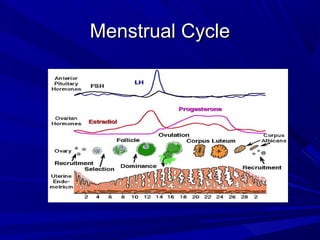
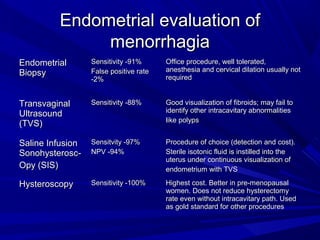
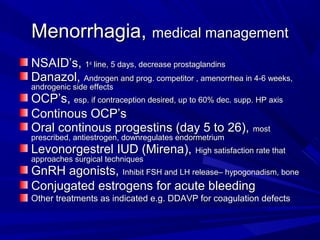
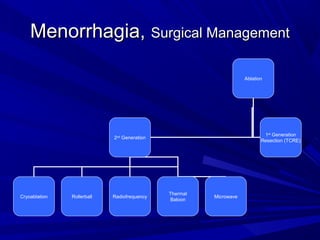
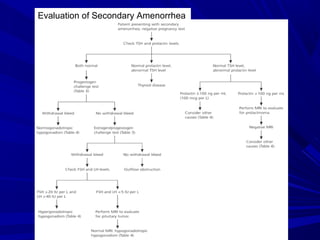
This document discusses menstrual disorders and their management. It defines conditions like menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea, and amenorrhea. It emphasizes taking a thorough history and physical exam to determine the cause and guide appropriate testing. For abnormal bleeding, it is important to determine if the bleeding is ovulatory or anovulatory. Treatment involves medical options like hormones or IUDs, or surgical procedures if medical management fails. Amenorrhea requires evaluating for problems of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, chronic illnesses, or structural issues.