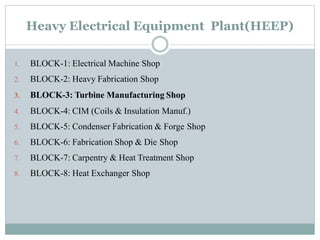
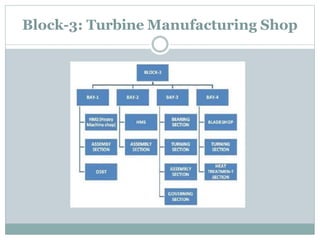
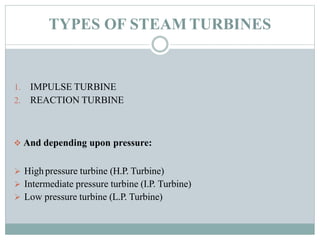
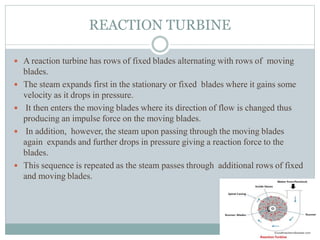
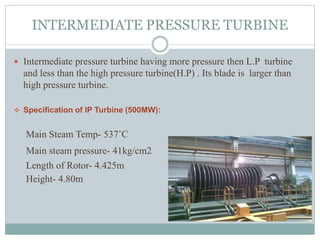
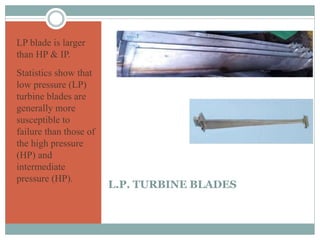
The document presents an industrial training report on Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), India's largest engineering and manufacturing enterprise, detailing its establishment, operations, and training experiences. It covers the types of steam turbines, their manufacturing processes, and the training received in turbine manufacturing at BHEL's Haridwar facility. The training emphasized the machining processes and concluded that BHEL is a key contributor to power generation in India.