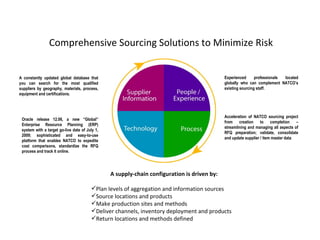
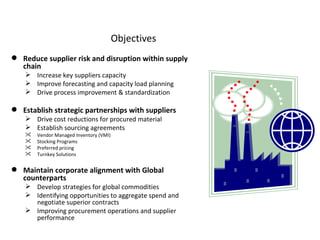
This document proposes developing strategic agreements and alliances with suppliers to minimize supply chain risks. It discusses implementing a new ERP system, qualifying suppliers globally through an updated database, and establishing a change management process. The objectives are reducing costs, increasing capacity and performance, and standardizing processes through strategic partnerships and sourcing agreements. An eight-step comprehensive sourcing solution is outlined. The supplier development strategy examines consolidating redundant suppliers through a selection policy and implementing solutions like vendor managed inventory programs.