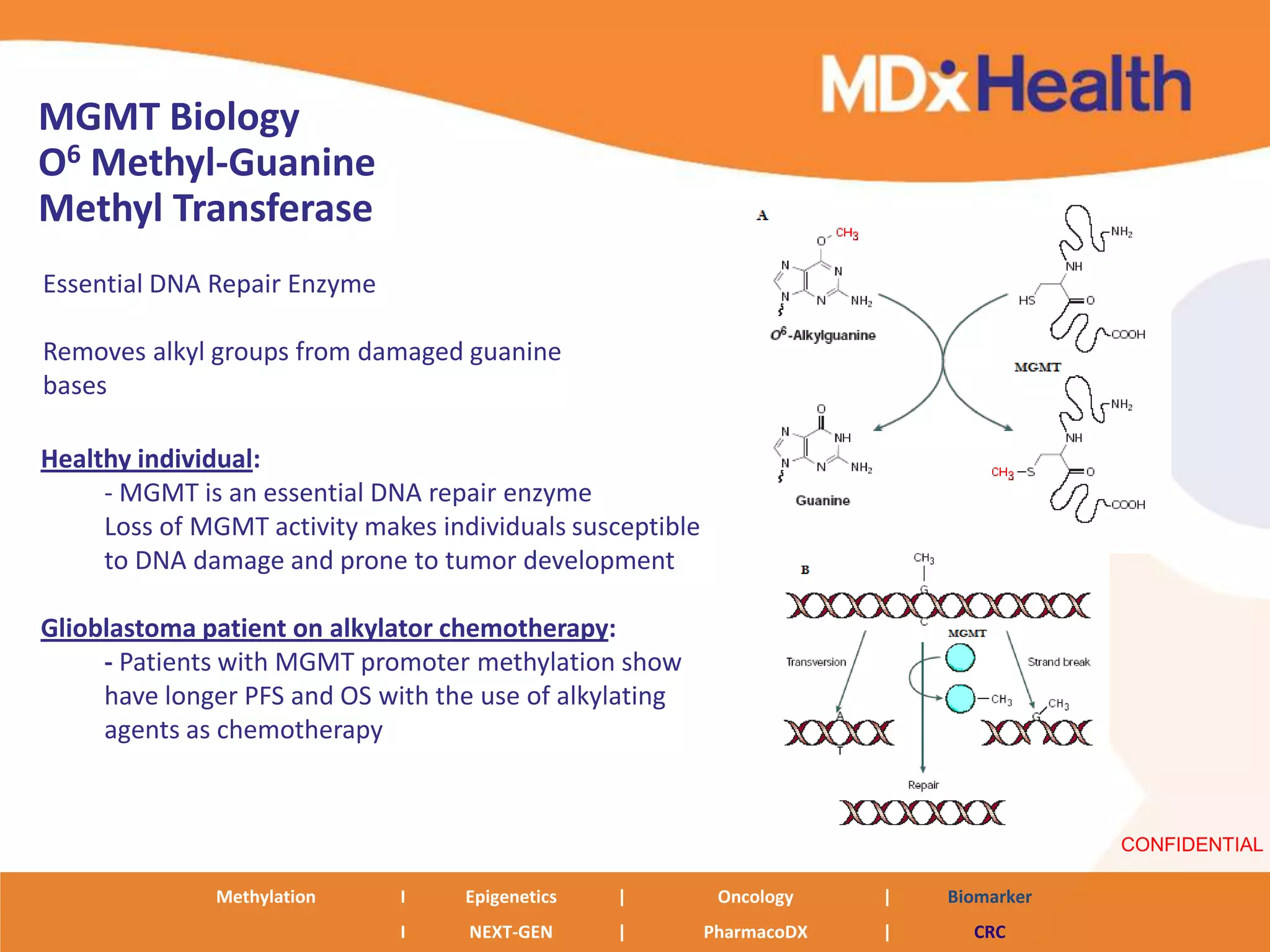
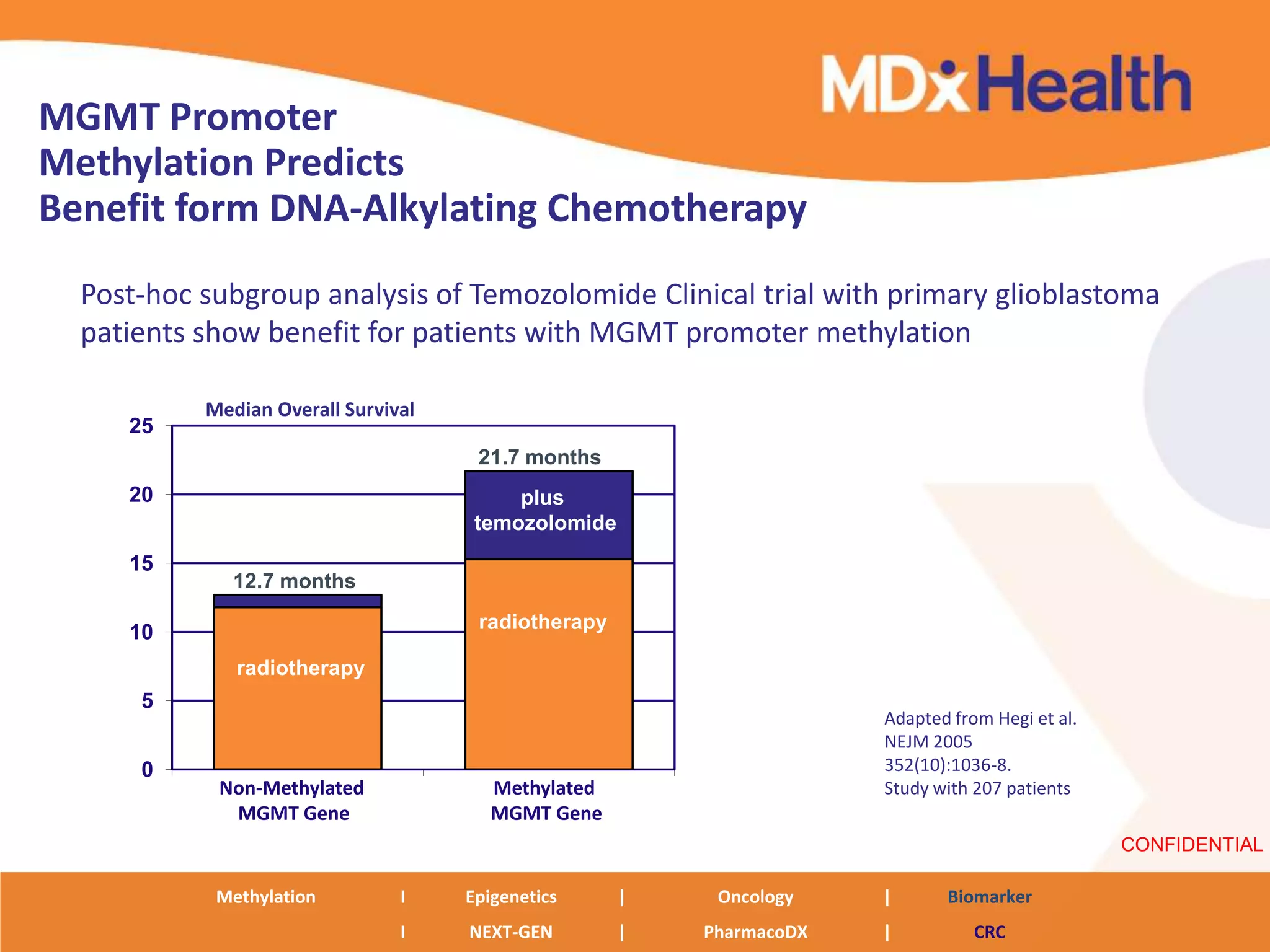
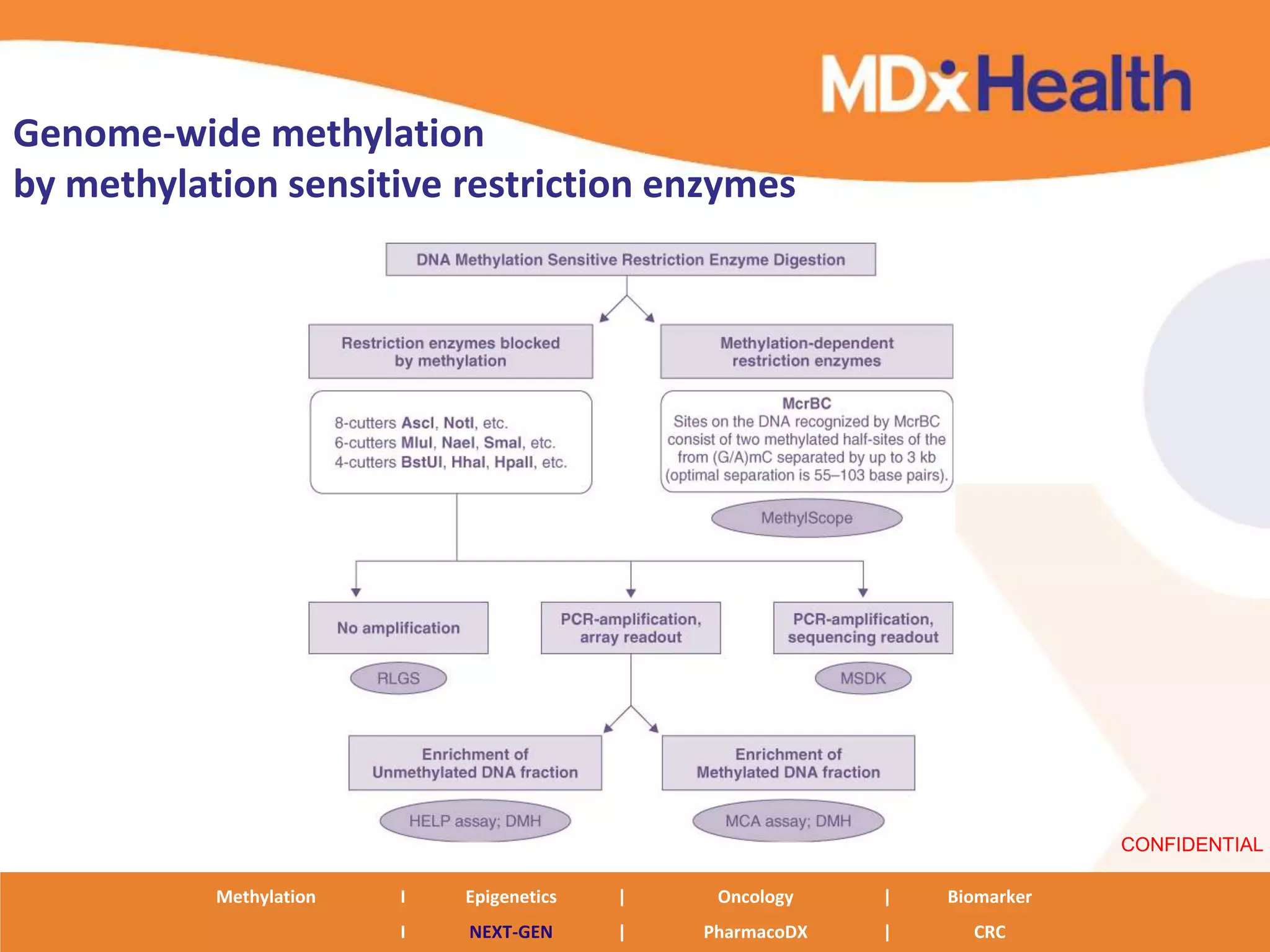
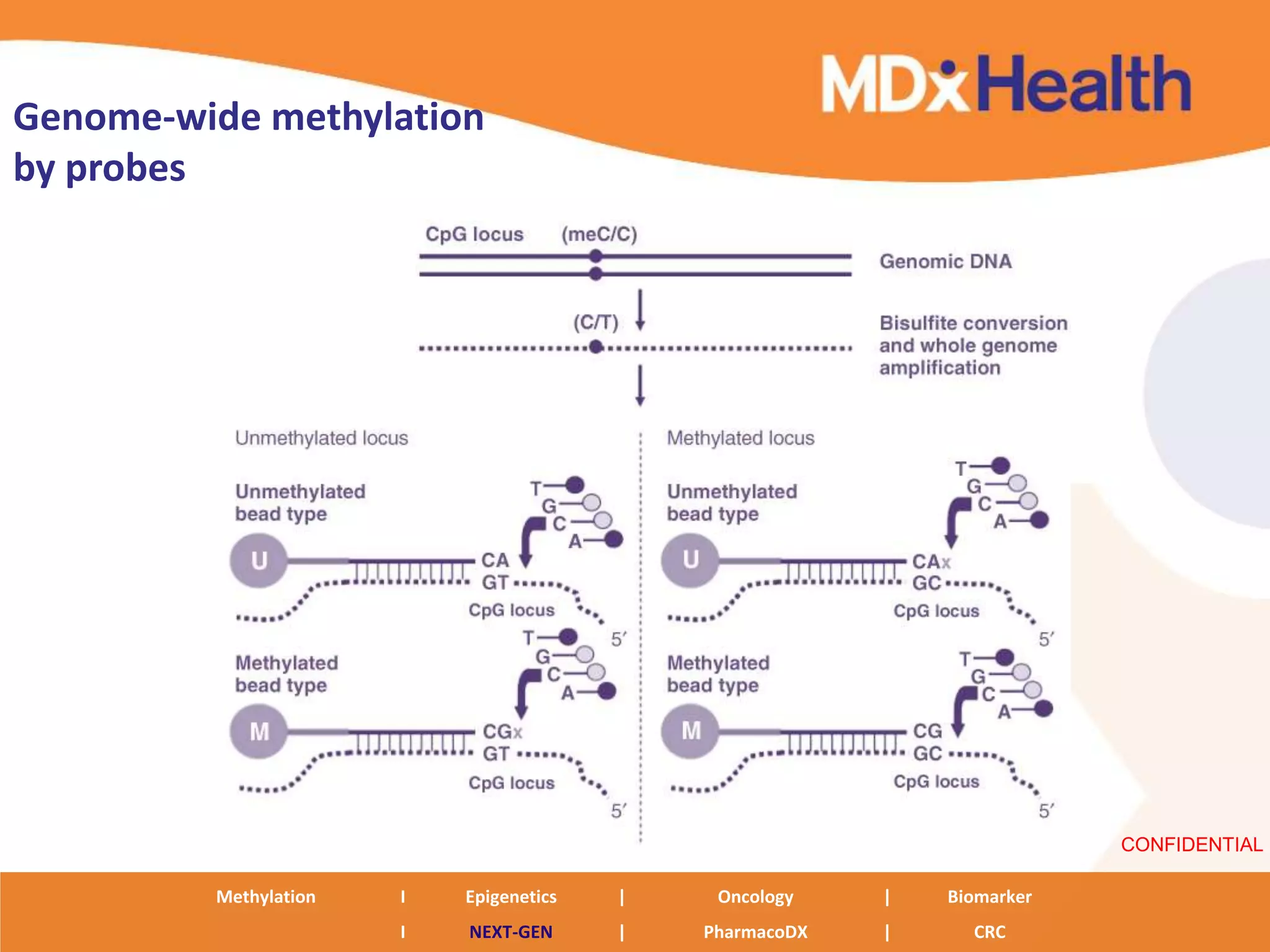
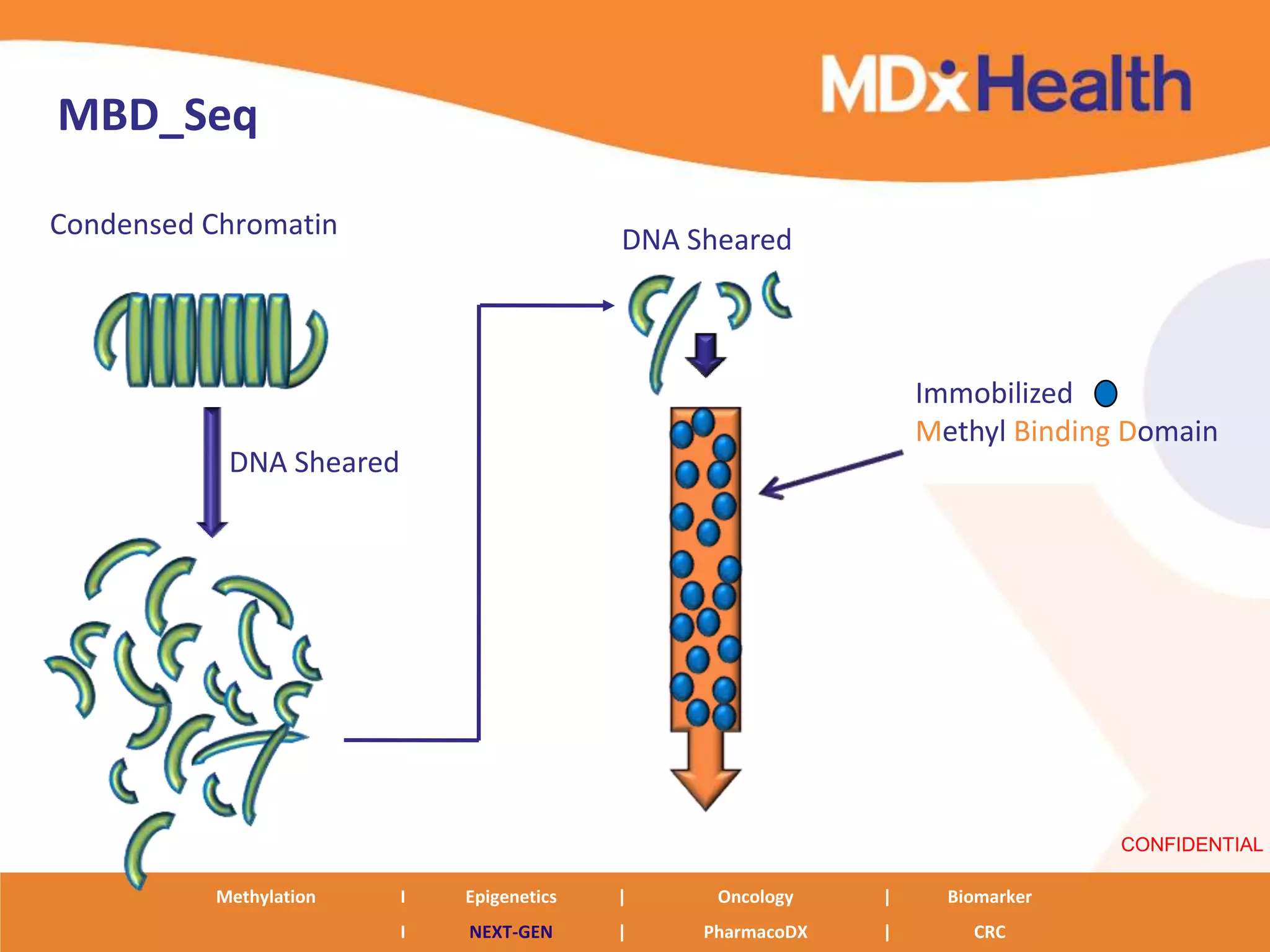
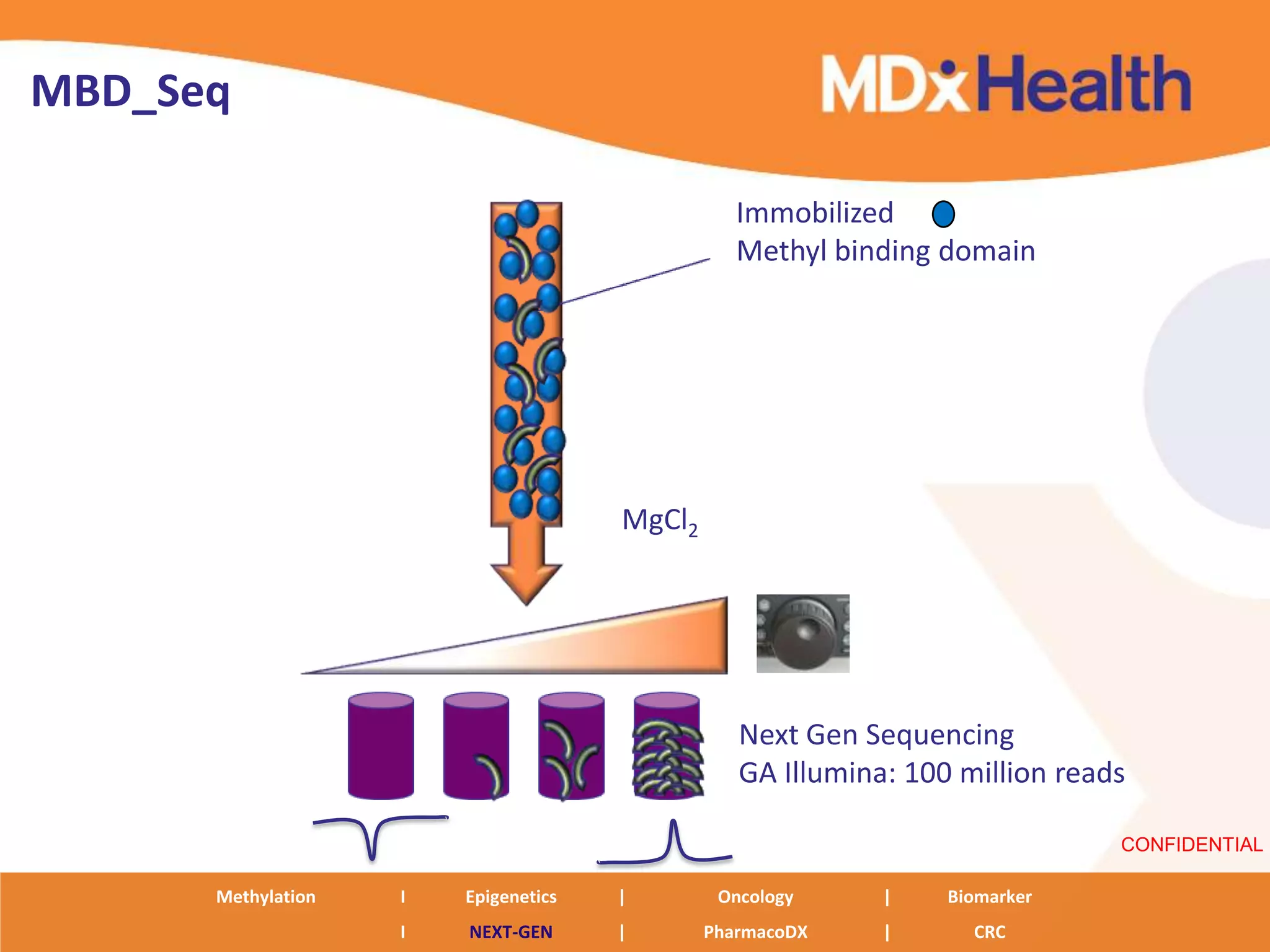
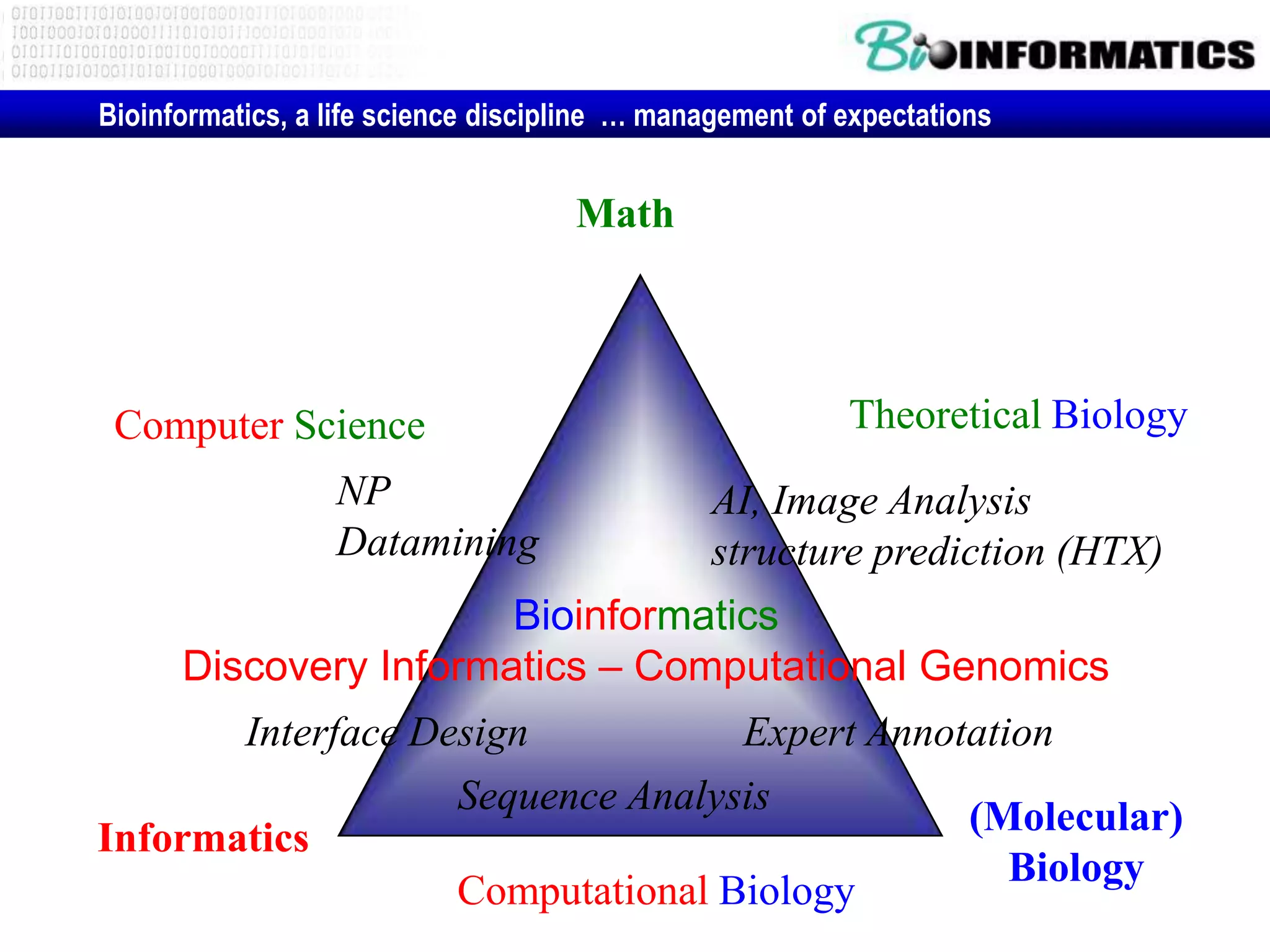
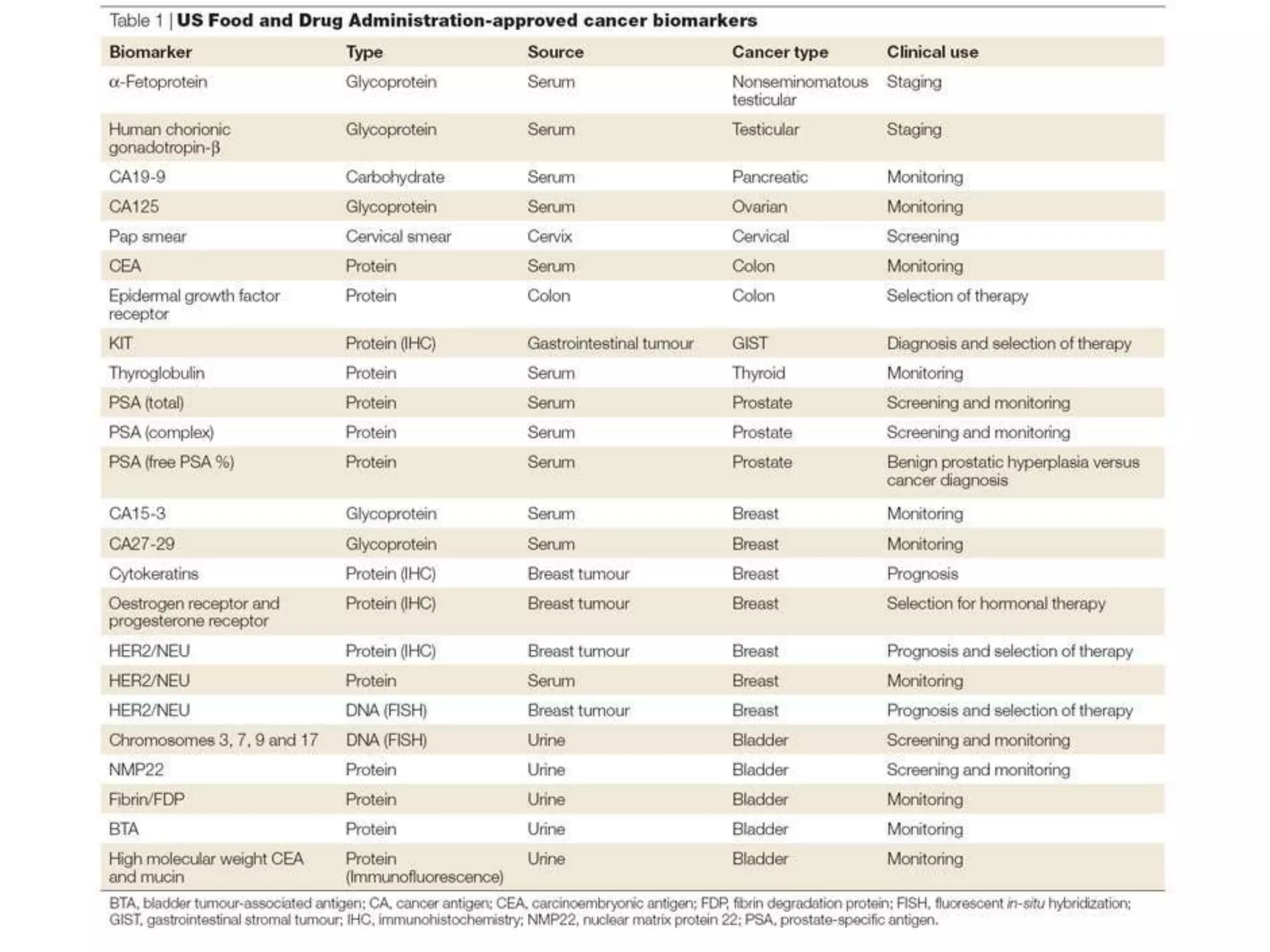
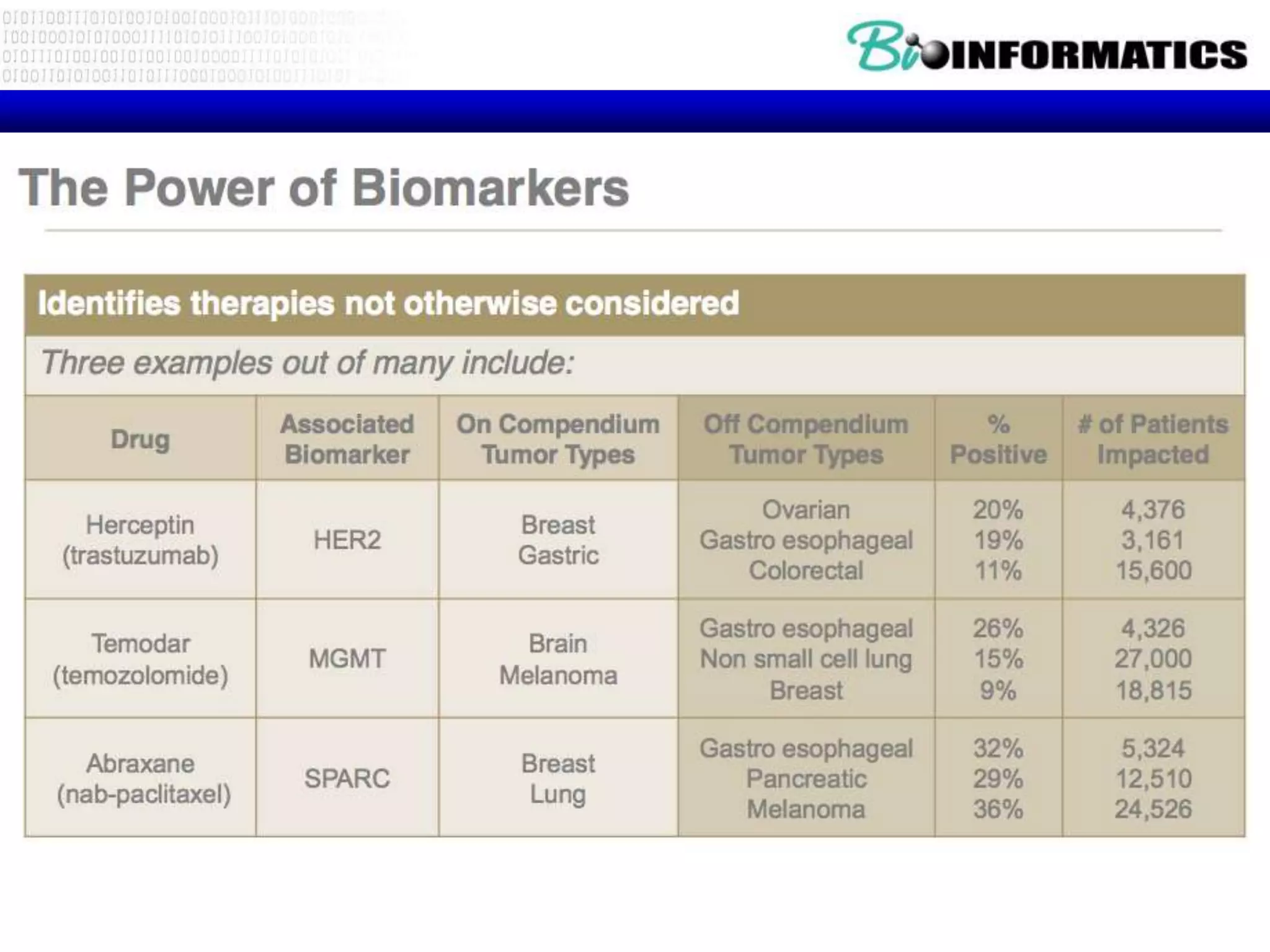
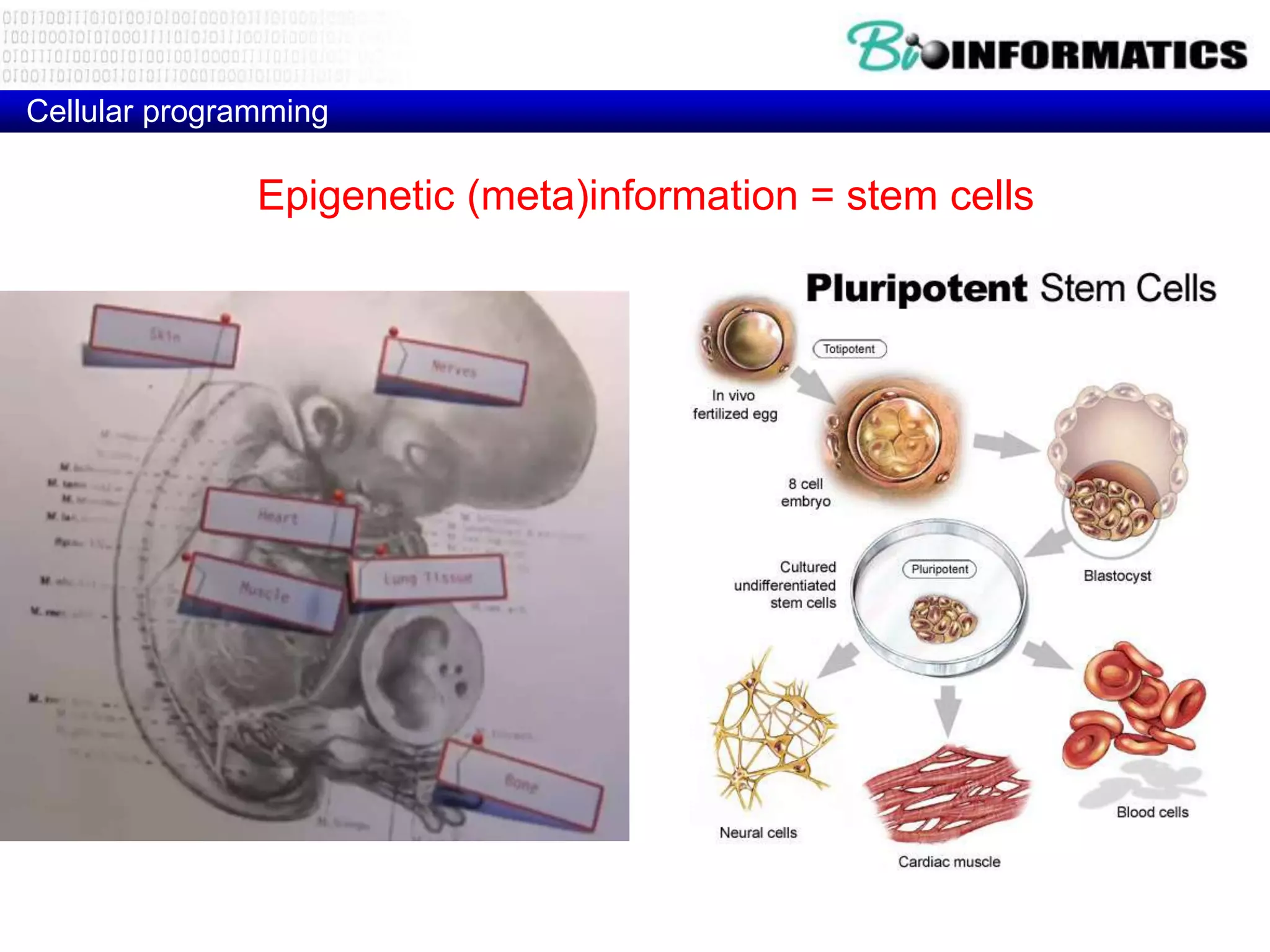
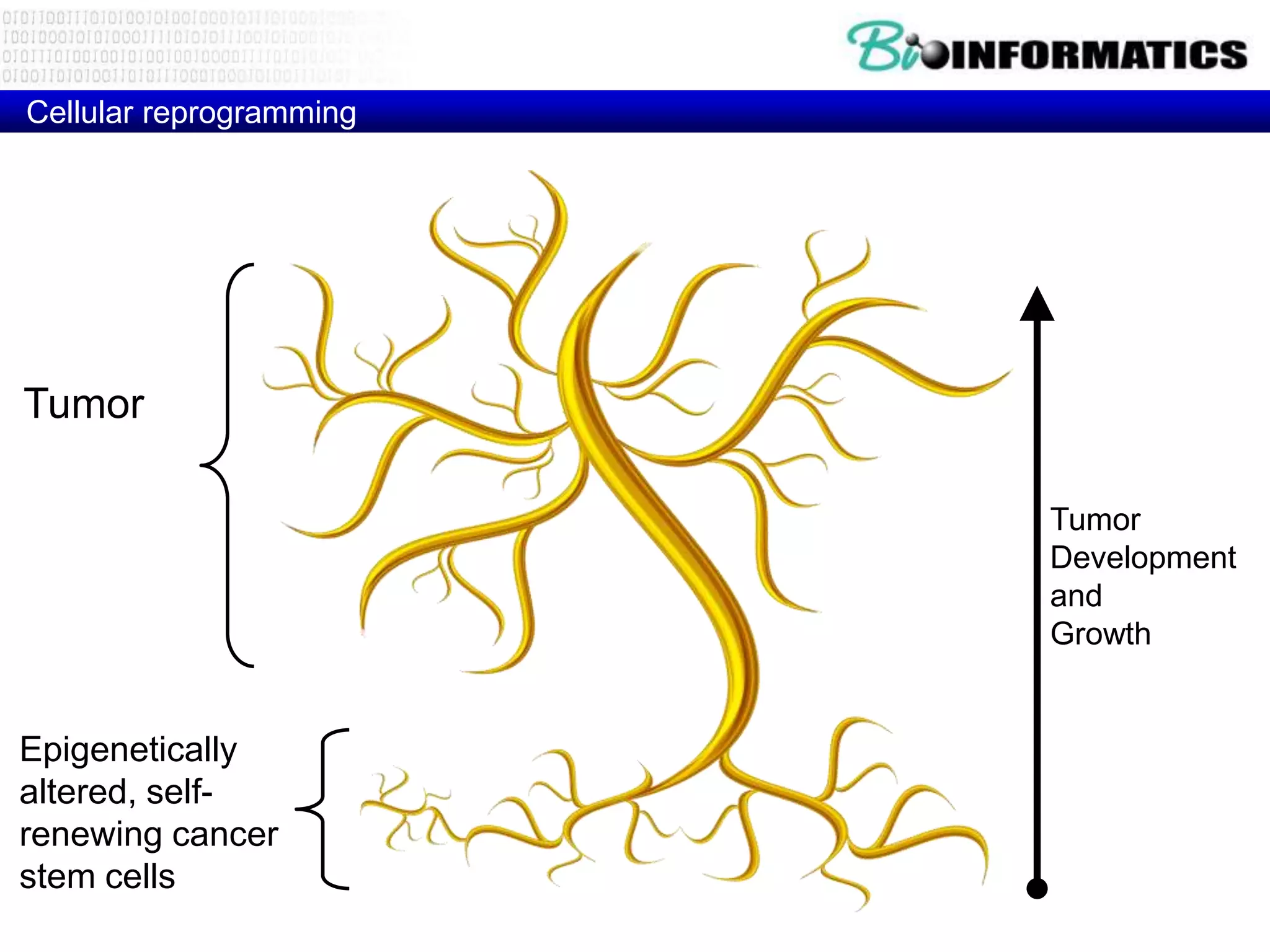
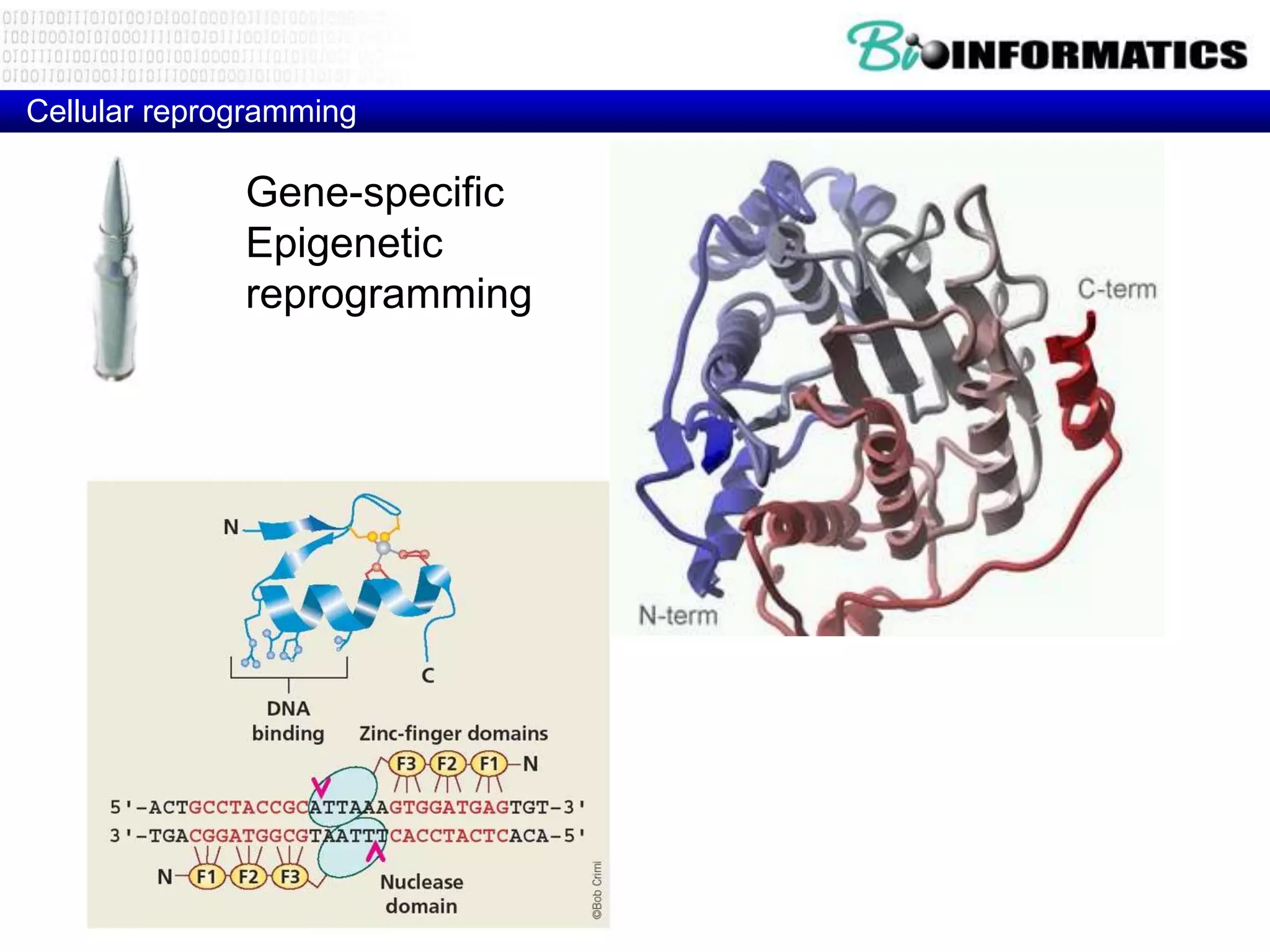
The document discusses next generation molecular profiling techniques. It begins with an overview of personalized medicine and biomarkers, then describes first generation molecular profiling methods like gene sequencing, microarrays, and fluorescence in situ hybridization. It then covers next generation sequencing technologies like Roche 454, Illumina, and ABI SOLID that allow high-throughput sequencing of DNA and RNA. Finally, it discusses next generation epigenetic profiling through techniques like methylation analysis and histone modification detection.