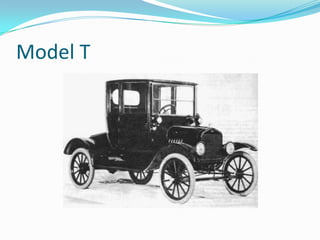
After World War I, America saw many transitions as it moved from a rural, agricultural society to a more urban, industrial one. There was a shift from isolationism to internationalism, as well as a transition from a cash economy to one fueled by consumer credit. Socially and culturally, the country struggled with clashes between rural, traditional conservatives and urban, liberal reformers over issues like prohibition, women's changing roles, and new social norms. While some embraced modern flappers and new opportunities, others reacted by trying to preserve older values and restrict immigration and dissent. Overall, the postwar period was one of significant change and conflict as America adjusted to its new place in the world.