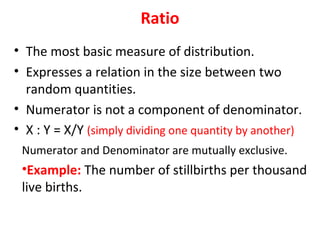
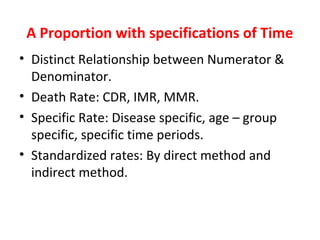
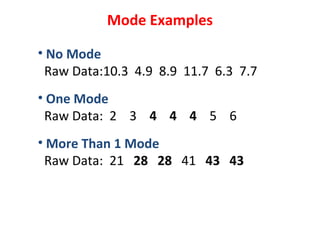
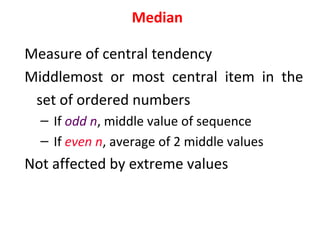
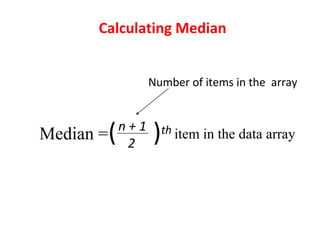
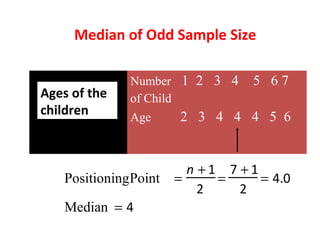
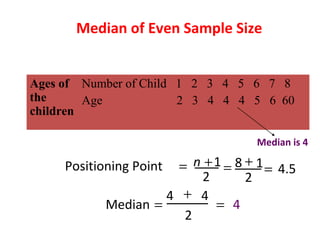
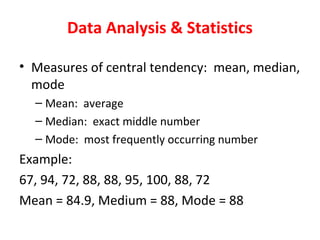
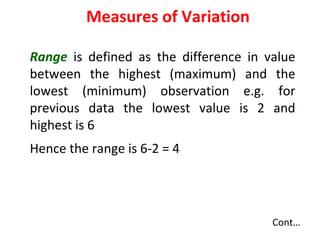
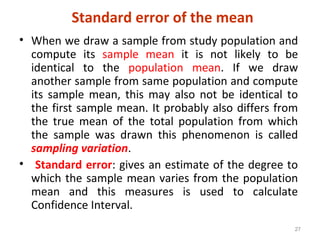
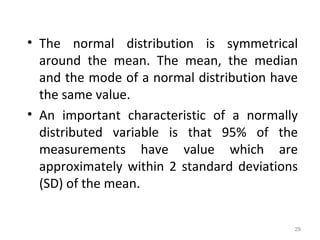
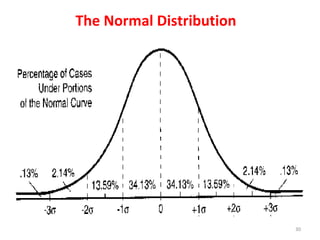
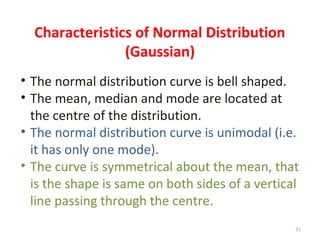
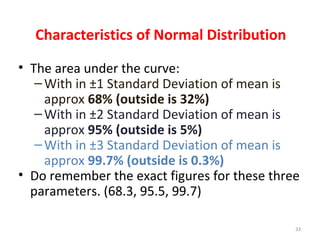
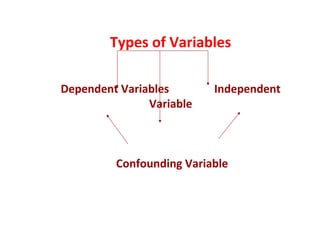
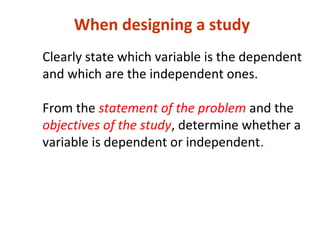
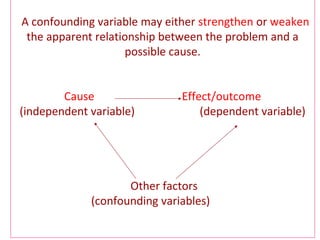
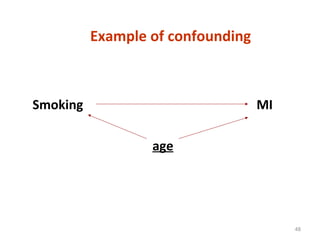
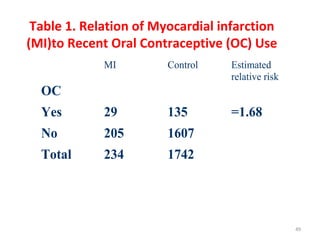
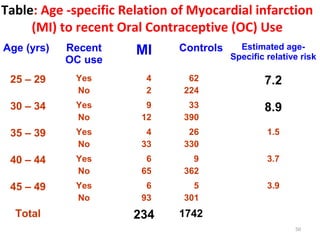
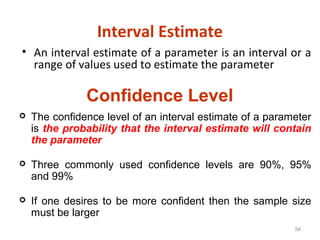
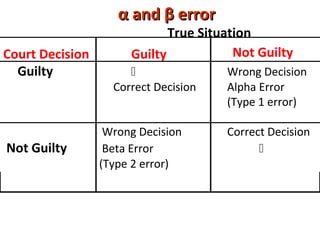
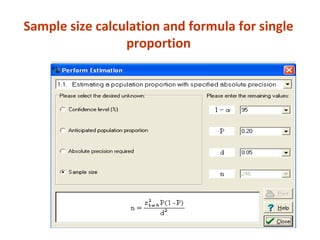
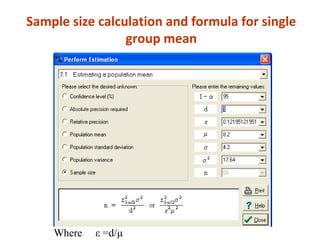
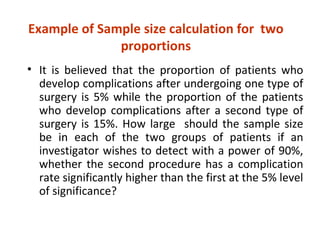
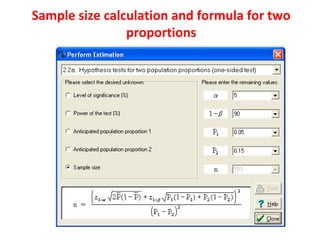
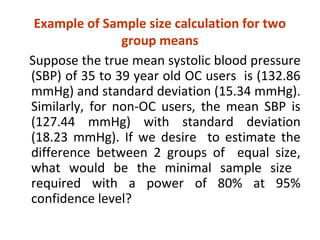
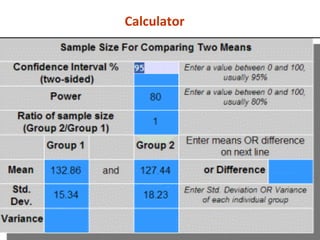
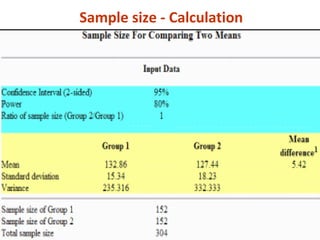
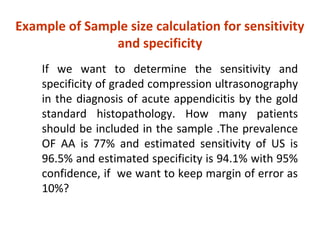
Measures of disease frequency include rates, ratios, and proportions. A ratio expresses the relation between two quantities where the numerator is not part of the denominator. A proportion indicates the relation of a part to the whole, with the numerator included in the denominator. A rate measures the occurrence of an event in a population during a time period. Other concepts discussed include incidence, prevalence, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), and measures of variation (range, standard deviation). Factors that can affect study outcomes include various types of biases such as selection, response, information, and confounding variables.