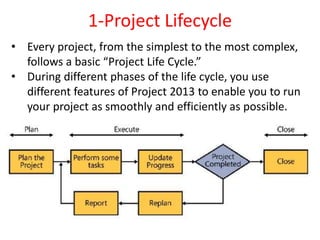
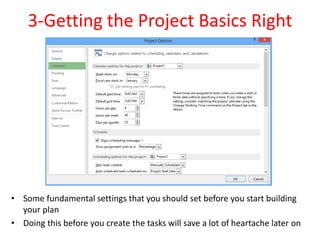
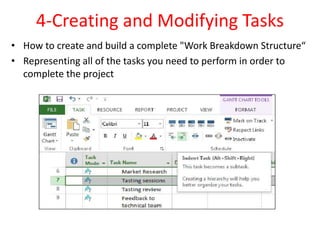
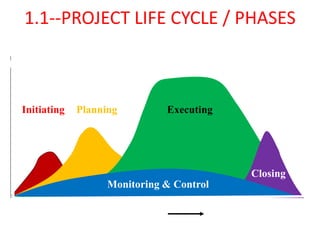
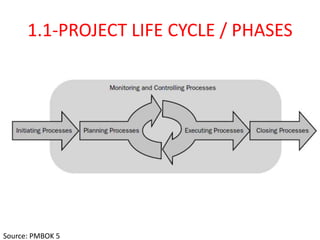
The document outlines the content covered in a Microsoft Project 2013 course. It discusses 12 main topics: 1) the project lifecycle and phases, 2) getting started with Project 2013, 3) setting up the project basics, 4) creating and modifying tasks, 5) setting estimates, 6) linking tasks, 7) assigning and managing resources, 8) adding external dependencies and deadlines, 9) communicating the plan, 10) updating and re-planning, 11) closing the project, and 12) Project Server 2013 features. Each section provides an overview of the key elements and configuration covered.