Embed presentation



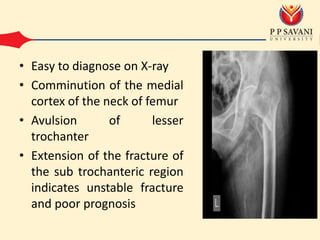

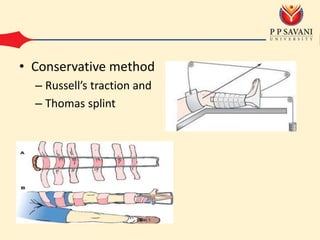

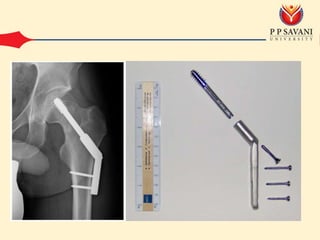

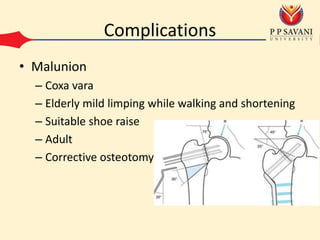
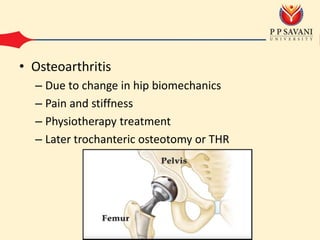


An intertrochanteric fracture occurs in the area between the greater and lesser trochanters of the femur. It is usually caused by a minor fall in elderly patients and major trauma in adults. Diagnosis is made through clinical examination finding pain and inability to move the leg as well as x-ray showing comminution of the medial femoral cortex. Treatment options include conservative methods like traction or operative fixation using devices like dynamic hip screws or gamma nails to maintain the normal femoral neck shaft angle and allow healing. Complications can include malunion leading to limping or shortening and osteoarthritis from changes in hip biomechanics.












