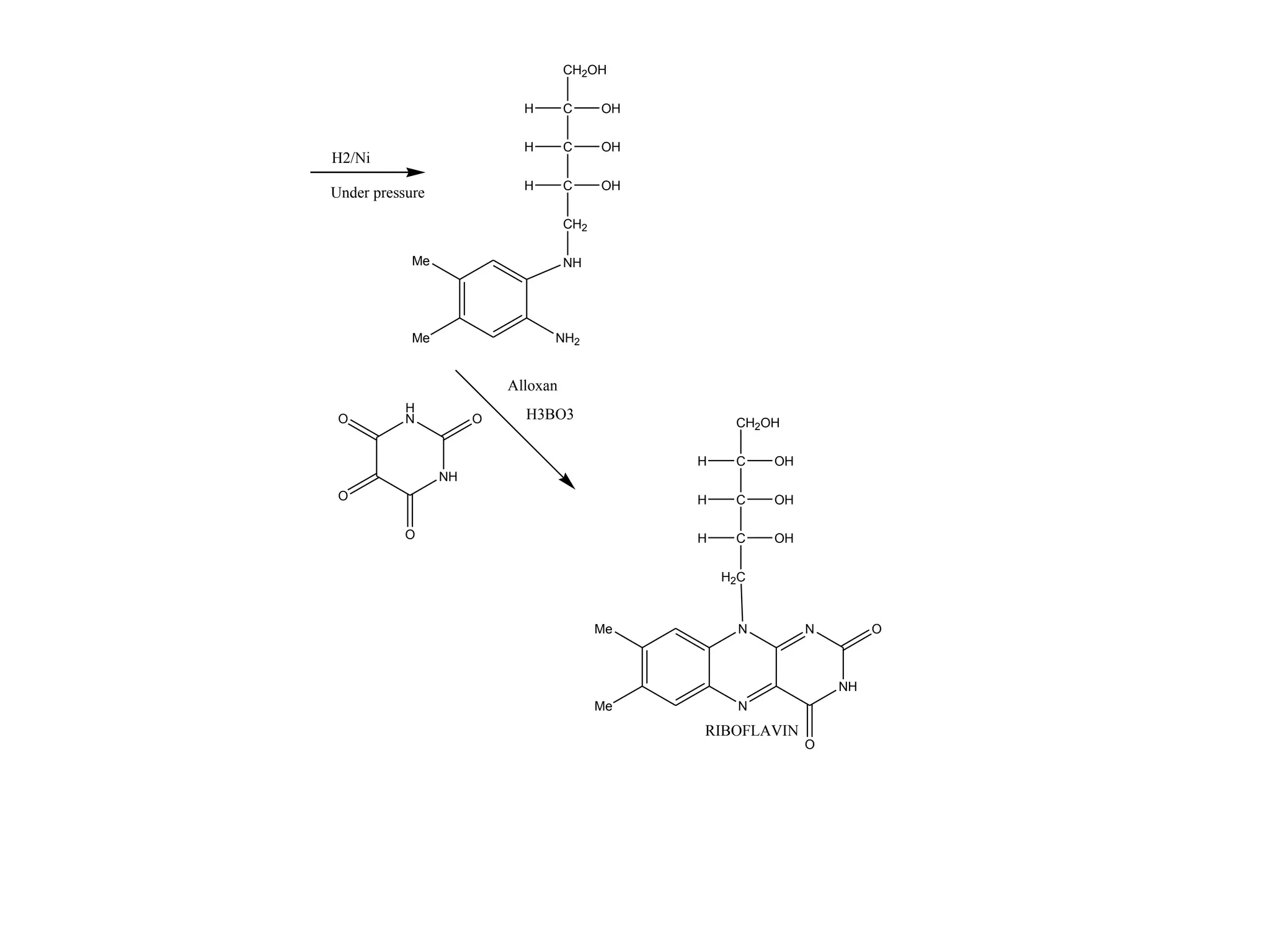
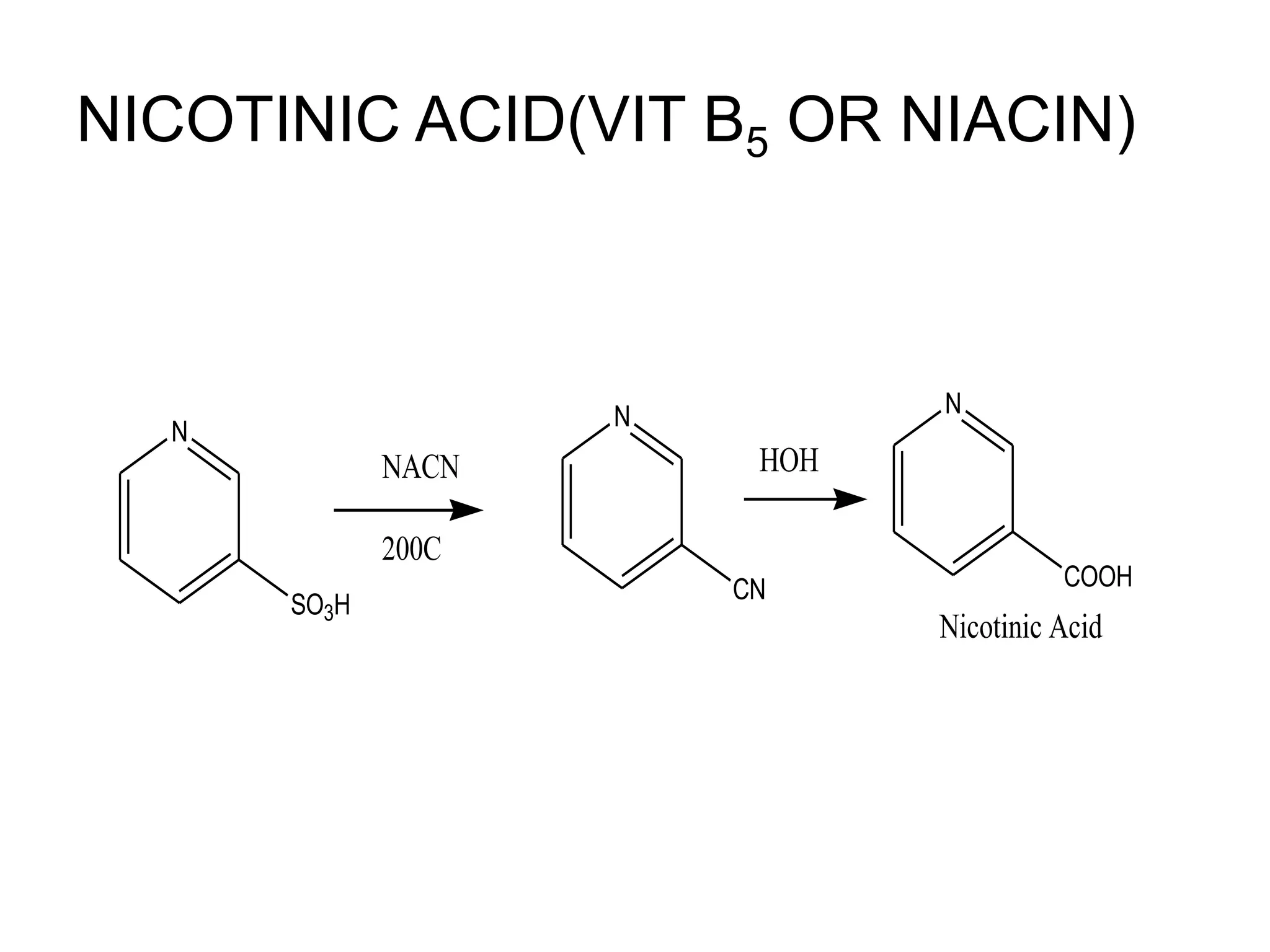
This document provides information on paracetamol (acetaminophen), including its history, physical properties, dosage forms, pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of action, indications, interactions, and toxicity. Paracetamol is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic that was first marketed in the United States in 1955 as Tylenol. It is generally safer for patients than NSAIDs in terms of gastrointestinal and renal toxicity, but overdose can cause hepatotoxicity. Paracetamol is metabolized in the liver and exhibits weak inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes.