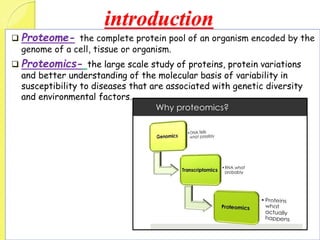
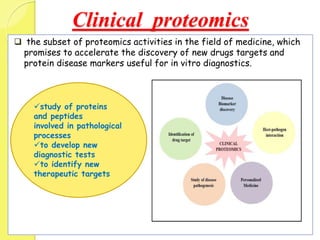
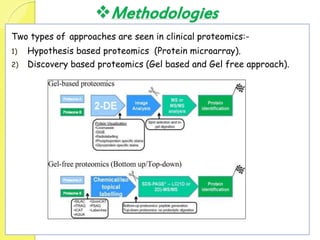
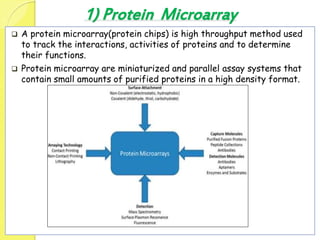
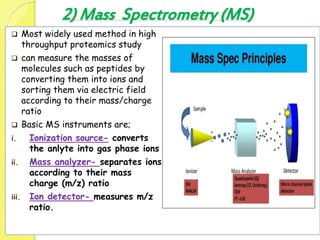
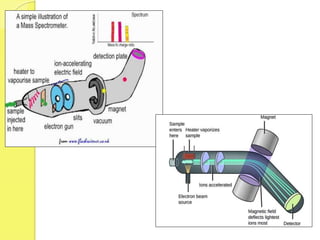
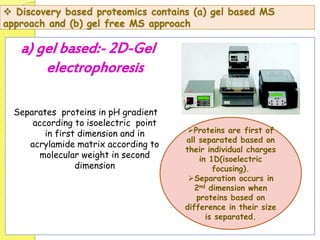
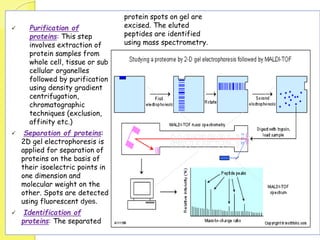
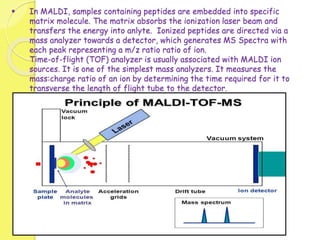
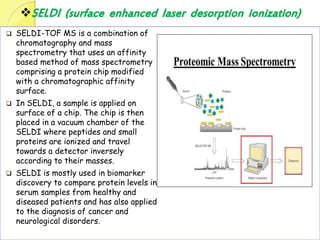
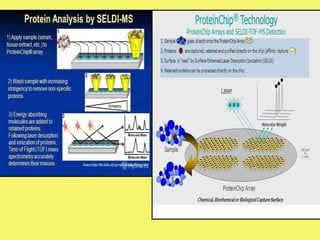
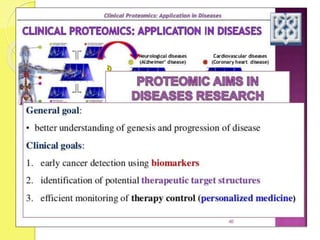
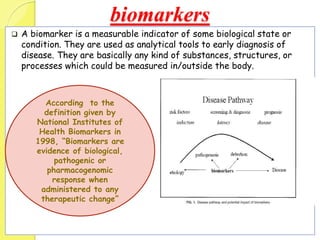
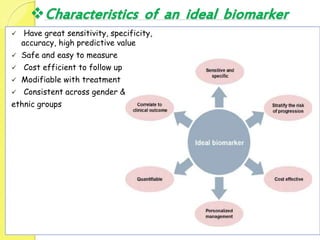
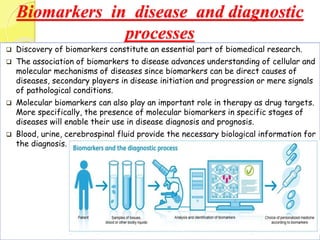
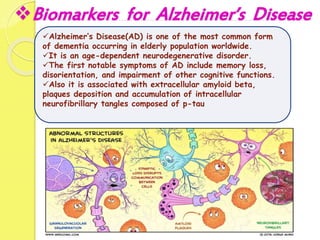
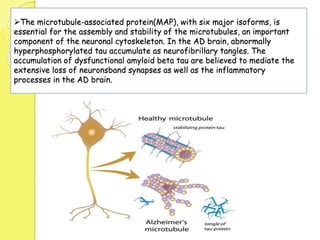
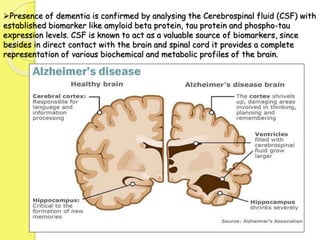
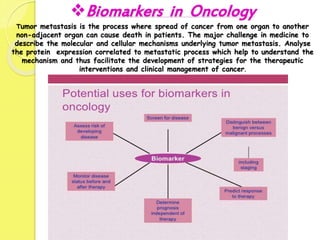
Clinical proteomics involves the large-scale study of proteins to better understand disease variability and identify new disease biomarkers and drug targets. There are two main approaches - hypothesis-based proteomics using protein microarrays, and discovery-based proteomics using gel-based or gel-free mass spectrometry techniques. Mass spectrometry allows identification of disease-associated changes in protein expression which can serve as biomarkers. Ideal biomarkers are sensitive, specific, accurate and cost-effective for diagnosing or monitoring diseases like Alzheimer's, cancer, and predicting disease progression or treatment response.