Embed presentation
Download to read offline



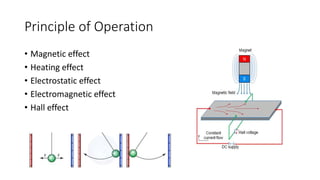



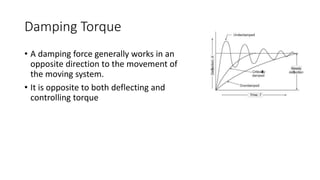


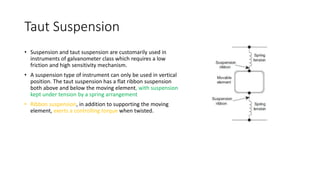
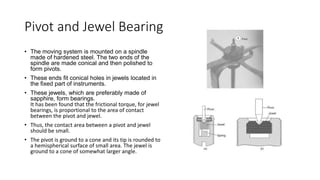

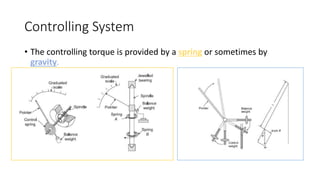

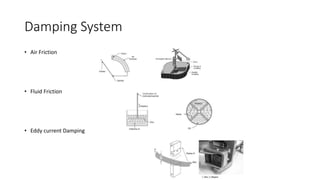
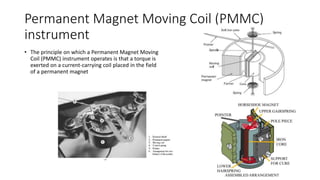
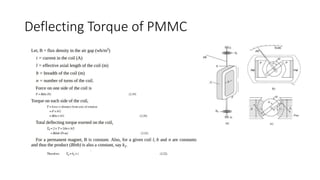
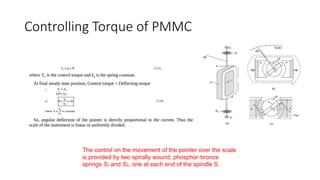







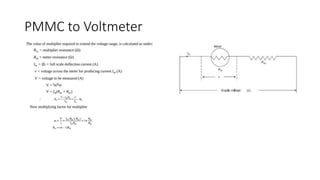



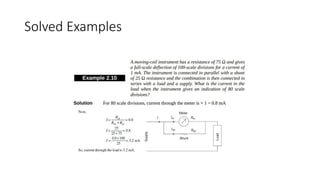

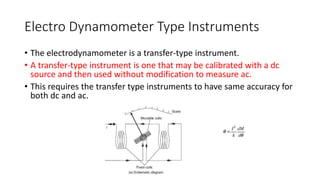


This document discusses the design and operation of analog electromechanical instruments such as galvanometers, ammeters, voltmeters, and ohmmeters. It describes the principles of electromagnetic, electrostatic, and electro-thermal effects that are used in various analog instruments. It also discusses the operating torques including deflecting, controlling and damping torques. Additionally, it covers topics such as suspension systems, pivot and jewel bearings, controlling systems, damping systems, and the operation of permanent magnet moving coil instruments and extending their measurement ranges to functions as ammeters, voltmeters and ohmmeters.

































