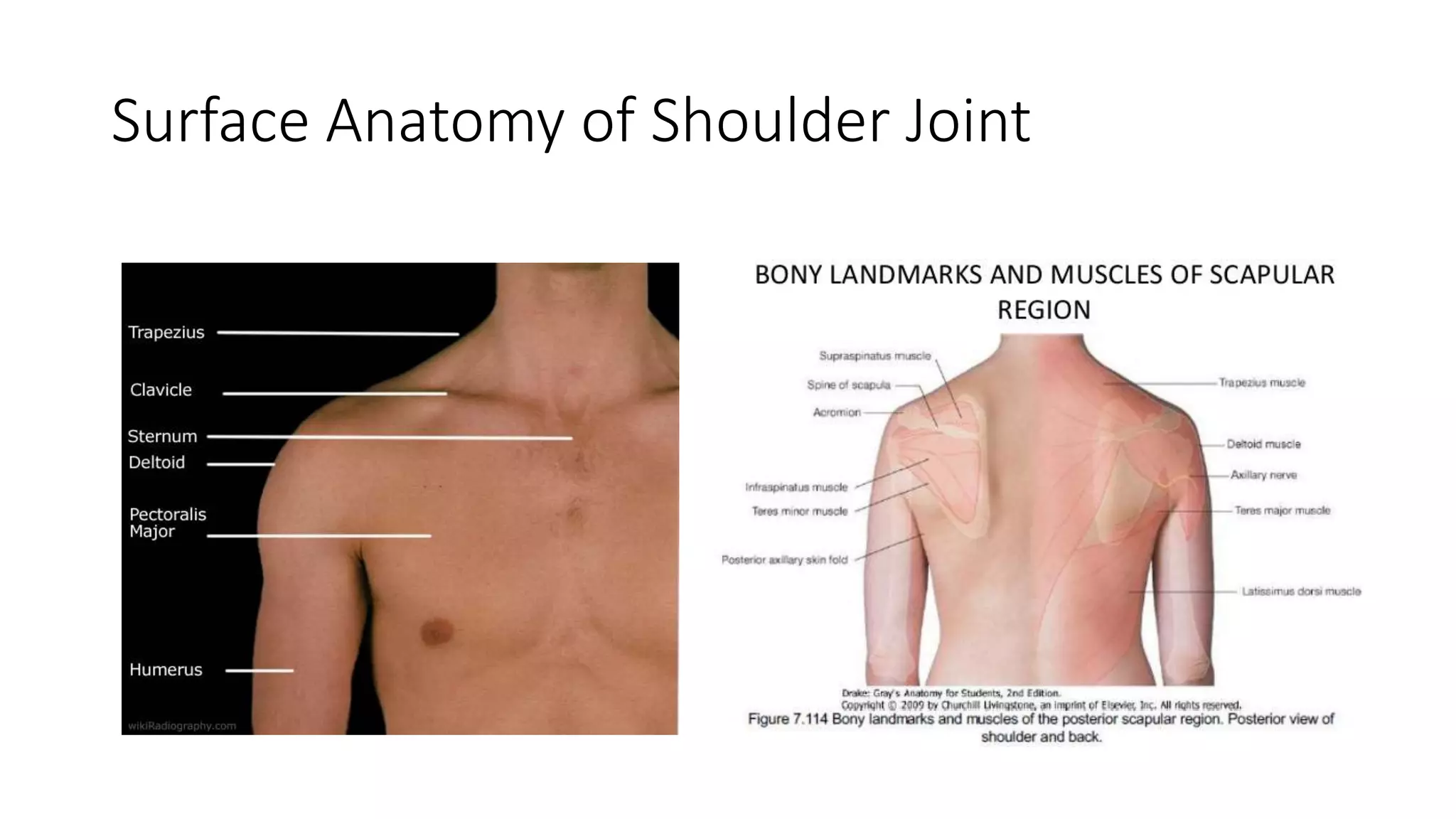
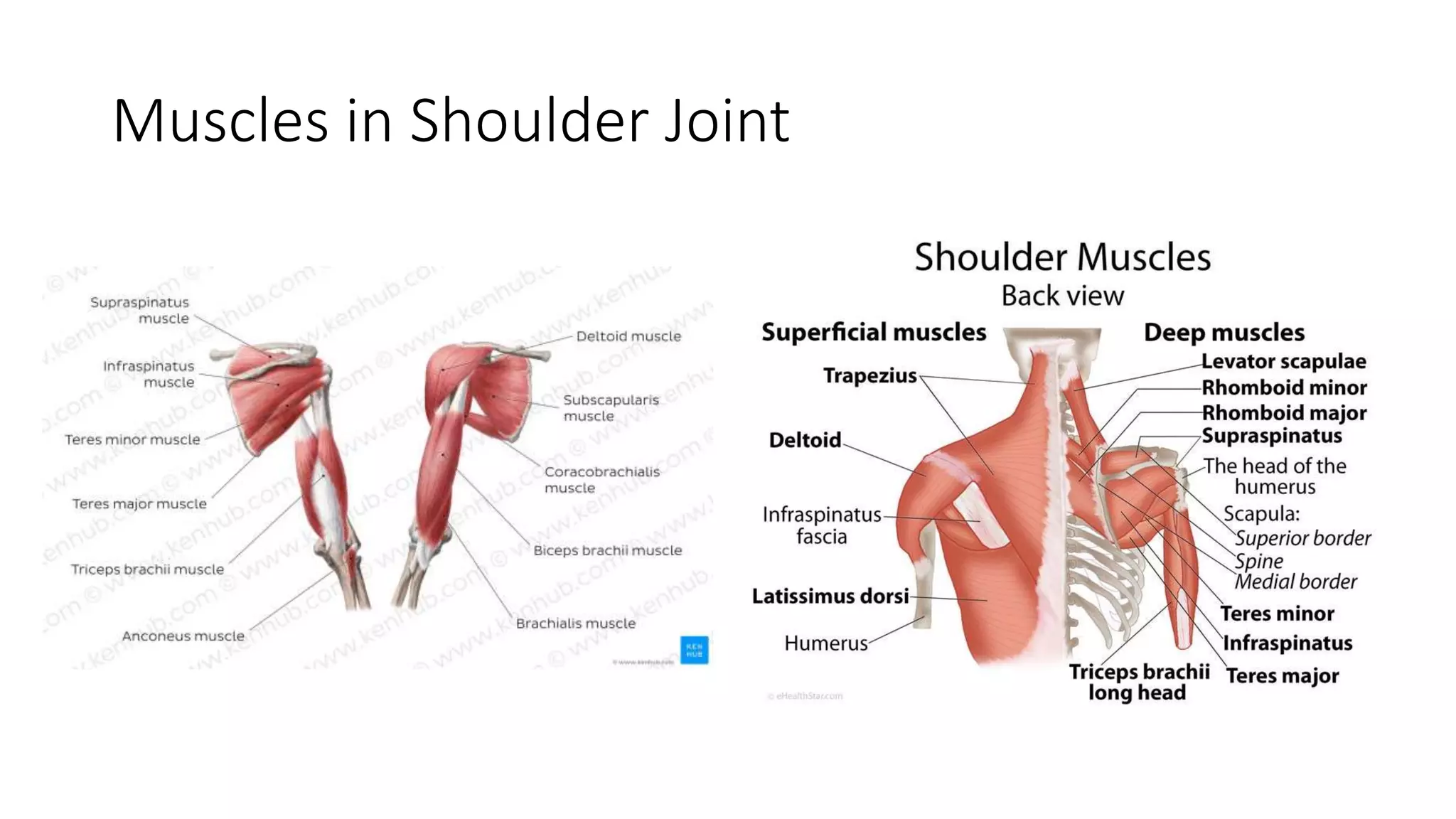
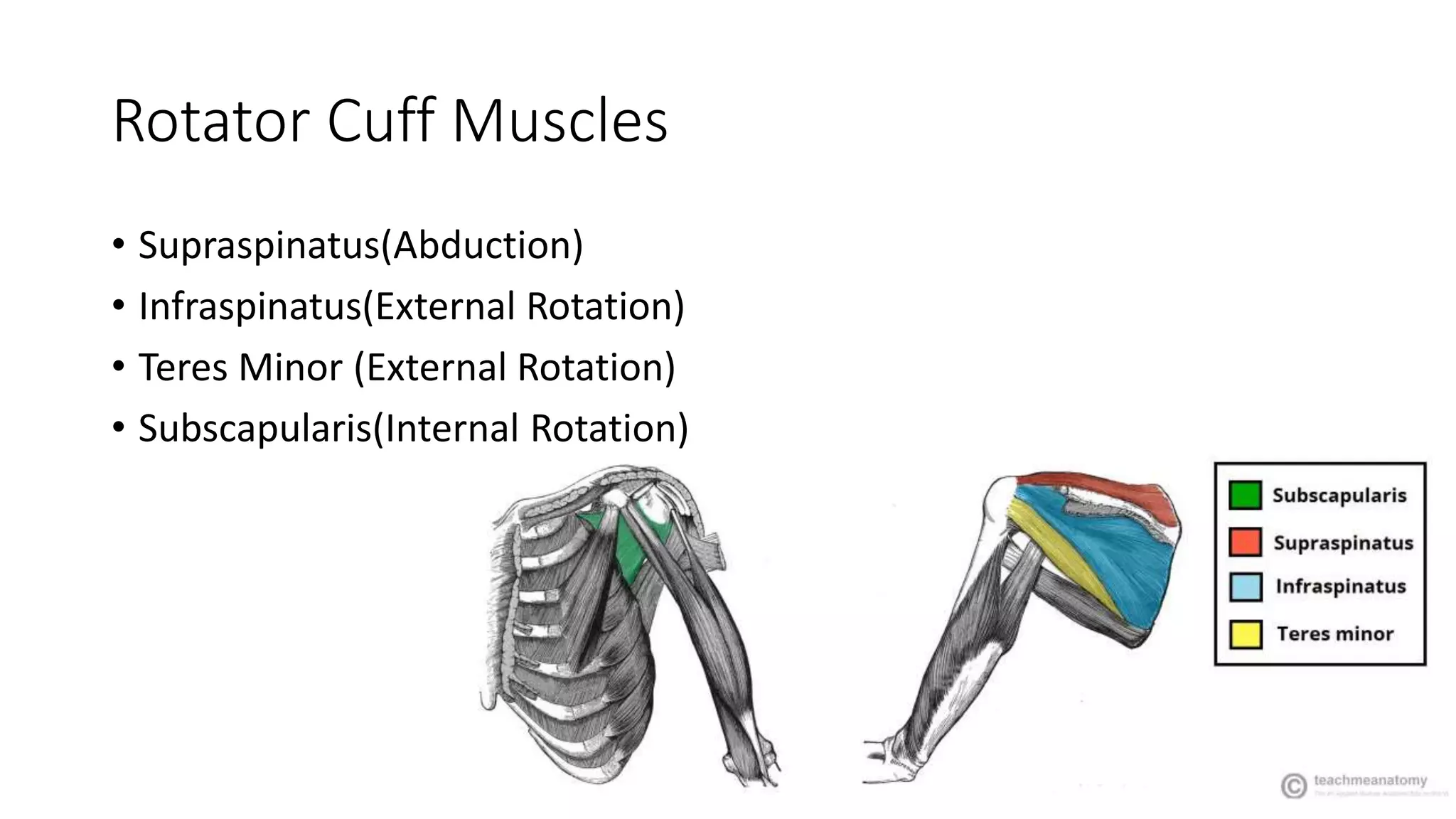
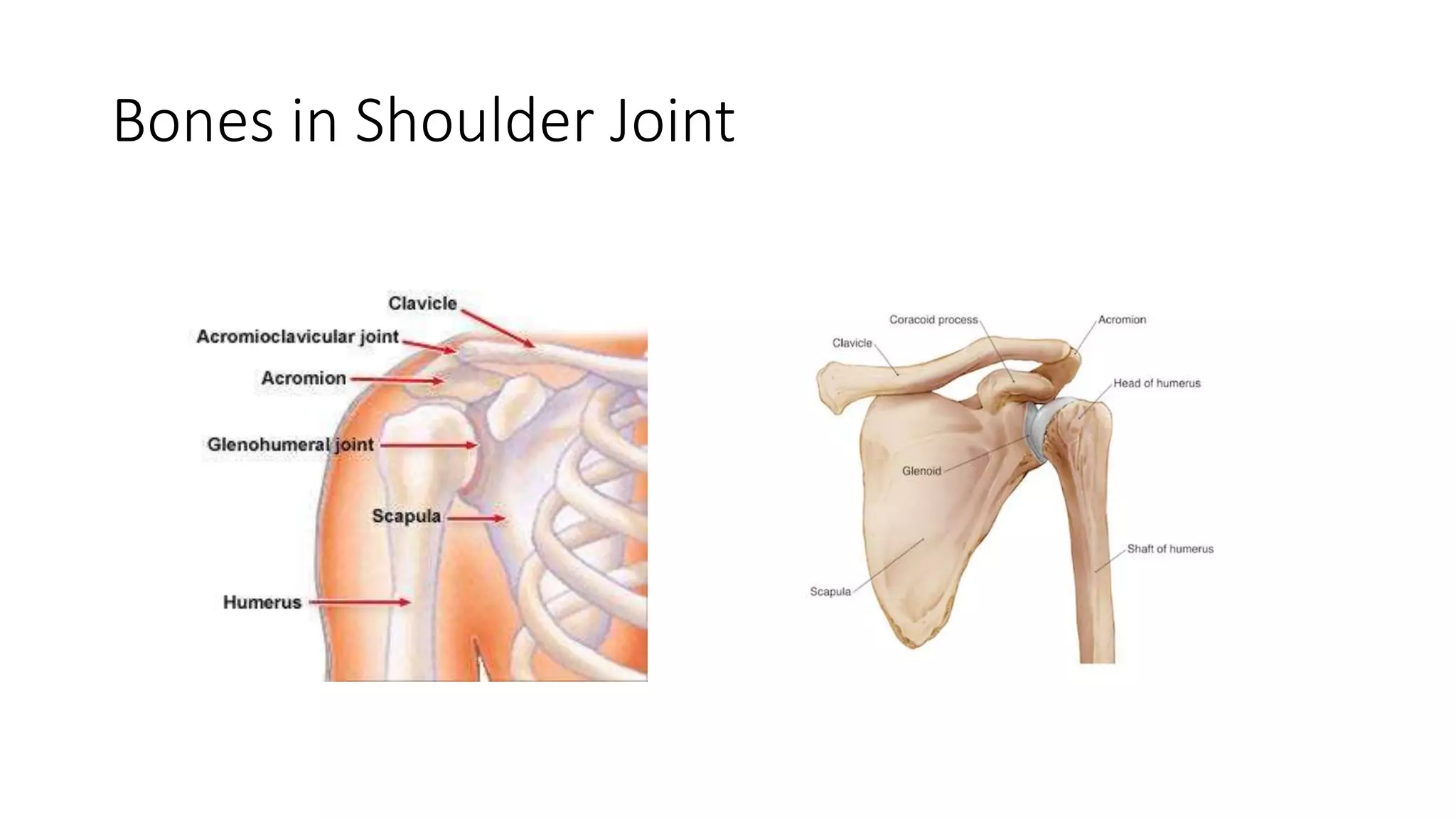
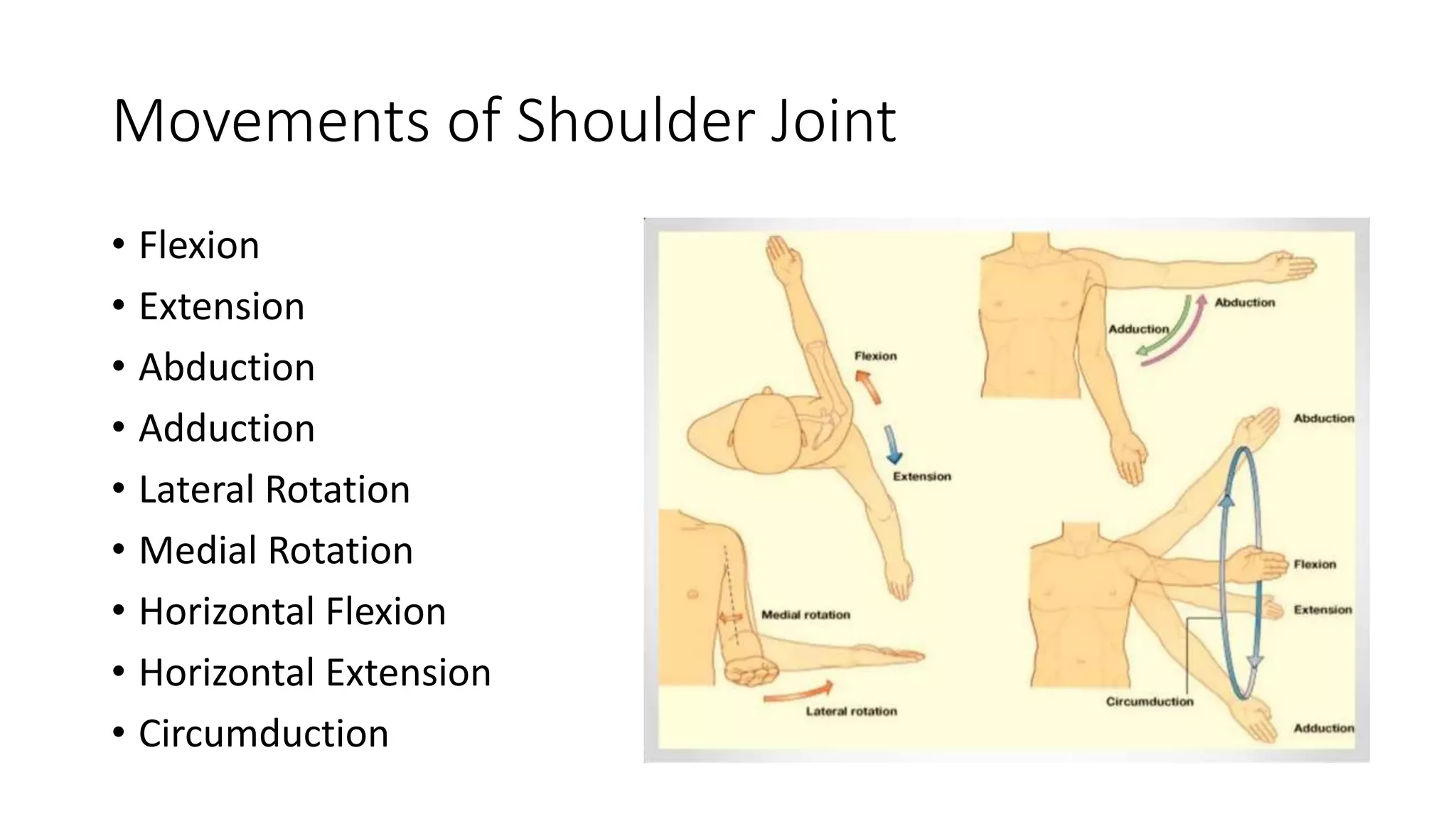
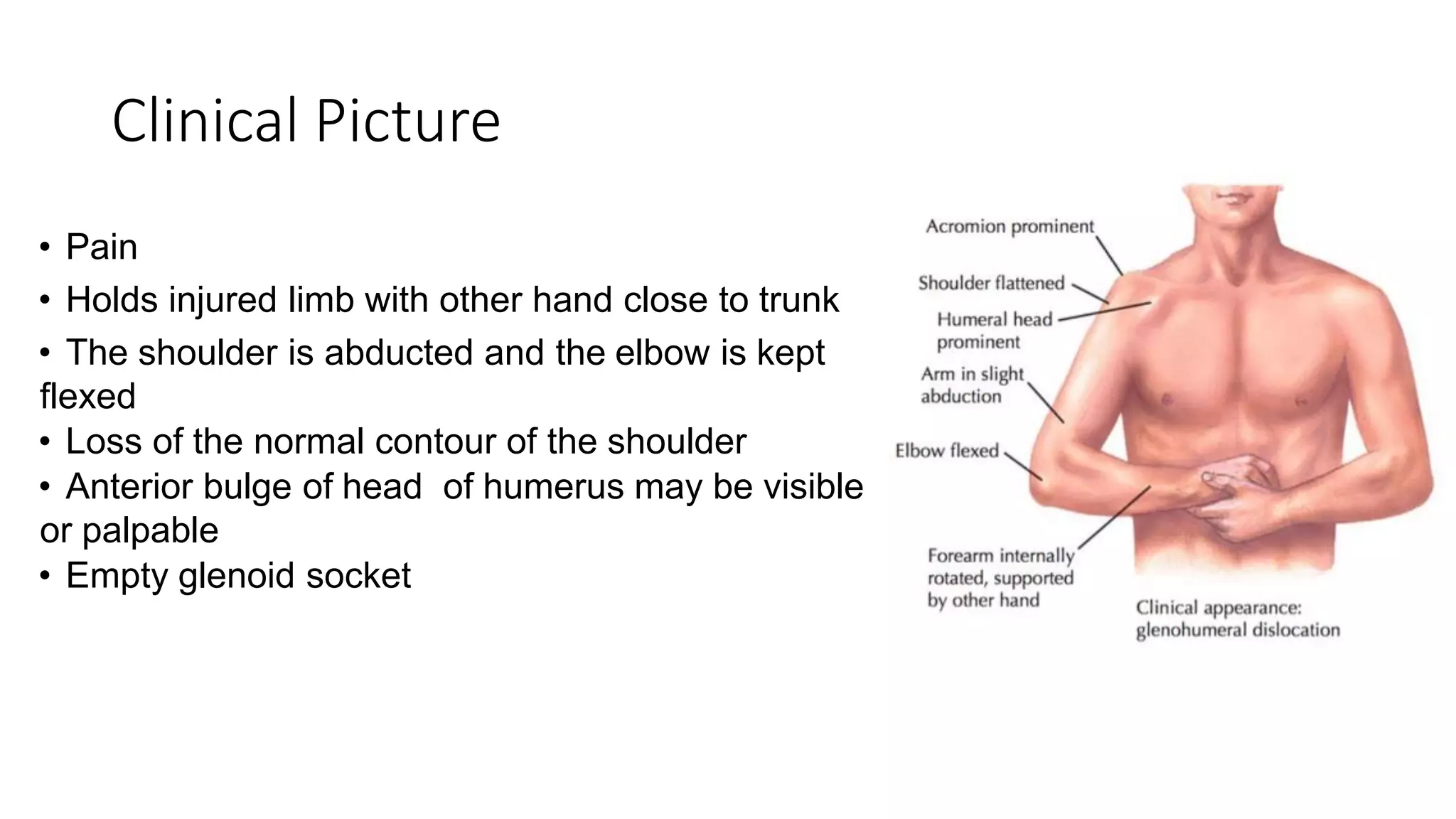
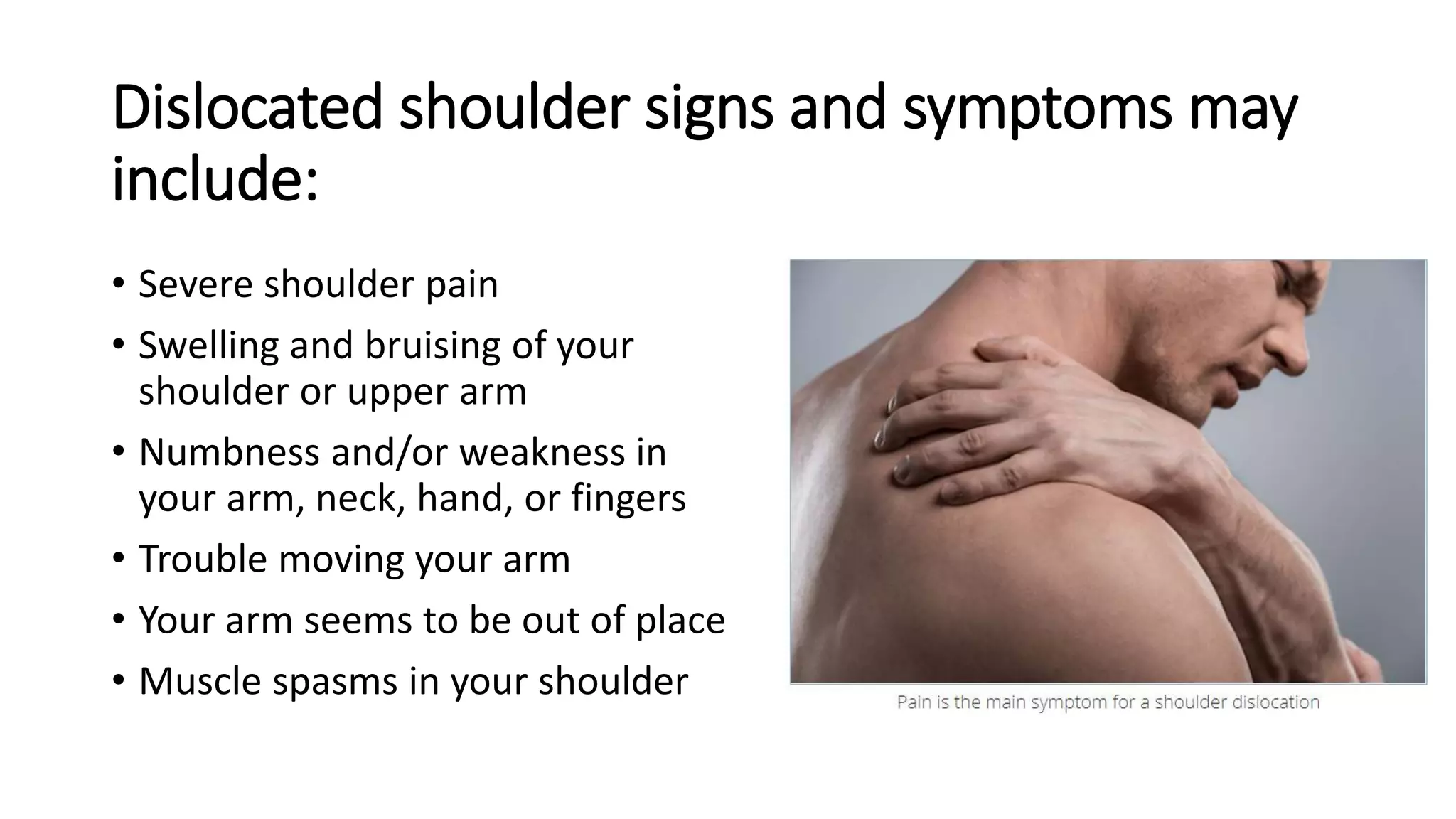
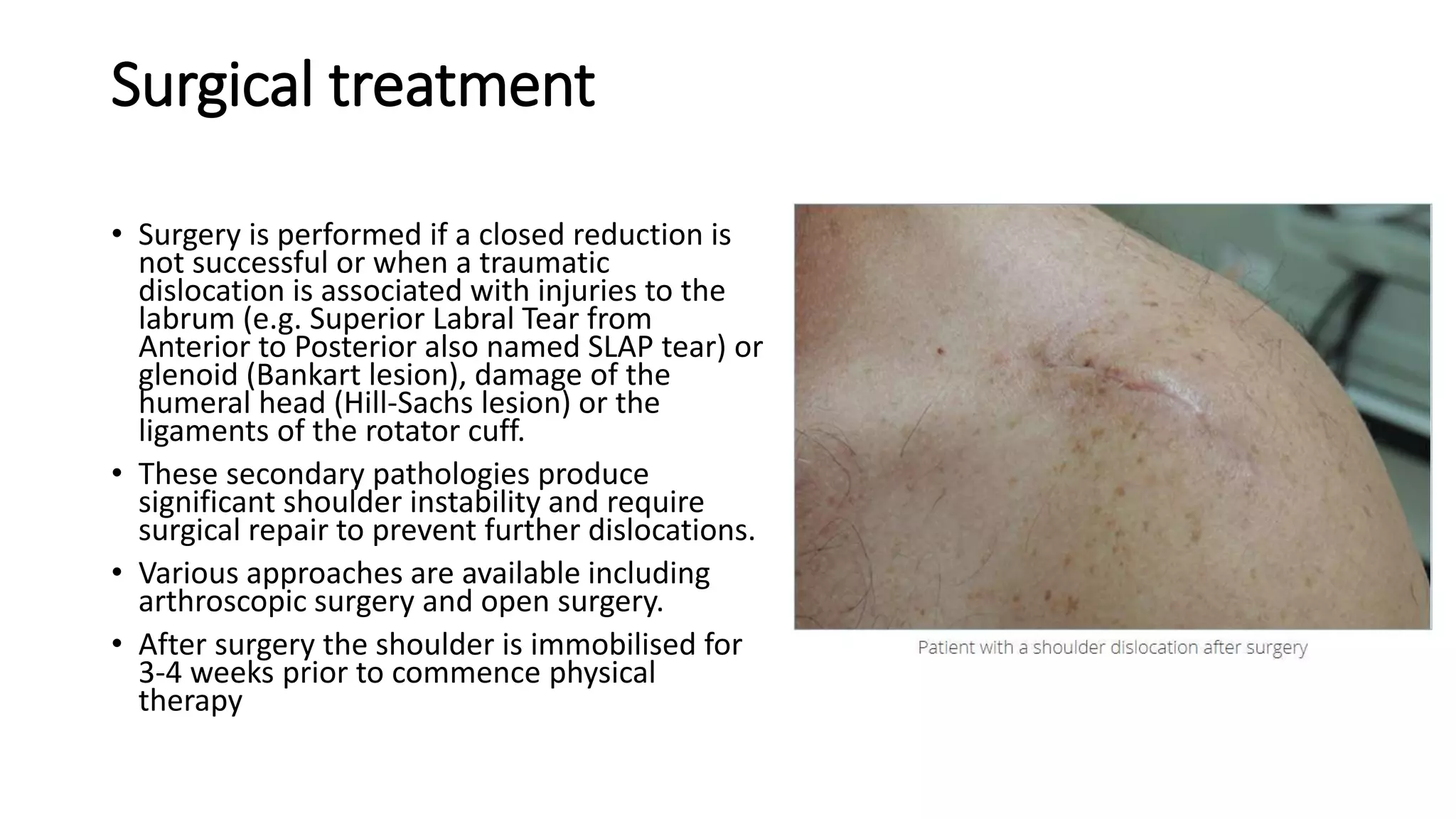
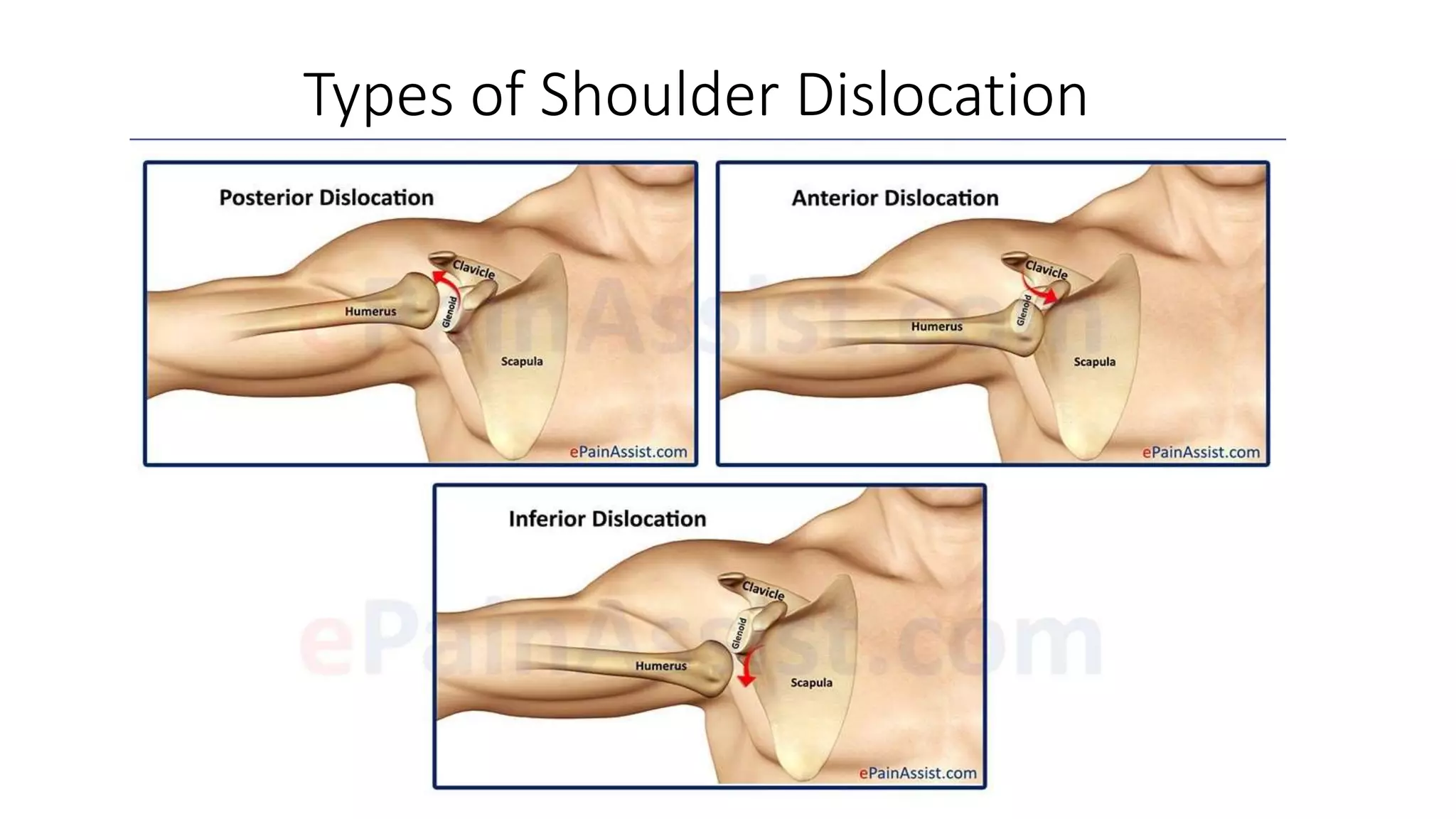
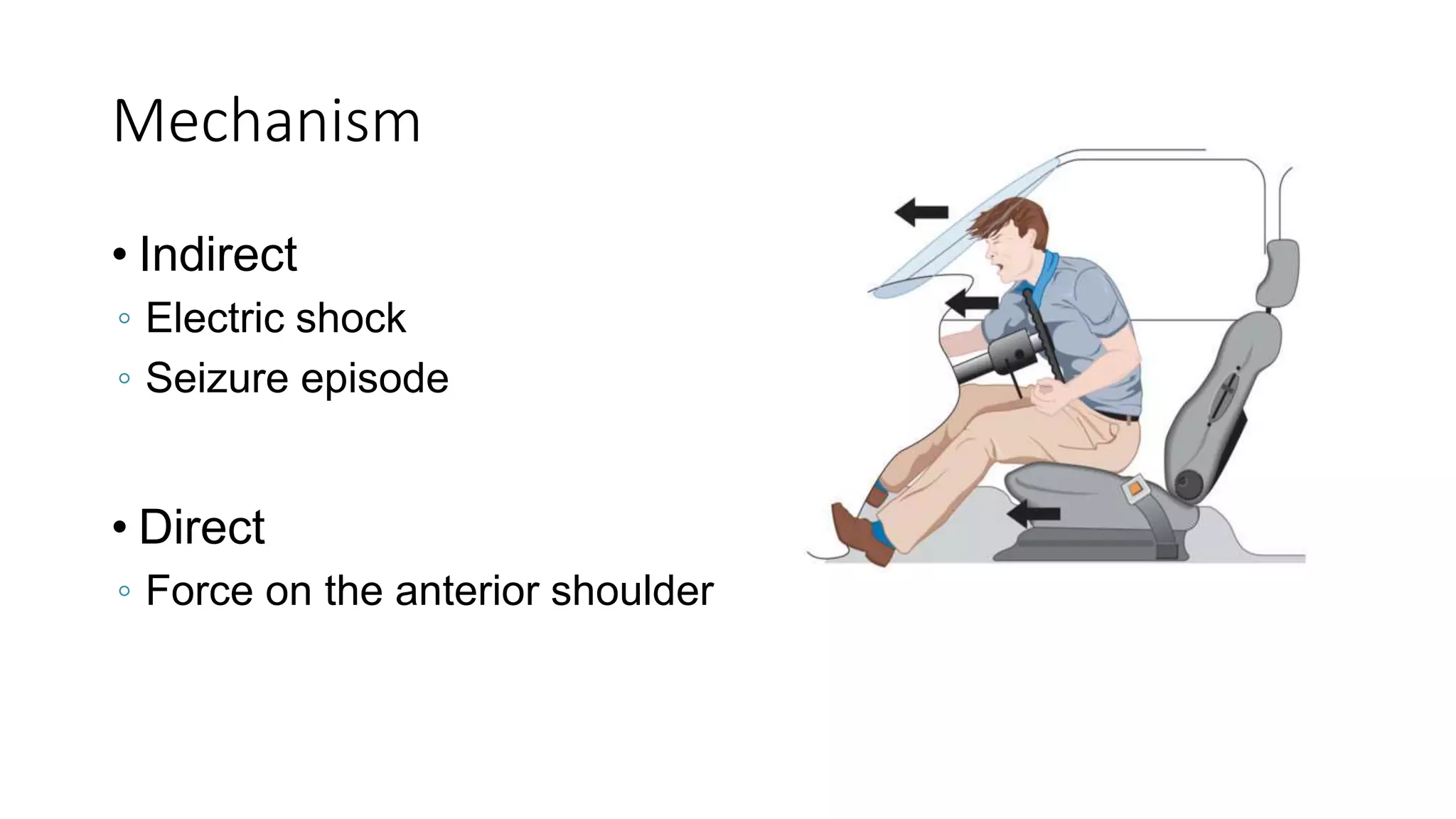
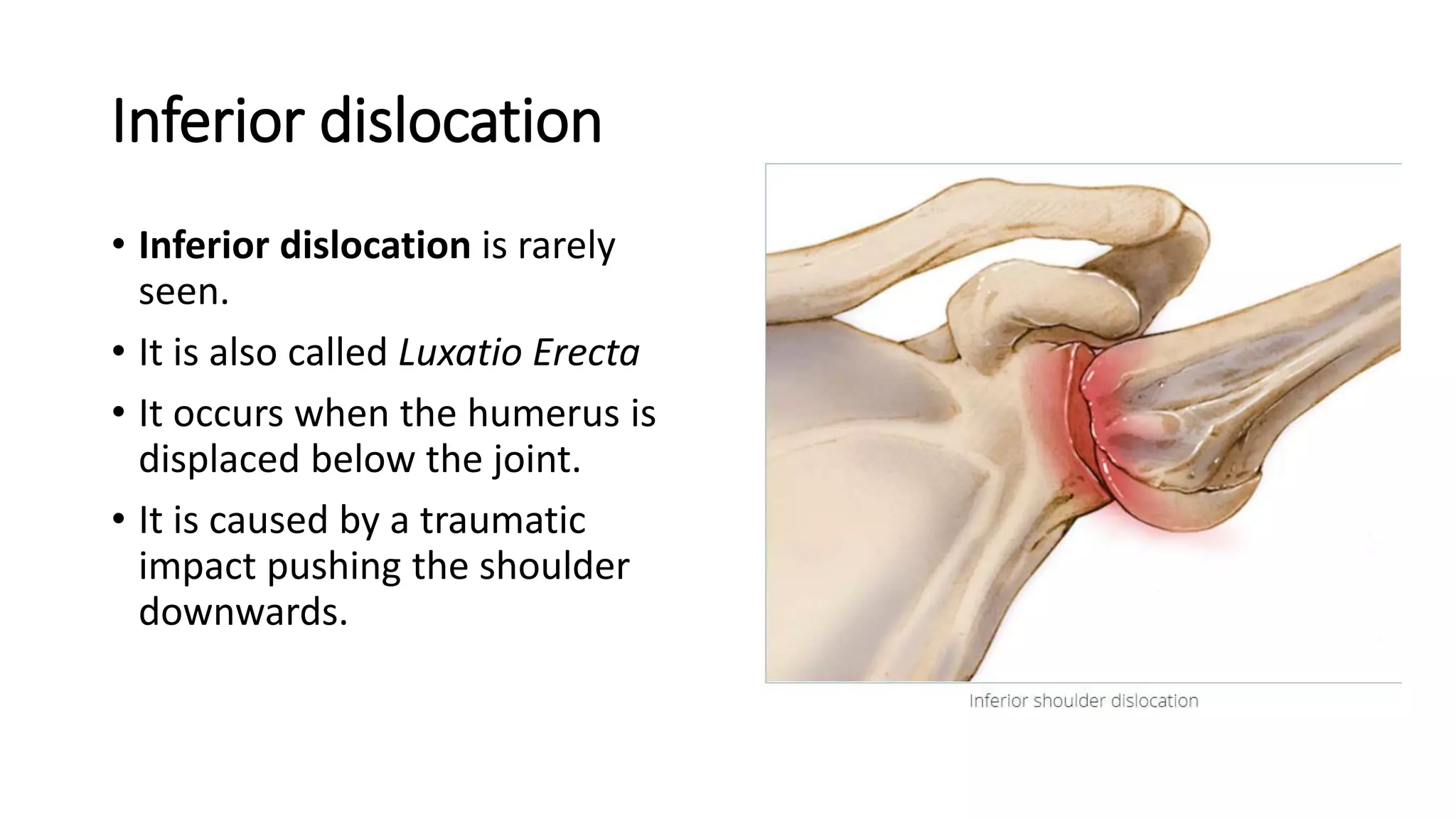
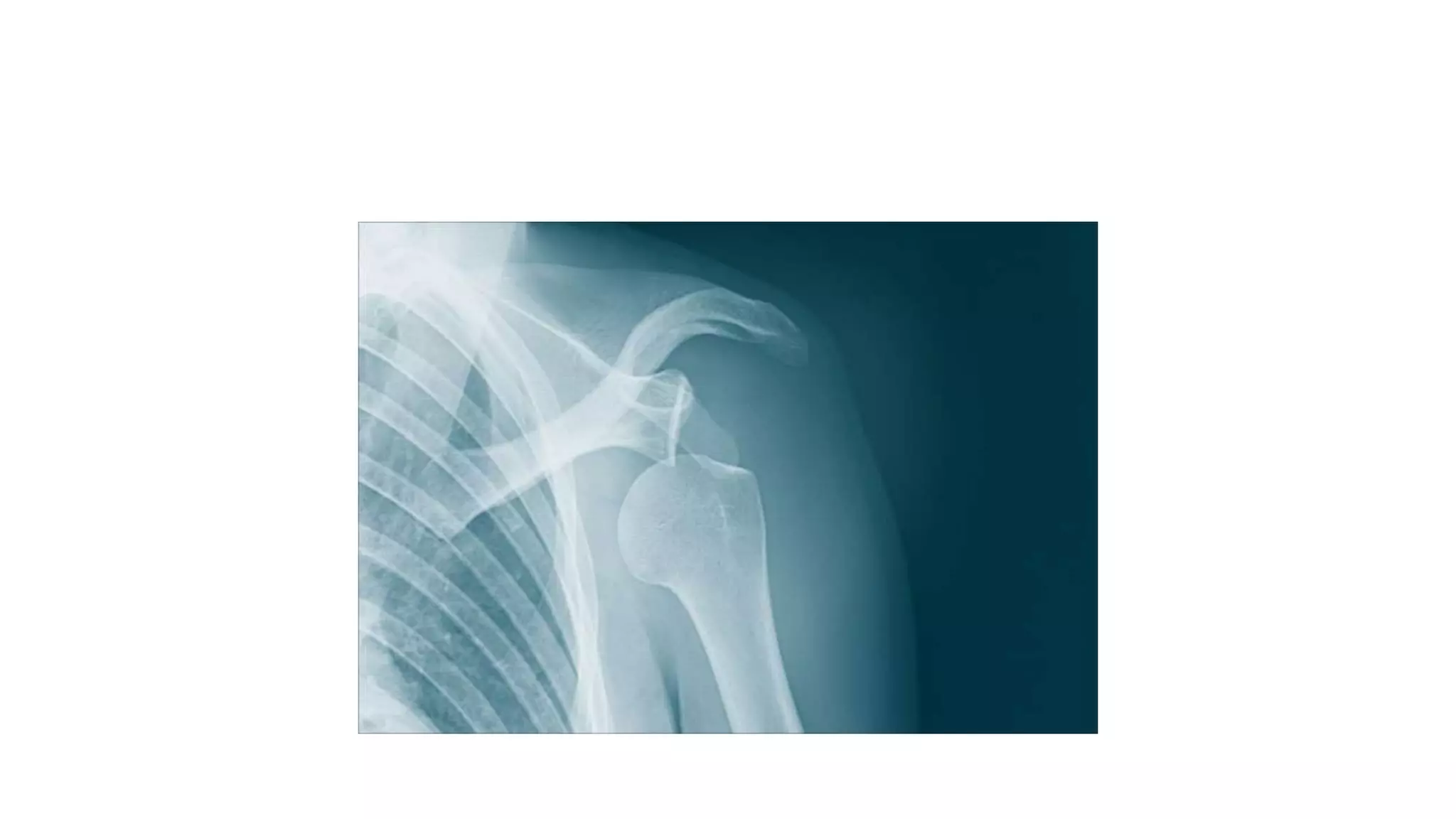
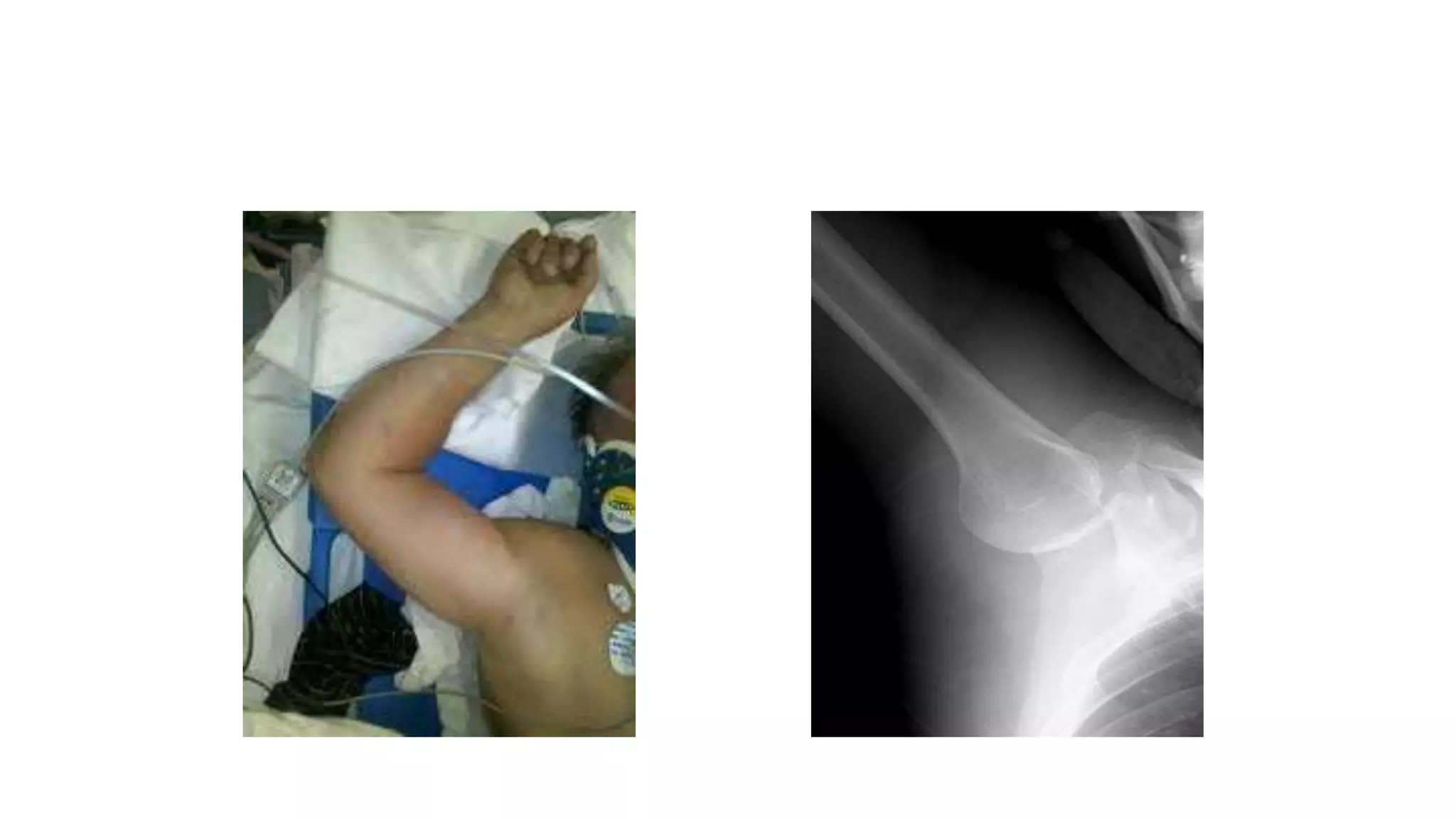
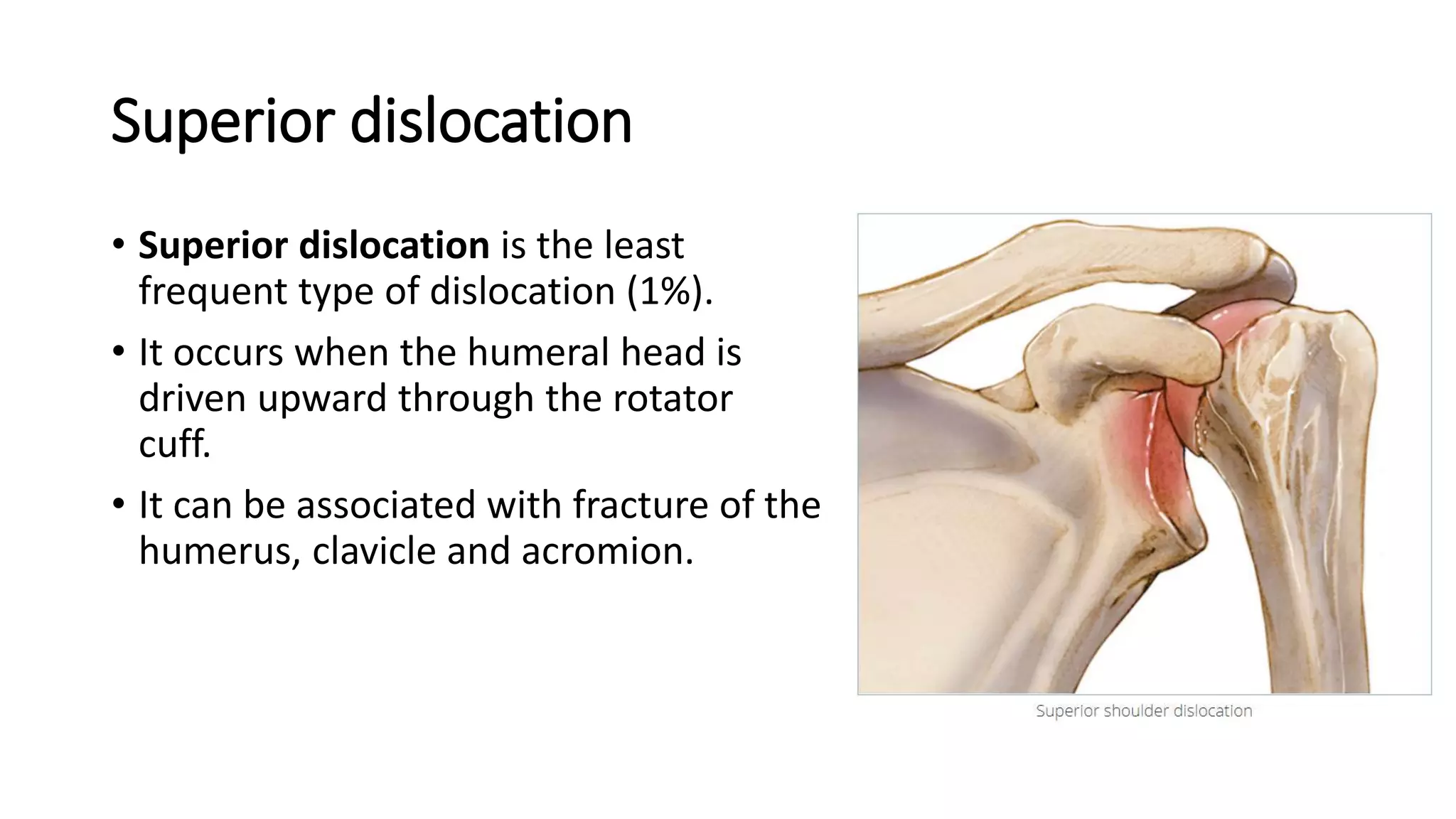
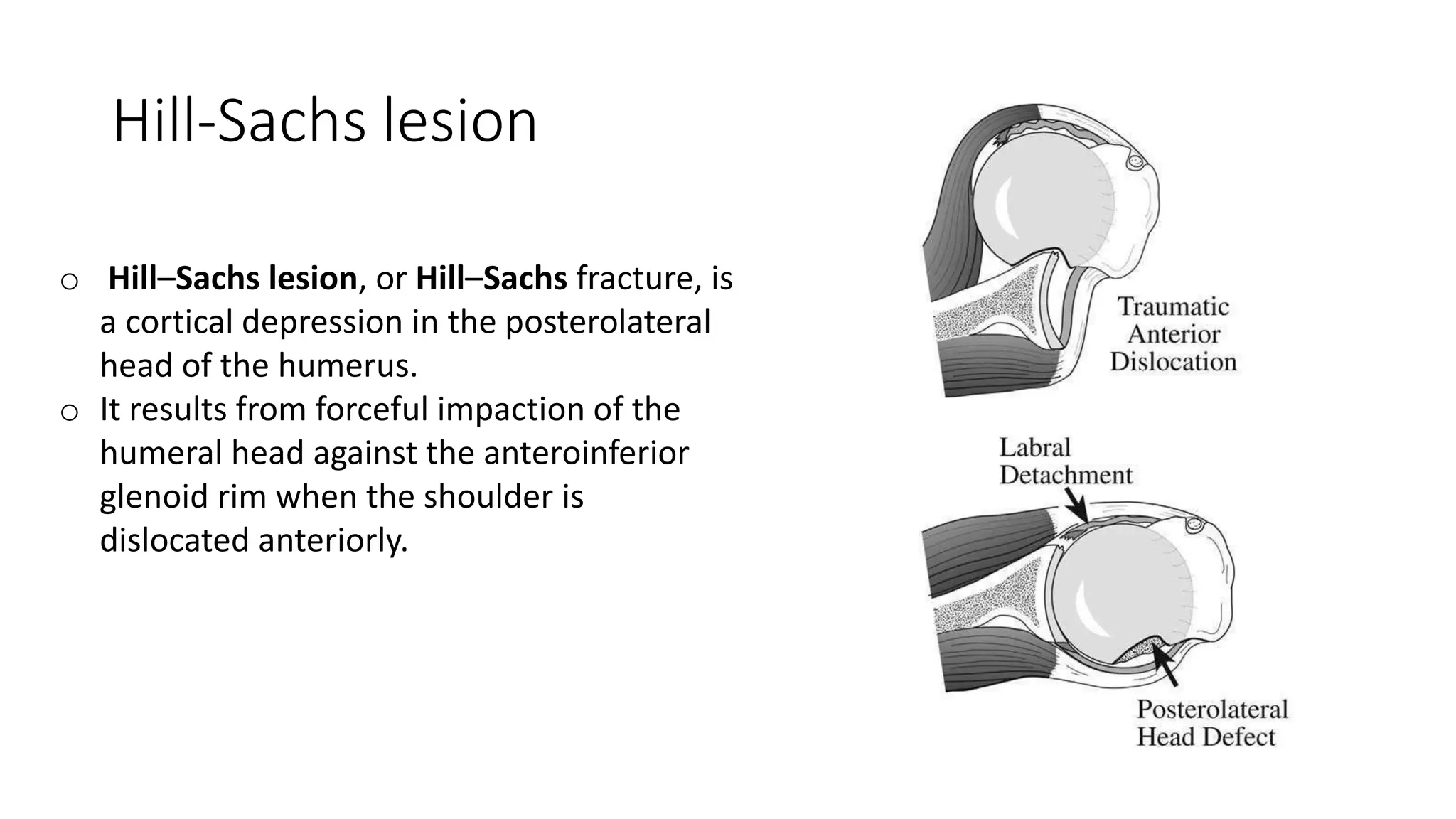
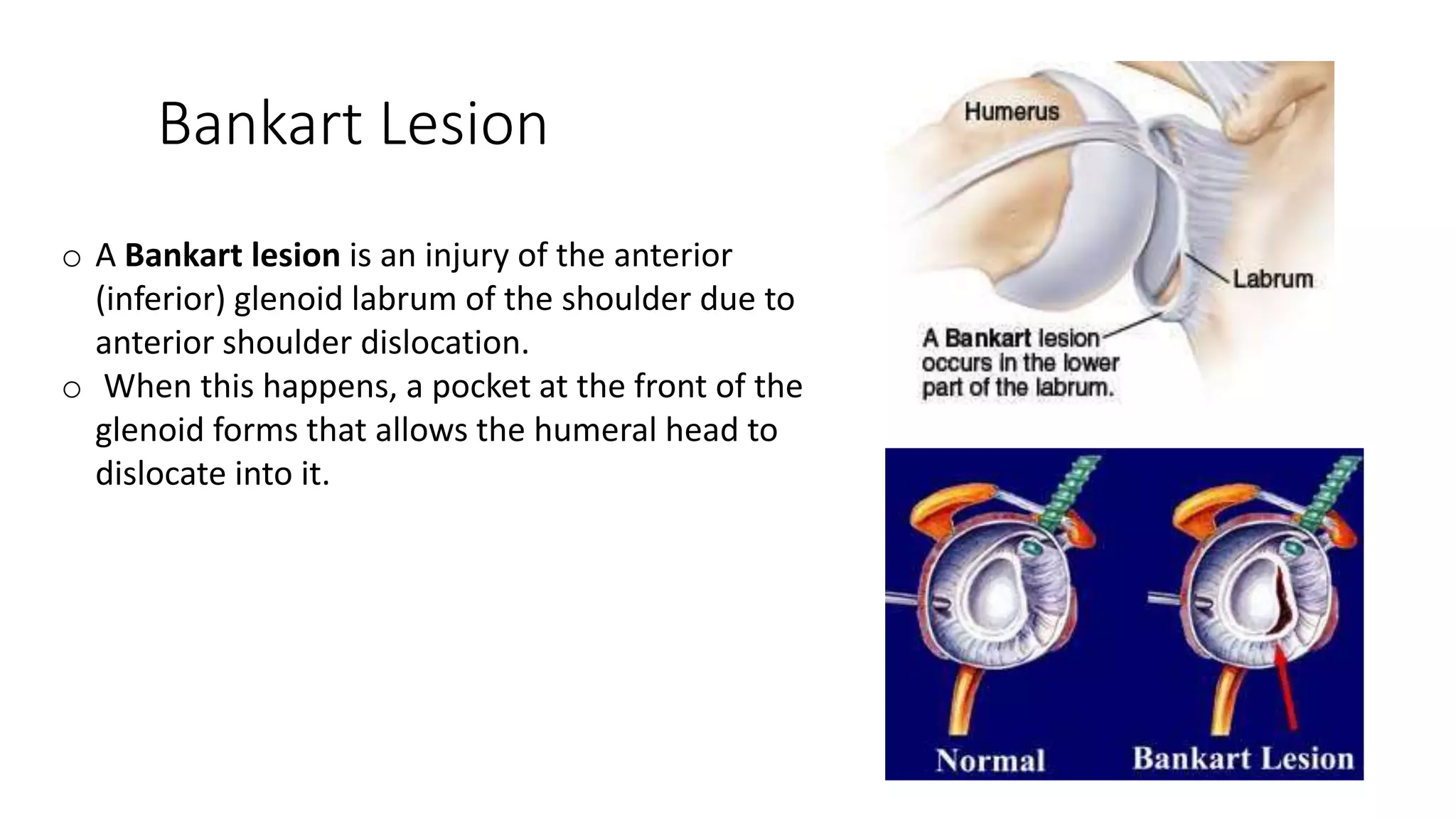
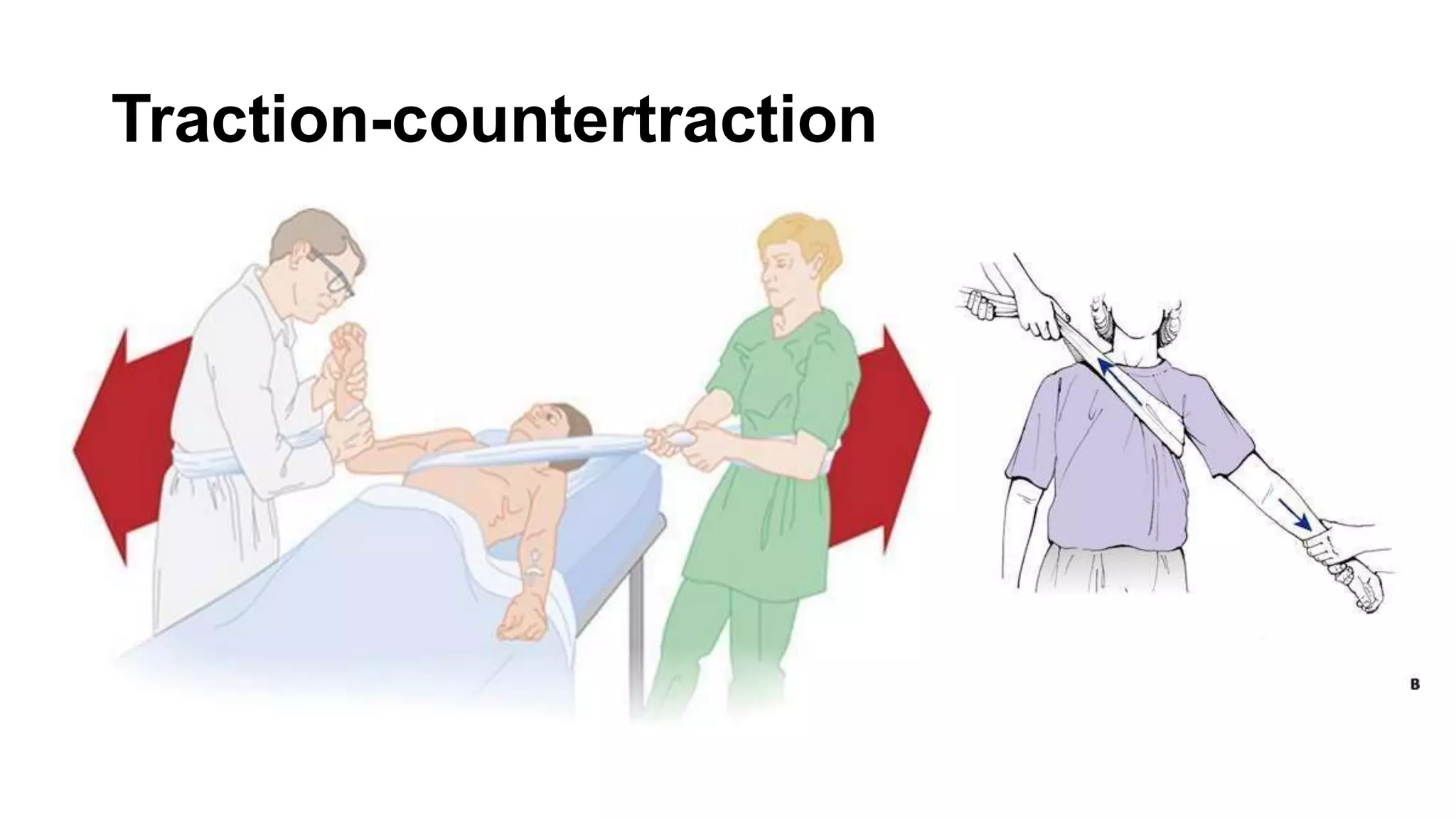
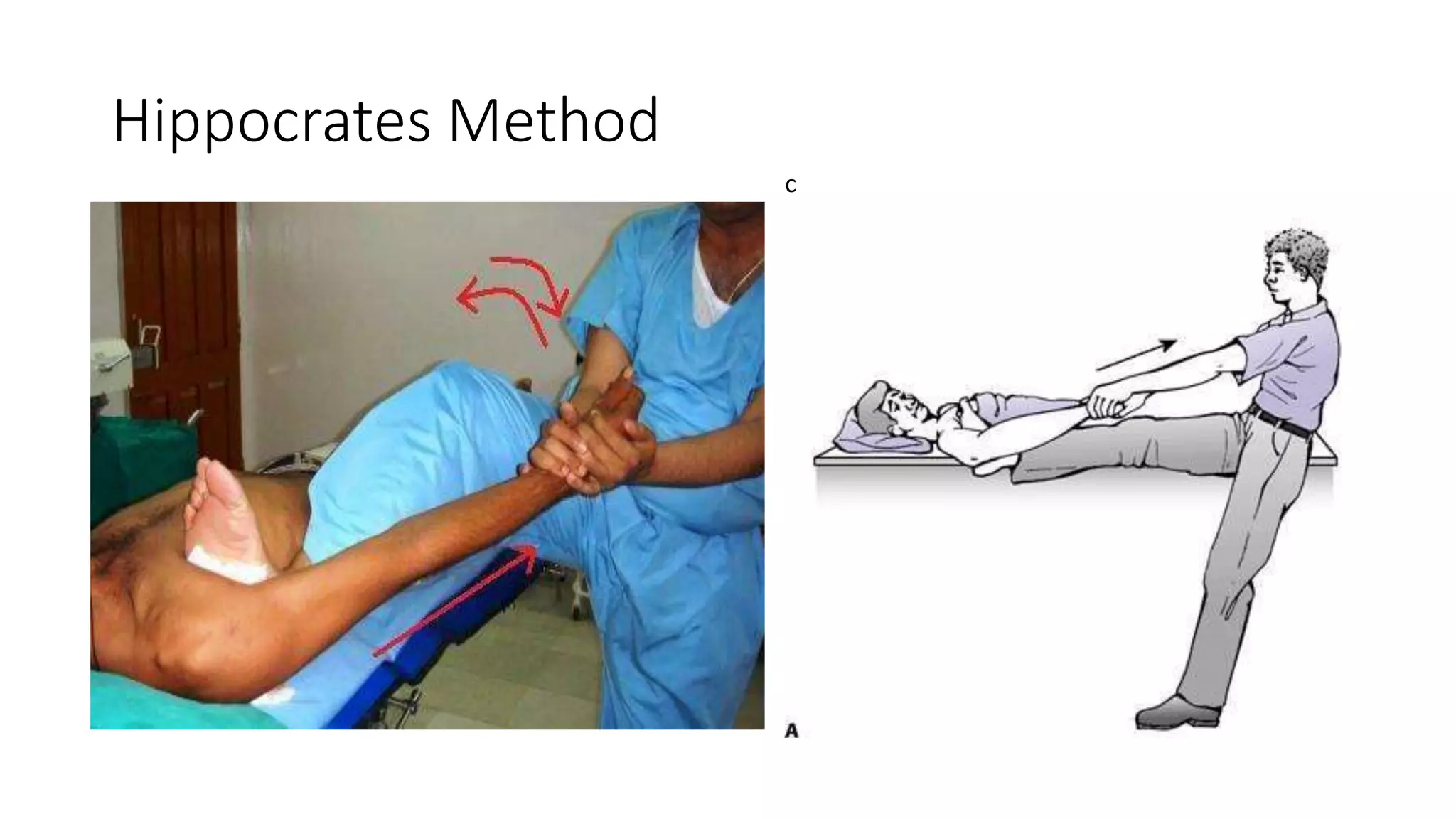
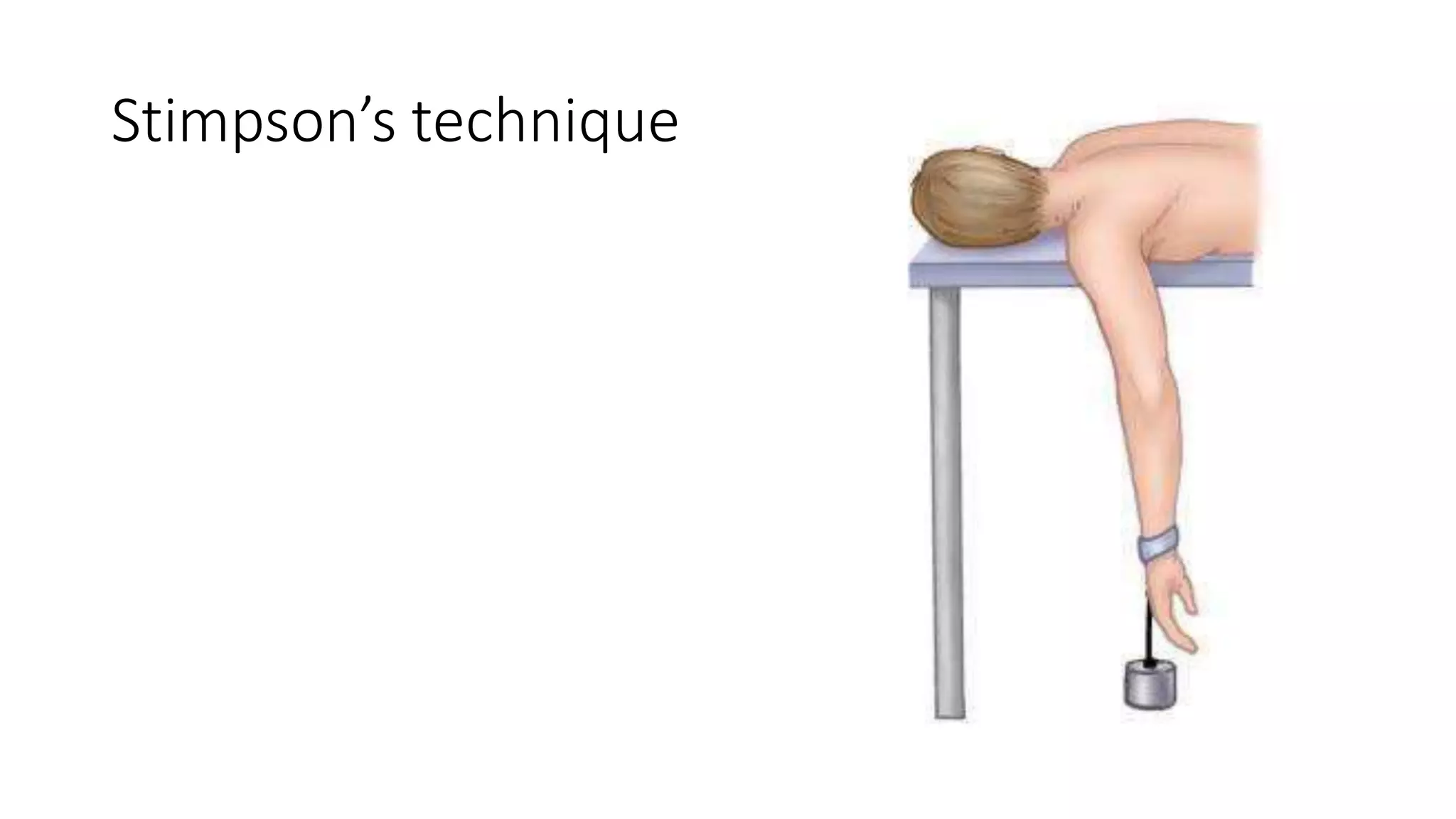
The document discusses shoulder dislocation, including the anatomy of the shoulder joint, causes of dislocation, signs and symptoms, types of dislocation, treatment options like closed reduction and surgery, rehabilitation, and complications. The most common type of dislocation is anterior dislocation, which can occur due to falls or impacts and results in the humeral head moving out of the glenoid socket in the front of the shoulder. Treatment depends on the severity of the dislocation and any associated injuries.