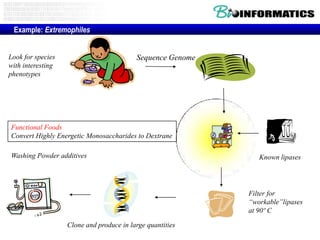
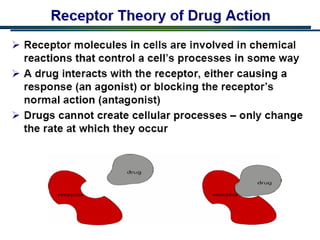
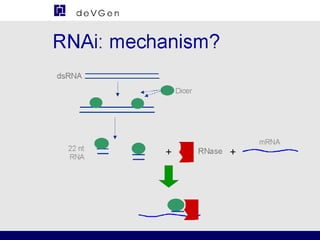
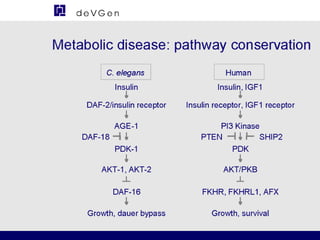
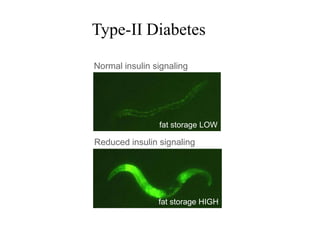
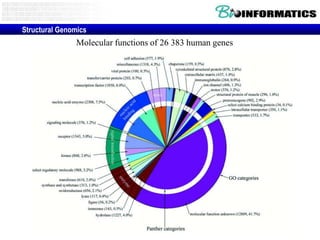
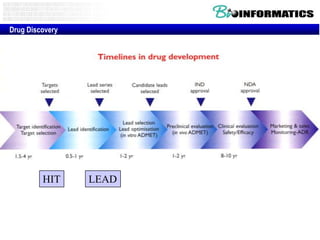
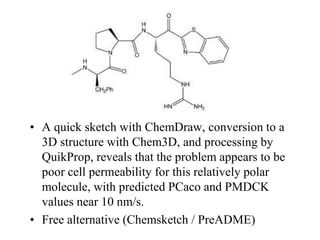
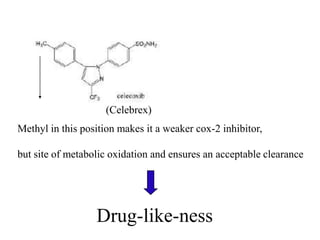
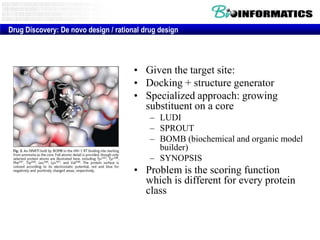
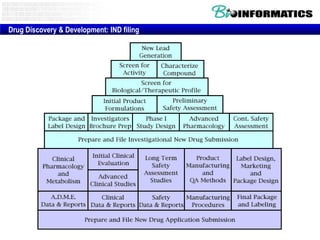
The document provides information about a bioinformatics lesson and exam. It states that there will be no lesson on December 4th. It then discusses the structure of the bioinformatics exam, which will randomly select images from a set of 713 images to display on a web page using JavaScript. The remainder of the document discusses various topics in comparative genomics, drug discovery, and other areas of bioinformatics.