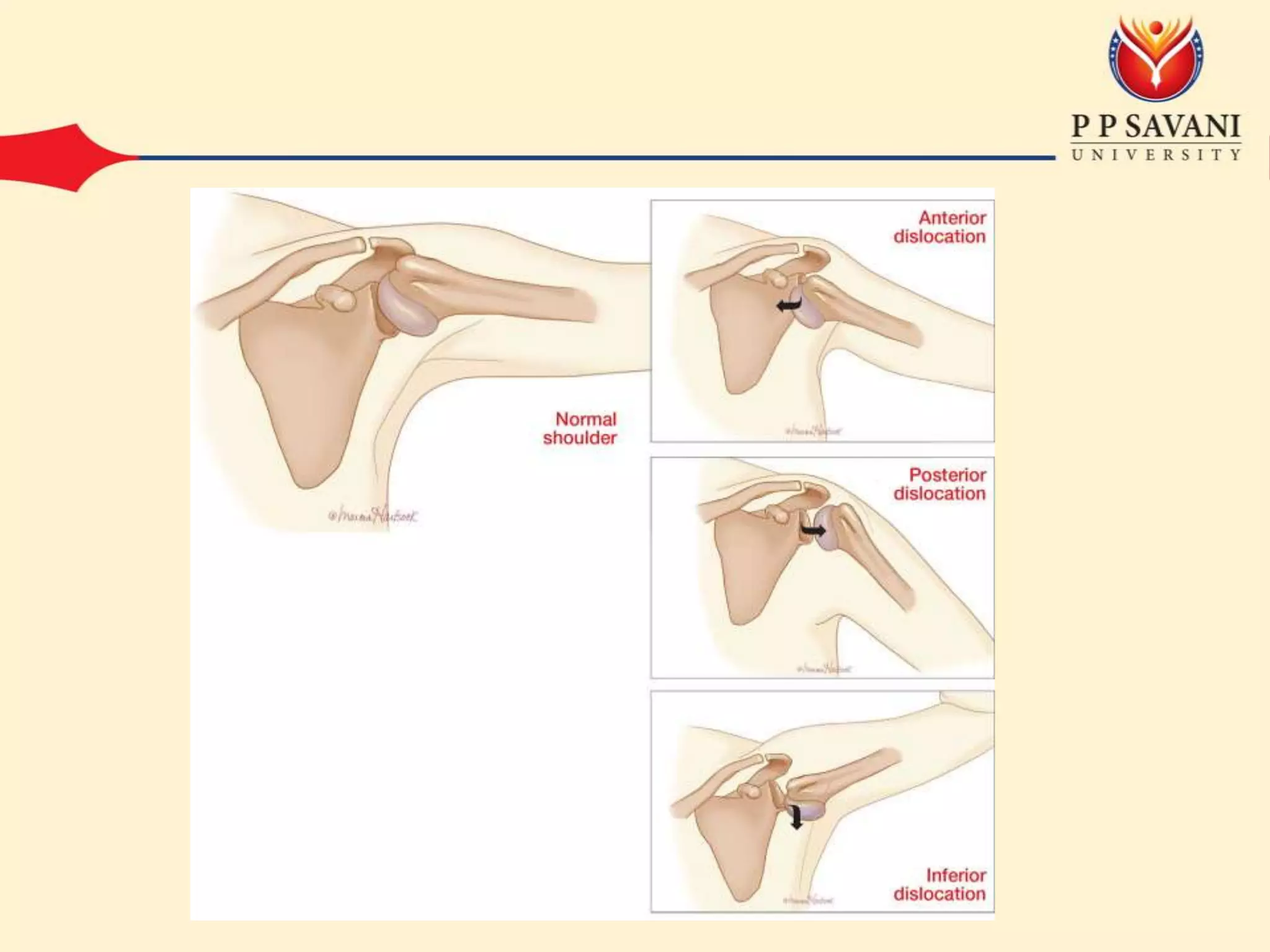
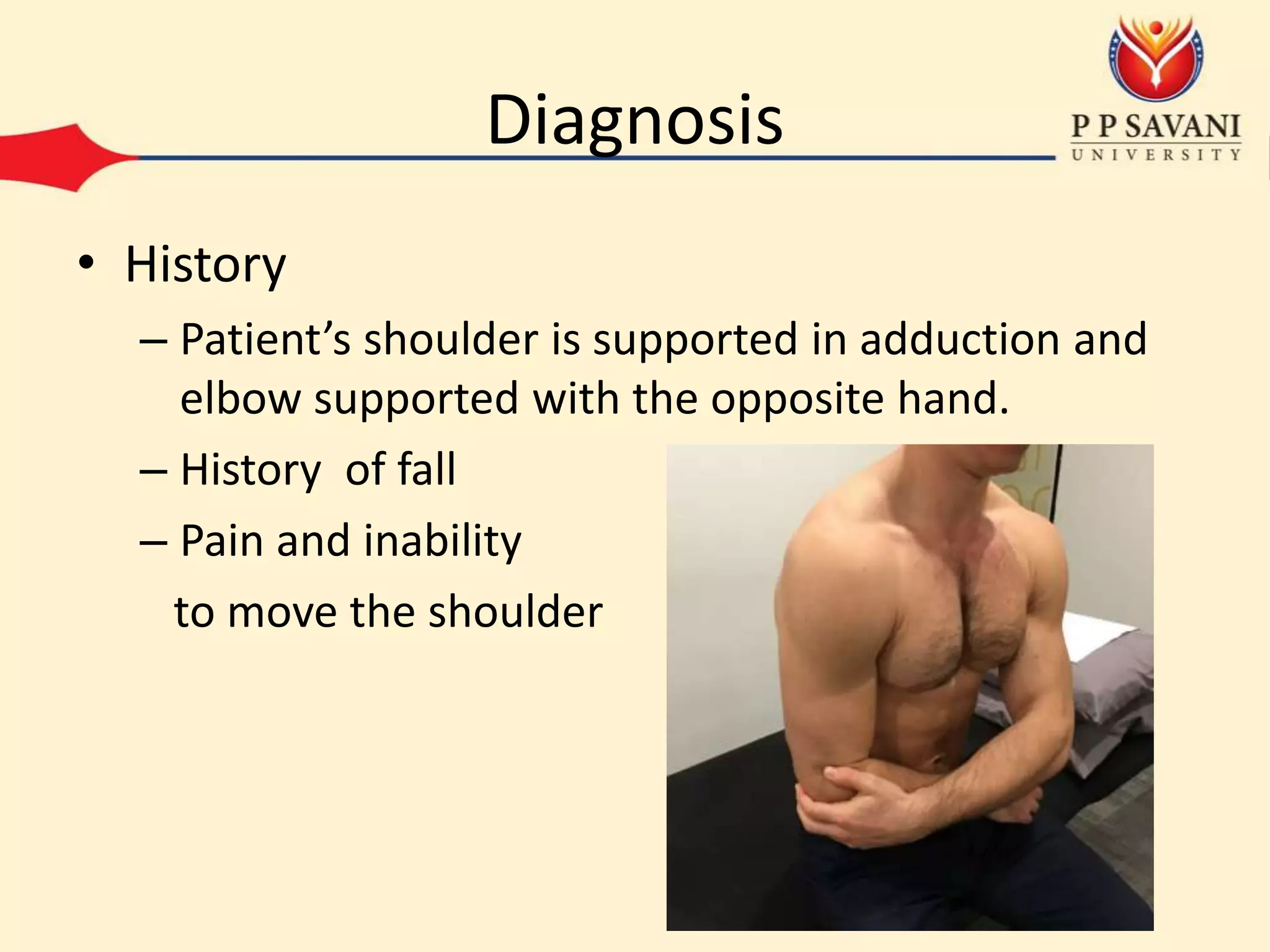
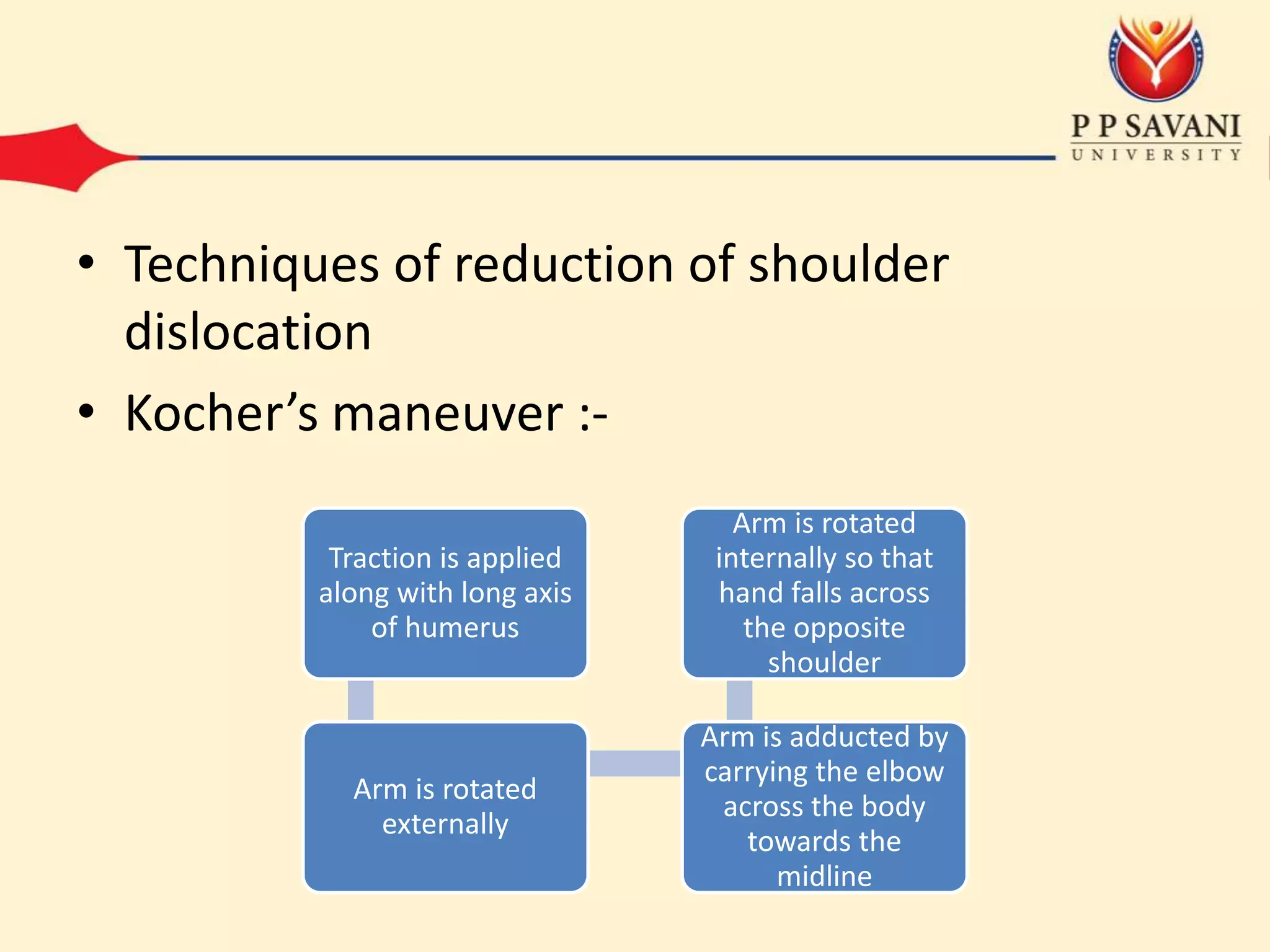
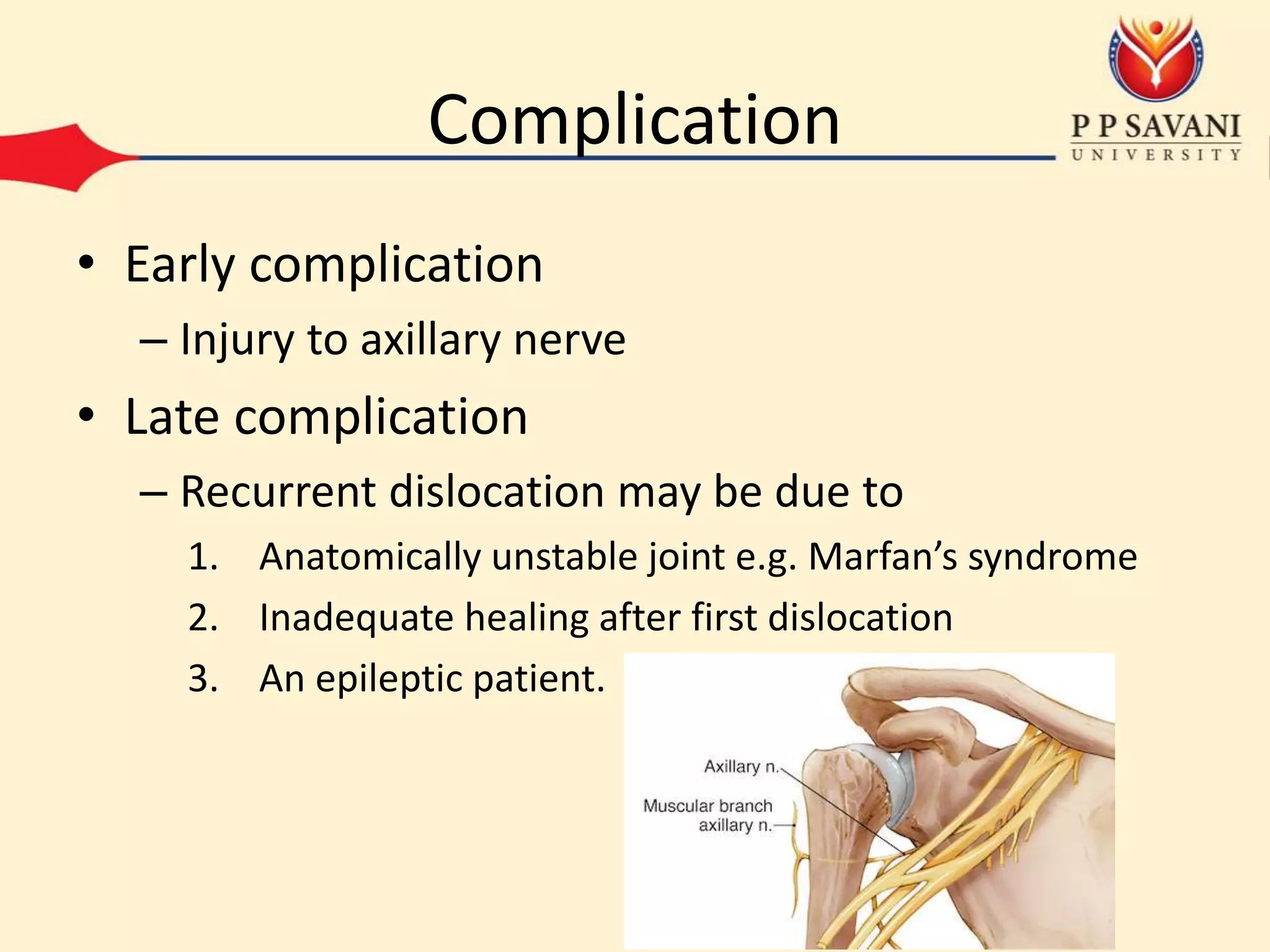
This document outlines the mechanisms and classifications of shoulder dislocations, including common causes and specific lesions associated with the injury. It describes the diagnosis through physical examination techniques and tests, as well as the recommended treatment options for acute dislocation. Additionally, it highlights potential complications that can arise, both early and late, and the surgical interventions available for recurrent dislocation.