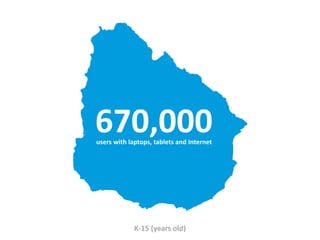
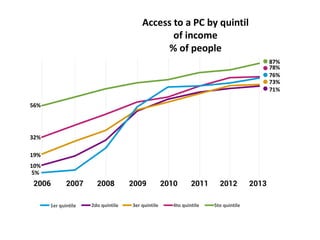
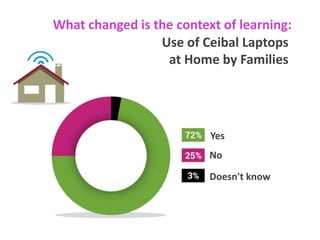
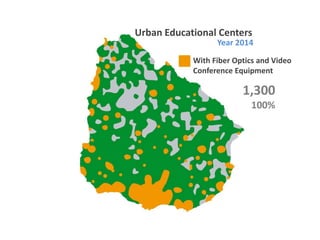
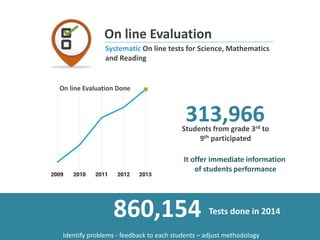
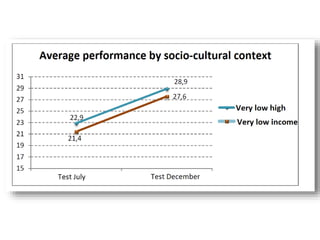
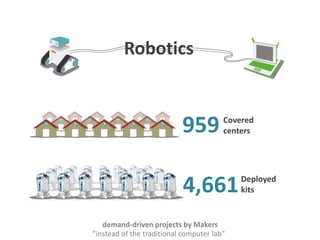
The document discusses the Plan Ceibal initiative in Uruguay, which aims to enhance educational equity and learning through technology, providing laptops and internet access to students. It highlights the positive impact on student engagement, teacher satisfaction, and the development of new pedagogical approaches, despite challenges such as the need for teacher training and effective assessment methods. The initiative emphasizes the importance of expanding educational environments and fostering creativity and self-directed learning in students.