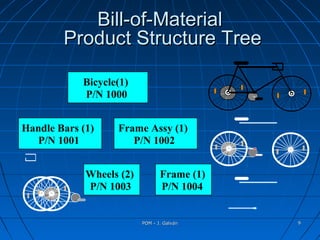
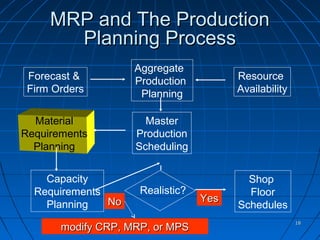
This document discusses material requirements planning (MRP). It defines MRP and distinguishes between dependent and independent demand. The key benefits of MRP are listed as increased customer satisfaction, faster response to changes, and reduced inventory levels while maintaining service. MRP uses a bill of materials, master production schedule, and inventory data to determine requirements for dependent demand items and to generate work orders, purchase orders, and schedules.