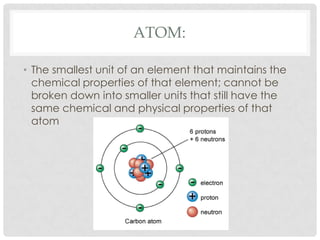
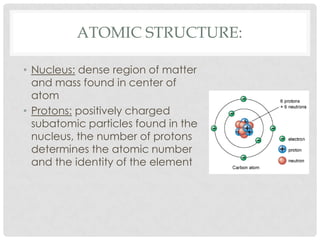
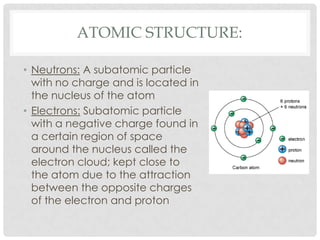
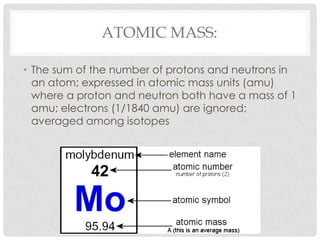
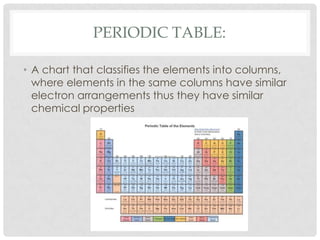
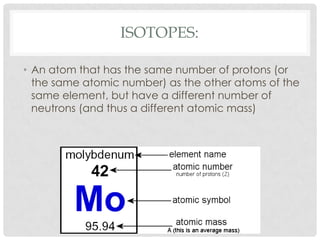
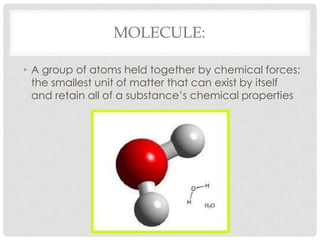
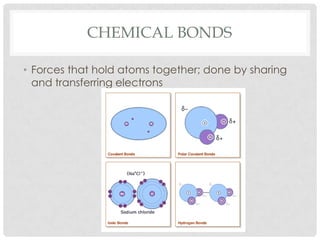
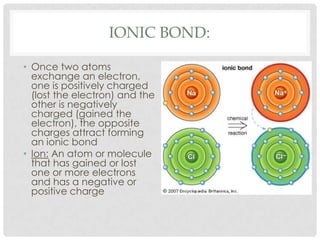
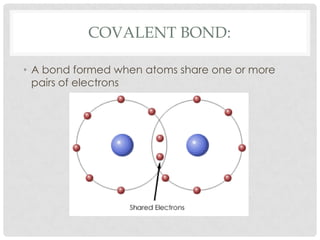
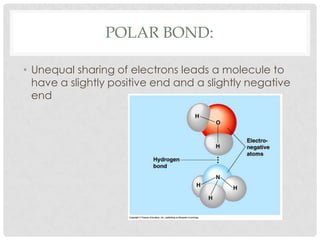
This document defines key terms related to matter and chemistry. It discusses the basic properties of matter, the structure of atoms including protons, neutrons and electrons, the difference between elements and compounds, and different types of chemical bonds including ionic bonds formed by electron transfer and covalent bonds formed by electron sharing. It provides the essential scientific definitions and descriptions of fundamental chemistry concepts.