The document summarizes key information about the Articles of Confederation and its weaknesses:
1) The Articles of Confederation created a very weak central government that gave most power to the individual states. This was done intentionally by the newly independent American states who wanted to avoid another strong central authority like the British monarchy.
2) However, the weak central government created under the Articles had several detrimental effects. Congress lacked power to tax, regulate trade between states, or enforce laws. Amendments required unanimous approval which was nearly impossible.
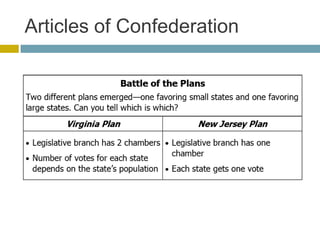
3) Debate between large and small states over representation in Congress also highlighted weaknesses. The Constitution was drafted as an improvement, creating a stronger central government with three branches but also a