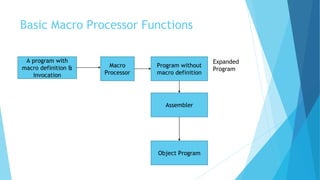
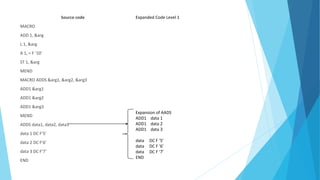
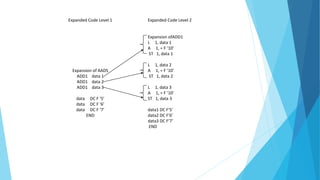
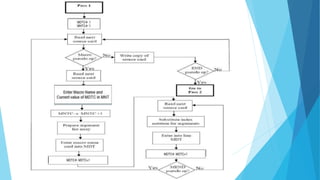
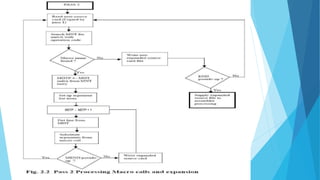
This document discusses macros and macro processing. It defines macros as units of code abbreviation that are expanded during compilation. The macro processor performs two passes: pass 1 reads macros and stores them in a table, pass 2 expands macros by substituting actual parameters. Advanced features like conditional expansion and looping are enabled using statements like AIF, AGO, and ANOP. Nested macro calls follow a LIFO expansion order.