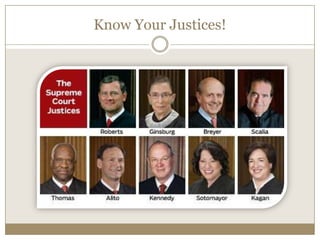
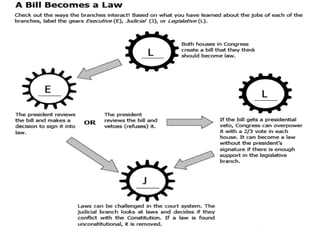
Article II of the Constitution describes the executive branch, headed by the president. It establishes the qualifications to be president, that the president is selected by the Electoral College, and the powers of the office. These powers include serving as commander-in-chief of the armed forces, appointing ambassadors and judges, making treaties, and enforcing laws. Article III establishes the judicial branch and the Supreme Court, giving the courts the power to interpret laws and review the constitutionality of other laws and actions.