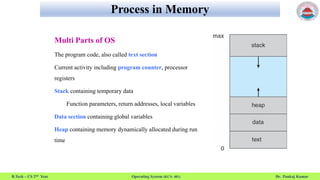
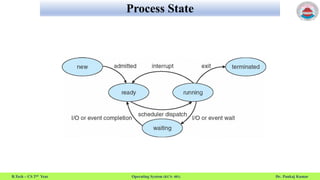
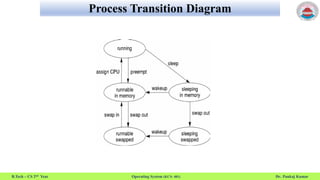
This document summarizes a lecture on operating system processes. It discusses process concepts like multiple parts of a process in memory including code, stack, data, and heap. It describes process states like new, running, waiting, ready, and terminated. It also explains the process control block which contains process information like ID, state, priority, registers, and more. Finally, it discusses process address space and process identification.