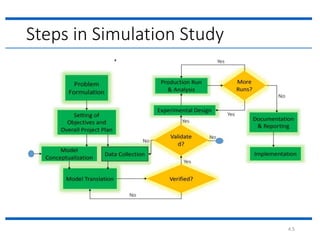
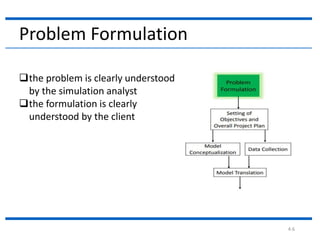
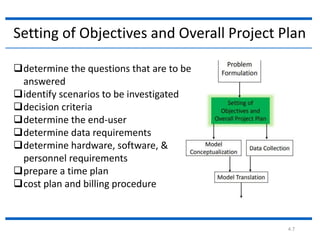
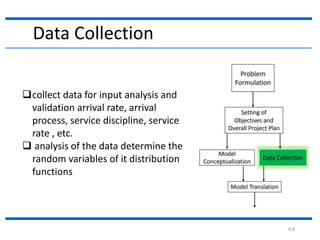
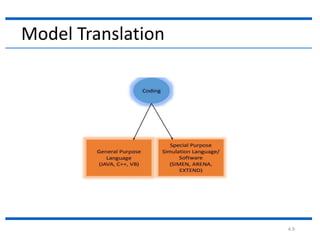
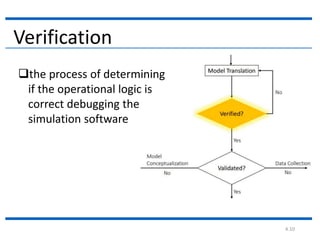
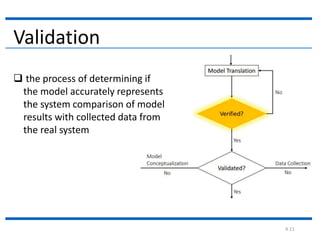
The document outlines the key steps in a simulation study:
1. Problem formulation to clearly define the problem and ensure the client understands it.
2. Setting objectives and an overall project plan to determine what questions will be answered and identify scenarios, requirements, and timelines.
3. Model conceptualization to develop the conceptual framework for the simulation model.
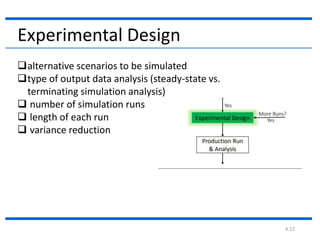
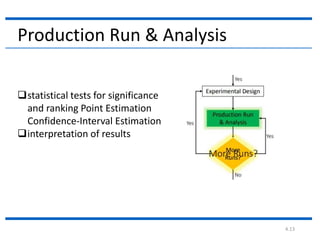
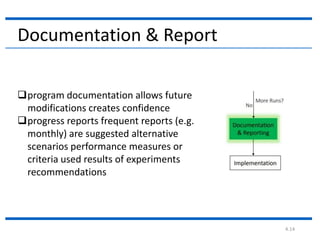
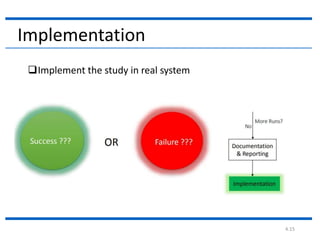
4. The document then continues to describe several additional steps in the simulation study process including data collection, model translation, verification, validation, experimental design, production runs and analysis, documentation, and potential implementation.