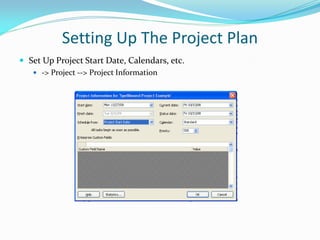
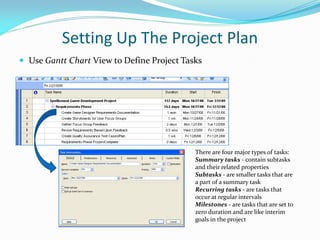
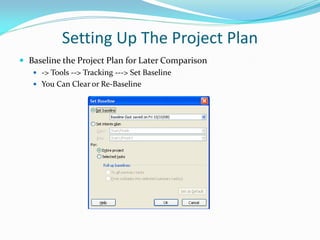
This presentation provides an overview of Microsoft Project for project planning and management. It discusses setting up a project plan by defining tasks, dates, dependencies and resources, baselining the plan, verifying the plan's viability by identifying overallocated resources, leveling if needed, executing and tracking the plan by updating progress, and comparing to the baseline to replan if required. The presentation concludes with a question and answer section and a request to submit feedback forms.