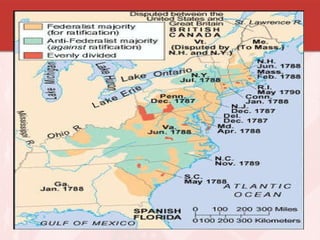
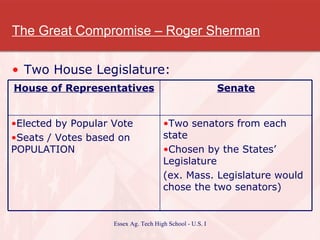
The document summarizes key events in the creation of the US Constitution. It describes the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and the various compromises reached at the Constitutional Convention to address state interests. Key issues included representation in Congress, the slave trade, and balancing state and federal power. The Constitution drew on ideas from ancient Rome, Enlightenment thinkers, and the English system. Its ratification was debated, with Federalists supporting it and Antifederalists wanting stronger protections for individual rights, leading to the addition of the Bill of Rights.























![Ratification Ratify – To approve [the Constitution] Federalists – wanted to ratify the Constitution without a bill of rights. They said it would be impossible to list everyone’s natural rights. Antifederalists – would not ratify unless a bill of rights was included. They said it was needed to protect basic rights (religion speech, etc…)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-creatingarepublic-110317113549-phpapp01/85/Chapter-7-Creating-a-Republic-25-320.jpg)

![The Bill of Rights Some states ratified the Constitution on the condition that a bill of rights was added later. Amend – to change [the Constitution]… The framers made it a difficult process. The new federal government came up with 12 amendments, however only 10 were ratified. These became the Bill of Rights . How many of the Ten Amendments can you name? 1._________________________ 2._________________________ 3._________________________ 4._________________________ 5._________________________ 6._________________________ 7._________________________ 8._________________________ 9._________________________ 10.________________________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-creatingarepublic-110317113549-phpapp01/85/Chapter-7-Creating-a-Republic-27-320.jpg)