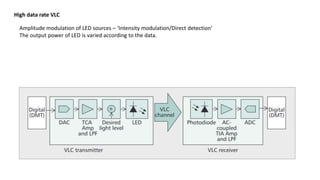
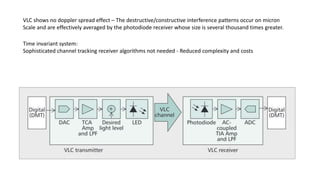
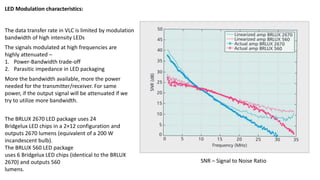
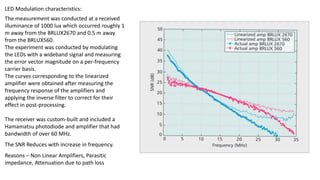
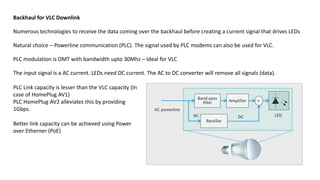
Visible Light Communication: Opportunities, Challenges and Path to Market discusses using visible light communication (VLC) to supplement radio frequency (RF) networks. VLC uses LED lights to transmit data and mobile phone cameras or specialized receivers to receive the data. The document outlines several potential uses of VLC including high-speed indoor connections, highly accurate indoor positioning, and low-speed applications using existing smartphone hardware. It also discusses challenges of VLC such as short range and non-outdoor use compared to RF networks, but argues that VLC can still provide benefits by complementing rather than replacing RF networks.